APPENDIX A: BASIC FDDI NETWORKS
Ethernet/802.3
Network
Single Attached
Stations ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() File
File
Server
Ethernet/802.3 Network
ETHERNET to
FDDI BRIDGE
DUAL ATTACHED CONCENTRATOR
ETHERNET
to FDDI
BRIDGE
FDDI
NETWORK
FDDI |
|
to | FDDI |
FDDI | NETWORK |
BRIDGE |
|
DAS |
|
DUAL
ATTACHED
STATION
Ethernet/802.3 | DUAL ATTACHED | |||||||
Network | ||||||||
CONCENTRATOR | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
ETHERNET to
FDDI BRIDGE
DUAL ATTACHED |
CONCENTRATOR |
SINGLE ATTACHED |
CONCENTRATOR |
Single Attached |
Stations |
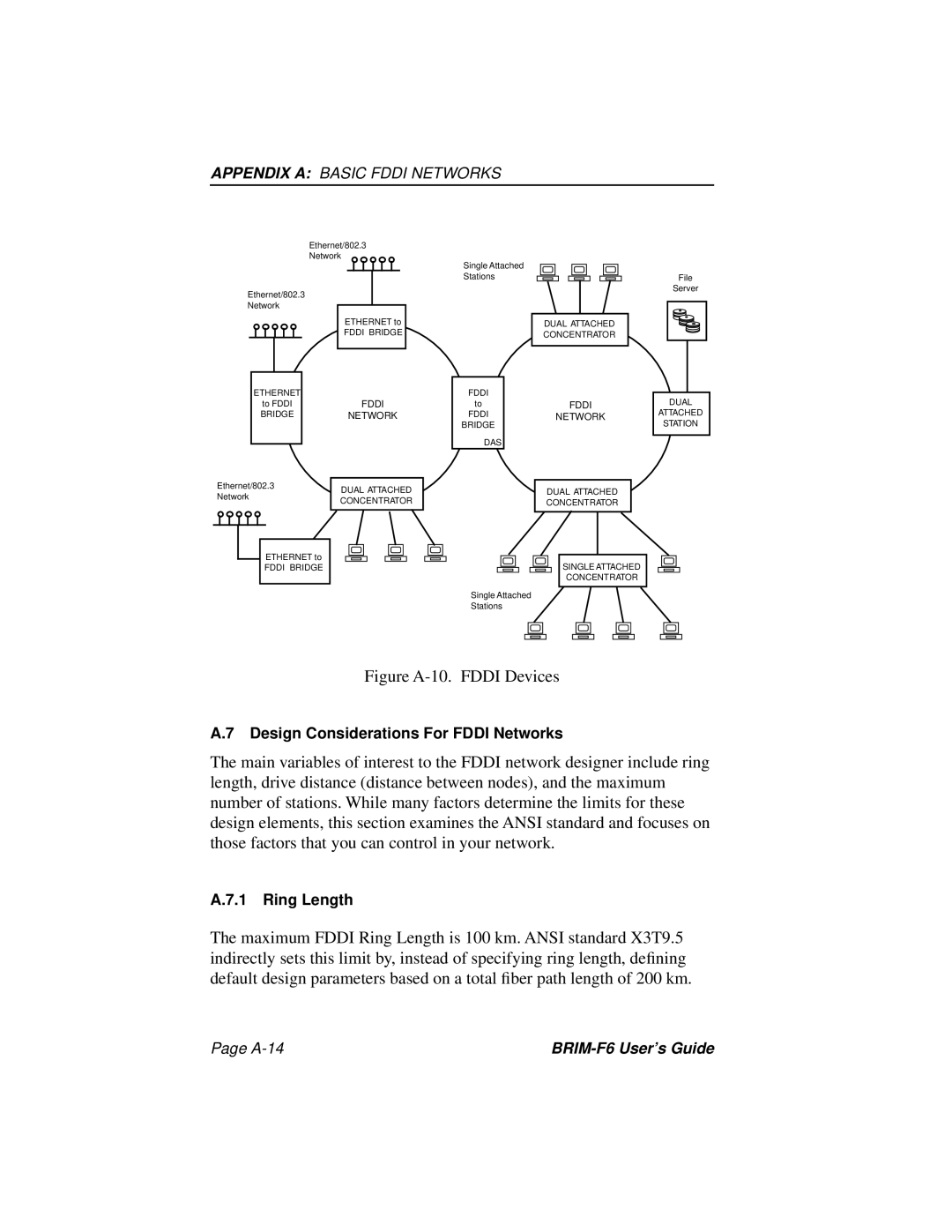
Figure A-10. FDDI Devices
A.7 Design Considerations For FDDI Networks
The main variables of interest to the FDDI network designer include ring length, drive distance (distance between nodes), and the maximum number of stations. While many factors determine the limits for these design elements, this section examines the ANSI standard and focuses on those factors that you can control in your network.
A.7.1 Ring Length
The maximum FDDI Ring Length is 100 km. ANSI standard X3T9.5 indirectly sets this limit by, instead of specifying ring length, defining default design parameters based on a total fiber path length of 200 km.
Page |
|