Americas Headquarters
First Published February 29 Last Modified March 22
Page
N T E N T S
Configuring VLANs
Configuring Private VLANs
Configuring Rapid PVST+
Configuring Multiple Spanning Tree
Configuring the Port Priority
Configuring Lldp
Configuring Igmp Snooping
Document Conventions
Preface
Audience
Convention Description
Italic screen font
Error and System Messages
Installation and Upgrade Guides
Configuration Guides
Release Notes
Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request
New and Changed Information for this Release
Feature Description Added or
Switching mode. There are two switching
Changed Release
OL-26590-01
VLANs
Layer 2 Ethernet Switching Overview
Overview
This chapter contains the following sections
STP Overview
Private VLANs
Spanning Tree
Rapid PVST+
STP Extensions
Overview STP Extensions
Information About Ethernet Interfaces
Configuring Ethernet Interfaces
About the Interface Command
About the Unidirectional Link Detection Parameter
Feature
Default Udld Configuration
Following table shows the default Udld configuration
Udld Aggressive and Nonaggressive Modes
Following table shows the default CDP configuration
About the Error-Disabled State
Default CDP Configuration
About Interface Speed
About MTU Configuration
Configuring Ethernet Interfaces
About the Debounce Timer Parameters
About Port Profiles
Switch# configure terminal
Configuring the Udld Mode
Command or Action Purpose Step
Aggressive
Running-config bootflash
Changing an Interface Port Mode
Command or Action
Running-config startup-config
Transceiver inserted into it
Configuring Interface Speed
Slot /port
Command or Action Purpose
Disabling Link Negotiation
Device-id mac-address
Configuring the CDP Characteristics
Advertise v1
Serial-number system-name
Enabling or Disabling CDP
Seconds
Enabling the Error-Disabled Detection
Example
Config t Enters configuration mode
Enabling the Error-Disabled Recovery
Configuring the Error-Disabled Recovery Interval
Copy running-config startup-config
Errdisable recovery interval interval
Configuring the Debounce Timer
Configuring the Description Parameter
Show interface status err-disabled
Disabling and Restarting Ethernet Interfaces
Switchconfig-if# shutdown Disables the interface
Displaying Interface Information
Command Purpose
Following example shows how to display the CDP neighbors
Displaying Input Packet Discard Information
Default Physical Ethernet Settings
Parameter Default Setting
Page
OL-26590-01
Understanding VLANs
Configuring VLANs
Information About VLANs
Vlan Ranges
VLANs as Logically Defined Networks
Creating, Deleting, and Modifying VLANs
VLANs Numbers Range Usage
Creating and Deleting a Vlan
Configuring a Vlan
About the Vlan Trunking Protocol
Guidelines and Limitations for VTP
Vlan vlan-id vlan-range
Configuring a Vlan
Vlan-id vlan-range
Active suspend
Switchconfig# interface ethernet
Adding Ports to a Vlan
Configure terminal Enters global configuration mode
Configuring a Vlan as a Routed SVI
Switchconfig-if# switchport access vlan
Feature interface-vlan Enables the creation of SVIs
You can configure routing protocols on this interface
Configuring a Vlan as a Management SVI
Configuring VTP
Copy running-config
Vtp password
Show vtp password
Startup-config
Switch# show vlan brief id vlanid vlanrange name name
Verifying Vlan Configuration
Switch# show running-config vlan vlanid vlanrange
Summary
Configuring Private VLANs
Information About Private VLANs
Three types of Pvlan ports are as follows
Primary and Secondary VLANs in Private VLANs
Private Vlan Ports
Primary, Isolated, and Community Private VLANs
Associating Primary and Secondary VLANs
Private Vlan Traffic Flows
Broadcast Traffic in Private VLANs
Private Vlan Promiscuous Trunks
Private Vlan Isolated Trunks
Private Vlan Port Isolation
Guidelines and Limitations for Private VLANs
Configuring a Private Vlan
Switchconfig# feature private-vlan
Enabling Private VLANs
Community isolated primary
Configuring a Vlan as a Private Vlan
Associating Secondary VLANs with a Primary Private Vlan
Association
Association add secondary-vlan-list
Remove secondary-vlan-list
Configuring an Interface as a Private Vlan Host Port
Configuring an Interface as a Private Vlan Promiscuous Port
Configuring the Allowed VLANs for Pvlan Trunking Ports
Configuring a Promiscuous Trunk Port
Configuring an Isolated Trunk Port
Switch# show feature
Verifying the Private Vlan Configuration
Configuring Native 802.1Q VLANs on Private VLANs
Switch# show interface switchport
OL-26590-01
Understanding Access and Trunk Interfaces
Configuring Access and Trunk Interfaces
Information About Access and Trunk Interfaces
Understanding Ieee 802.1Q Encapsulation
Devices in a Trunking Environment
Understanding Access VLANs
Header without and with 802.1Q Tag Included
Understanding Native 802.1Q VLANs
Understanding the Native Vlan ID for Trunk Ports
Understanding Allowed VLANs
Configuring Access and Trunk Interfaces
Configuring a LAN Interface as an Ethernet Access Port
Switchconfig-if# switchport host
Configuring Access Host Ports
Configuring Trunk Ports
On bpdu filtering and bpdu guard
Specified trunk, use the switchport trunk allowed vlan
Configuring the Native Vlan for 802.1Q Trunking Ports
Configuring the Allowed VLANs for Trunking Ports
Port-channel number
Configuring Native 802.1Q VLANs
Switch# configure terminal Enters configuration mode
Switch# show vlan dot1q tag native
Verifying Interface Configuration
Switchconfig# no vlan dot1q tag
Switch# show interface
OL-26590-01
Cut-Through Switching Mode
Configuring Switching Modes
Information About Switching Modes
Store-and-Forward Switching Mode
Cut-Through Switching Mode Guidelines and Limitations
Guidelines and Limitations for Switching Modes
Licensing Requirements for Switching Modes
Store-and-Forward Switching Mode Guidelines and Limitations
Enabling Store-and-Forward Switching
Default Settings for Switching Modes
Configuring Switching Modes
Reenabling Cut-Through Switching
This example shows how to reenable cut-through switching
Feature History for Switching Modes
Saves the change persistently through reboots
Feature Name Releases Information
Understanding STP
Configuring Rapid PVST+
Information About Rapid PVST+
STP Overview
Understanding How a Topology is Created
Understanding the Bridge ID
Bit
Bit extended system ID field is part of the bridge ID
Bridge Priority Value
8192 4096 2048 1024 512 256 128
Understanding BPDUs
Election of the Root Bridge
Creating the Spanning Tree Topology
Understanding Rapid PVST+
Rapid PVST+ Overview
Rapid PVST+ BPDUs
Rapid PVST+ Flag Byte in Bpdu
Proposal and Agreement Handshake
Proposal and Agreement Handshaking for Rapid Convergence
Variable Description
Protocol Timers
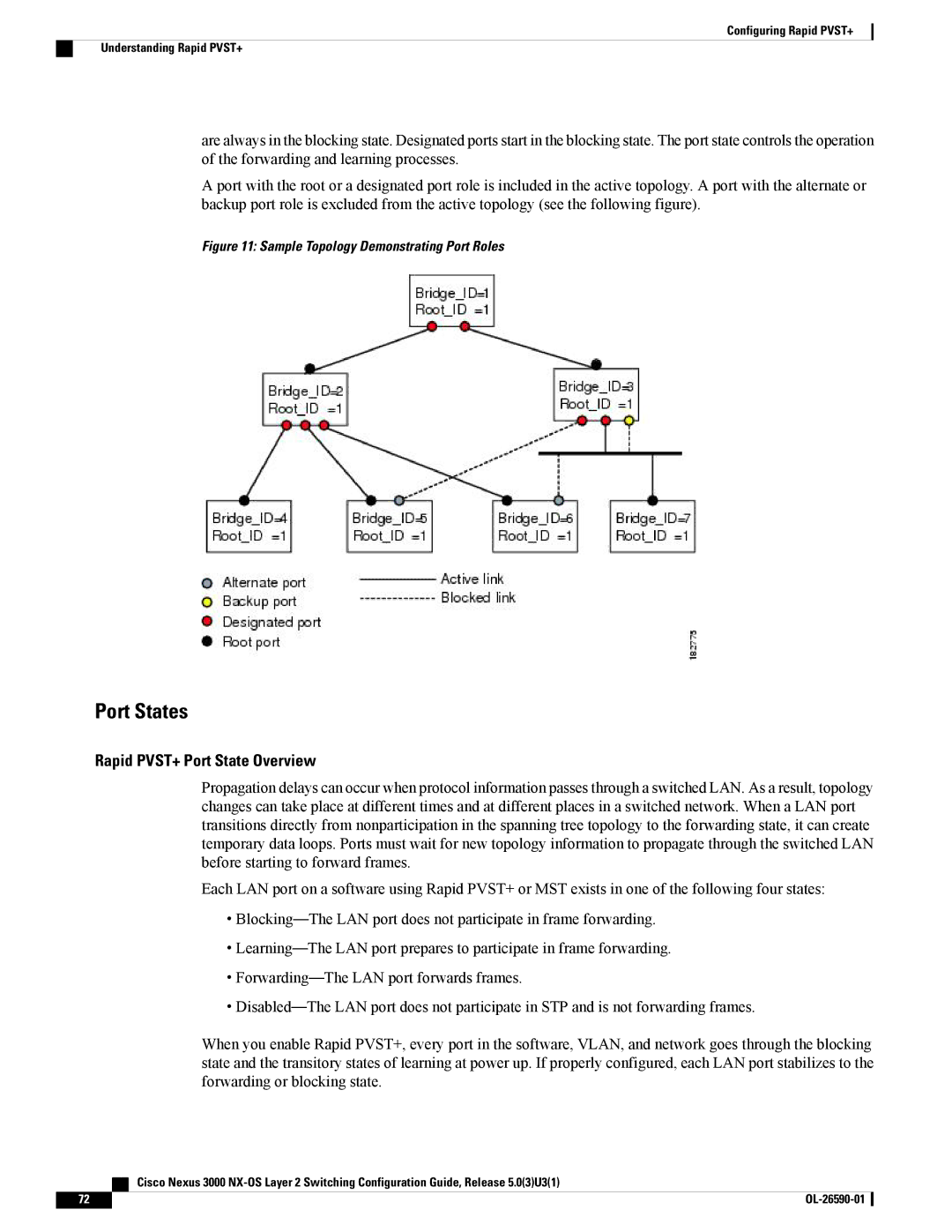
Port Roles
Port States
Rapid PVST+ Port State Overview
Blocking State
Operational Status Port State
Enabled Blocking Learning Yes Forwarding Disabled
Synchronization of Port Roles
Topology?
Processing Superior Bpdu Information
Spanning-Tree Dispute Mechanism
Port Cost
Port Priority
Rapid PVST+ and Ieee 802.1Q Trunks
Rapid PVST+ Interoperation with Legacy 802.1D STP
Bandwidth
Enabling Rapid PVST+
Configuring Rapid PVST+
Rapid PVST+ Interoperation with 802.1s MST
Enabling Rapid PVST+ per Vlan
Mode rapid-pvst
Switch# configure
Terminal
Configuring the Root Bridge ID
Configuring a Secondary Root Bridge
Spanning-tree mst max-ageconfiguration commands
Configuring the Rapid PVST+ Port Priority
Vlan vlan-list port-priority priority
Pathcost method long short
Configuring the Rapid PVST+ Pathcost Method and Port Cost
Configuring the Rapid PVST+ Bridge Priority of a Vlan
Vlan vlan-id cost value auto
Vlan-range hello-time hello-time
Configuring the Rapid PVST+ Hello Time for a Vlan
Switchconfig# spanning-tree vlan
Specifying the Link Type
Configuring the Rapid PVST+ Forward Delay Time for a Vlan
Configuring the Rapid PVST+ Maximum Age Time for a Vlan
Vlan-range forward-time forward-time
Switch# show running-config spanning-tree all
Verifying Rapid PVST+ Configurations
Switch# clear spanning-tree detected-protocol
Restarting the Protocol
This example shows how to display spanning tree status
Switch# show spanning-tree options
Spanning tree configuration
OL-26590-01
MST Overview
Configuring Multiple Spanning Tree
Information About MST
MST Regions
MST BPDUs
IST, CIST, and CST Overview
MST Configuration Information
IST, CIST, and CST
Spanning Tree Operation Within an MST Region
Spanning Tree Operations Between MST Regions
MST Terminology
MST Regions, Cist Regional Roots, and CST Root
Hop Count
Boundary Ports
Spanning-Tree Dispute Mechanism
MST Boundary Ports
Port Cost and Port Priority
Interoperability with Ieee 802.1D
You must enable MST Rapid PVST+ is the default
Configuring MST
MST Configuration Guidelines
Enabling MST
Switchconfig# no spanning-tree mode mst
Entering MST Configuration Mode
Switchconfig# spanning-tree mode mst
Mst configuration
Spanning-tree mst
Switchconfig# spanning-tree mst
Specifying the MST Name
Instance-id vlan vlan-range
Specifying the MST Configuration Revision Number
Specifying the Configuration on an MST Region
Name
Version
Mapping and Unmapping VLANs to MST Instances
Default MSTI, which is the Cist
This example shows how to map Vlan 200 to Msti
Same Msti and their associated primary Vlan
Configuring the Root Bridge
Synchronize
For all private VLANs
104
Mst instance-id root
Configuring the Port Priority
Switchconfig# no spanning-tree Optional
Configuring the Port Cost
Configuring the Switch Priority
Hello-time seconds
Configuring the Hello Time
Configures the hello time for all MST instances. The hello
Switch is alive. For seconds, the range is from 1 to 10,
Configuring the Forwarding-Delay Time
Configuring the Maximum-Aging Time
Mst max-age seconds
Configuring the Maximum-Hop Count
Configuring Pvst Simulation Globally
Max-hops hop-count
Configuring Pvst Simulation Per Port
Switchconfig-if#spanning-tree mst simulate pvst disable
Command
Verifying MST Configurations
Restarts MST on entire switch or
Specified interfaces
Information About STP Extensions
Configuring STP Extensions
About STP Extensions
Understanding STP Port Types
Understanding Bridge Assurance
Understanding Bpdu Guard
Understanding Bpdu Filtering
Is disabled
Default Enable Disable Enabled/Disabled
Port returns to
Understanding Loop Guard
Understanding Root Guard
Configuring Spanning Tree Port Types Globally
Configuring STP Extensions
STP Extensions Configuration Guidelines
Port type edge default
Port type network default
Port type edge
Switchconfig# interface type
Switchconfig-if# spanning-tree
Edge ports. Edge ports immediately transition to
Port type network
Ports. If you enable Bridge Assurance, it automatically
Enabling Bpdu Guard Globally
Enabling Bpdu Guard on Specified Interfaces
Edge bpdufilter default
Switchconfig-if# no spanning-tree bpduguard
Enables Bpdu Filtering by default on all
Filtering is disabled by default
Bpdufilter
Bpdufilter enable disable
Enabling Bpdu Filtering on Specified Interfaces
Guard is disabled
Loopguard default
Normal and network ports. By default, global Loop
Enabling Loop Guard Globally
Verifying STP Extension Configuration
Guard loop root none
126
Configuring Lldp
Configuring Global Lldp Commands
Optionalswitch# show lldp Displays Lldp configurations
Ensure that the Lldp feature is enabled on the switch
Holdtime reinit timer
Configuring Interface Lldp Commands
Transmit
This example shows how to display Lldp timer information
This example shows how to display Lldp counters
Configuring a Static MAC Address
Configuring the MAC Address Table
Configuring MAC Addresses
Information About MAC Addresses
Switch# configure terminal Enters global configuration mode
Configuring the Aging Time for the MAC Table
Switchconfig-# no mac-address-table static
Macaddress vlan vlan-id
Switch# show mac-address-table aging-time
Verifying the MAC Address Configuration
Switchconfig# clear mac-address-table dynamic
Defined in the switch
This example shows how to display the MAC address table
This example shows how to display the current aging time
Configuring Igmp Snooping
Information About Igmp Snooping
Igmp Snooping Switch
IGMPv1 and IGMPv2
Igmp Forwarding
IGMPv3
Igmp Snooping Querier
Configuring Igmp Snooping Parameters
Parameter Description
Snooping
No ip igmp snooping mrouter vpc-peer-link
No ip igmp snooping mrouter
Last-member-query-interval
Snooping explicit-tracking
Snooping fast-leave
Snooping querier IP-address
Verifying Igmp Snooping Configuration
141
142
Configuring Traffic Storm Control
Information About Traffic Storm Control
Traffic Storm Guidelines and Limitations
Broadcast Suppression
Configures traffic storm control for traffic
Configuring Traffic Storm Control
Switchconfig-if# storm-control broadcast
On the interface. The default state is
Verifying Traffic Storm Control Configuration
Traffic Storm Control Example Configuration
Default Traffic Storm Settings
Parameters Default
D E
Mstp Cist root 93 CIST, described 91 CST 91
Rstp 68, 71, 75, 89 active topology 71 Bpdu
Adding ports to Private Configuring
VLANs