Chapter 1 Introduction to PNNI
The Hierarchical PNNI Network Topology
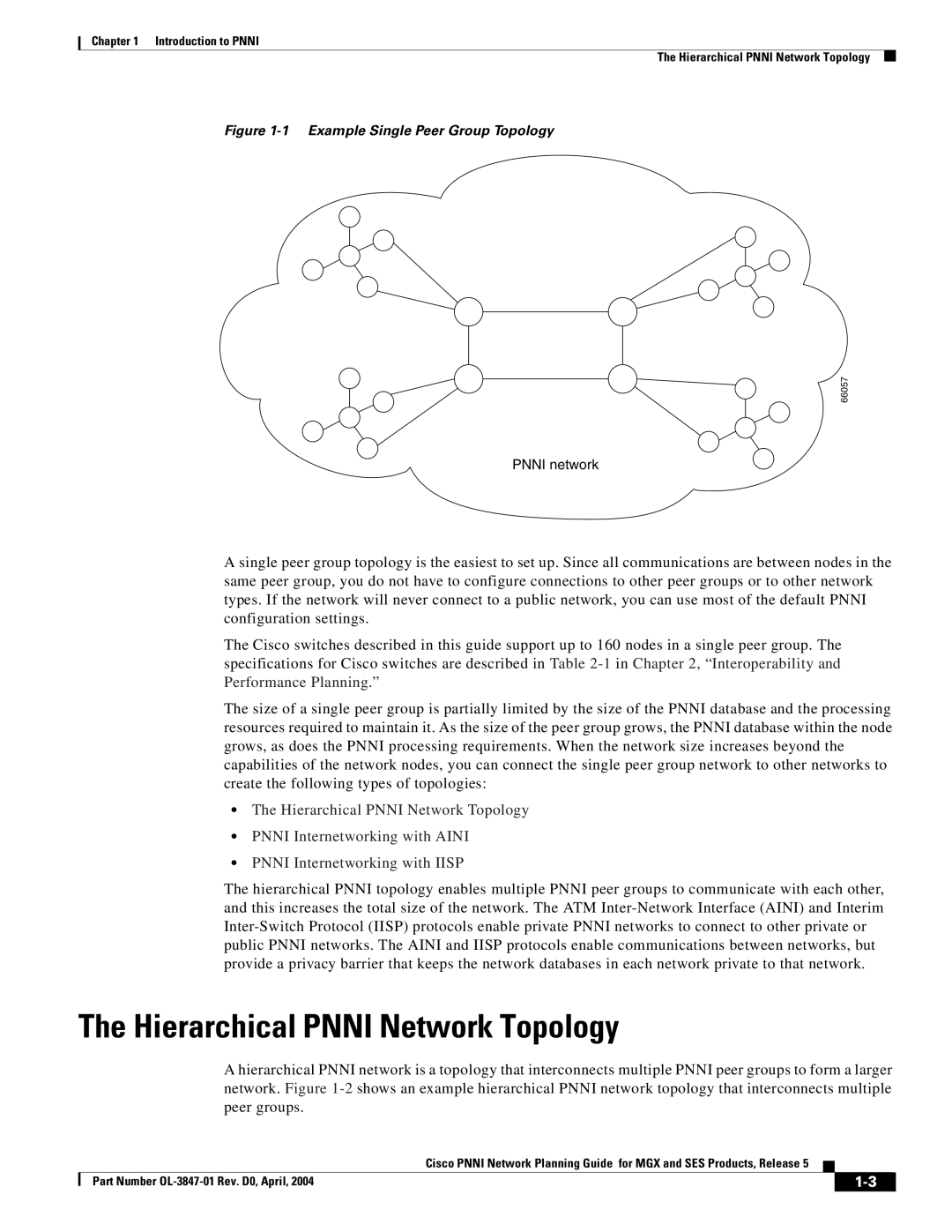
Figure 1-1 Example Single Peer Group Topology
66057
PNNI network
A single peer group topology is the easiest to set up. Since all communications are between nodes in the same peer group, you do not have to configure connections to other peer groups or to other network types. If the network will never connect to a public network, you can use most of the default PNNI configuration settings.
The Cisco switches described in this guide support up to 160 nodes in a single peer group. The specifications for Cisco switches are described in Table
The size of a single peer group is partially limited by the size of the PNNI database and the processing resources required to maintain it. As the size of the peer group grows, the PNNI database within the node grows, as does the PNNI processing requirements. When the network size increases beyond the capabilities of the network nodes, you can connect the single peer group network to other networks to create the following types of topologies:
•The Hierarchical PNNI Network Topology
•PNNI Internetworking with AINI
•PNNI Internetworking with IISP
The hierarchical PNNI topology enables multiple PNNI peer groups to communicate with each other, and this increases the total size of the network. The ATM
The Hierarchical PNNI Network Topology
A hierarchical PNNI network is a topology that interconnects multiple PNNI peer groups to form a larger network. Figure
|
| Cisco PNNI Network Planning Guide for MGX and SES Products, Release 5 |
|
| |
|
|
| |||
| Part Number |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
| ||