Chapter 4 Planning Intermediate Route Selection
Additional Routing Features in MGX and SES Nodes
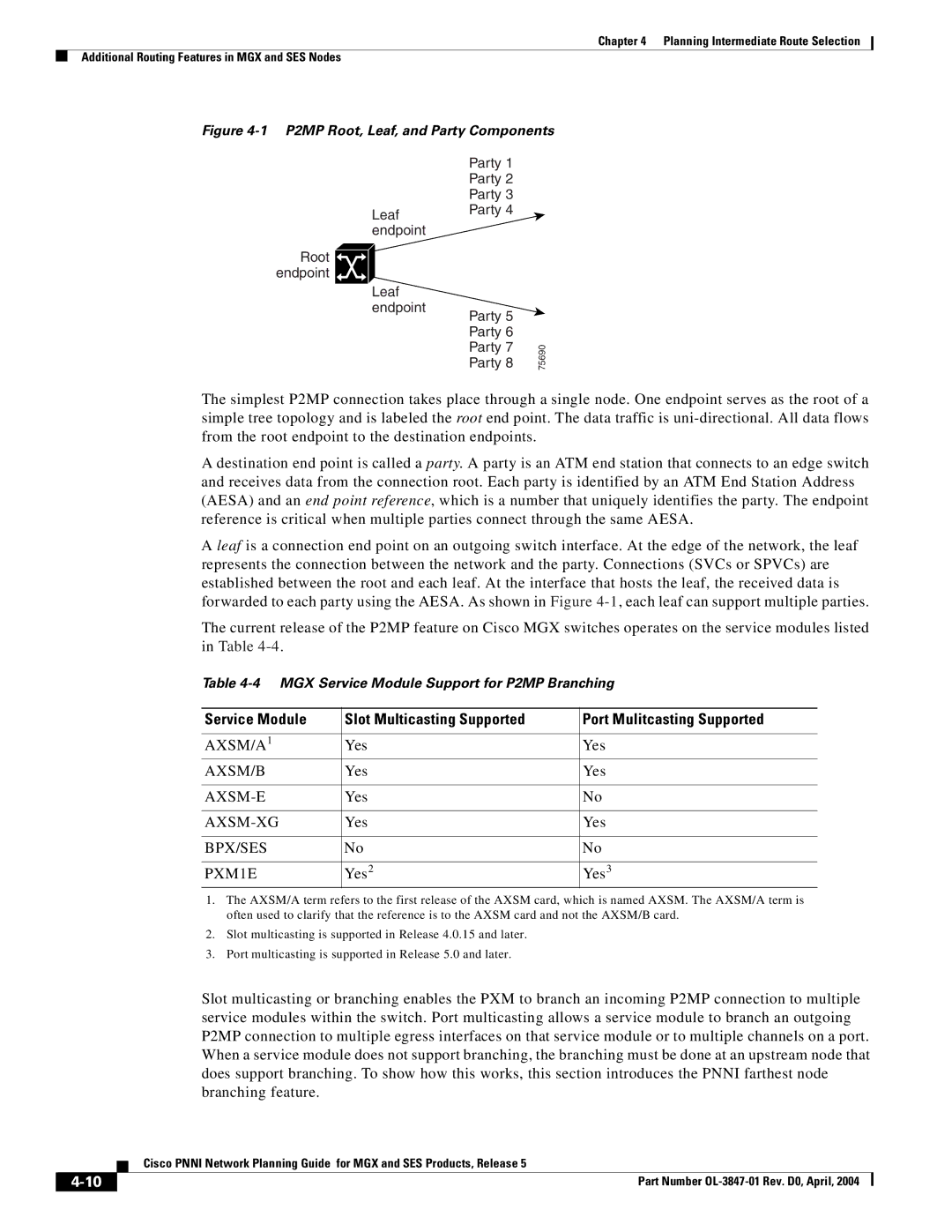
Figure 4-1 P2MP Root, Leaf, and Party Components
Leaf endpoint
Root endpoint
Leaf endpoint
Party 1
Party 2
Party 3
Party 4
Party 5
Party 6
Party 7
Party 8
75690
The simplest P2MP connection takes place through a single node. One endpoint serves as the root of a simple tree topology and is labeled the root end point. The data traffic is
A destination end point is called a party. A party is an ATM end station that connects to an edge switch and receives data from the connection root. Each party is identified by an ATM End Station Address (AESA) and an end point reference, which is a number that uniquely identifies the party. The endpoint reference is critical when multiple parties connect through the same AESA.
A leaf is a connection end point on an outgoing switch interface. At the edge of the network, the leaf represents the connection between the network and the party. Connections (SVCs or SPVCs) are established between the root and each leaf. At the interface that hosts the leaf, the received data is forwarded to each party using the AESA. As shown in Figure
The current release of the P2MP feature on Cisco MGX switches operates on the service modules listed in Table
Table
Service Module | Slot Multicasting Supported | Port Mulitcasting Supported |
|
|
|
AXSM/A1 | Yes | Yes |
AXSM/B | Yes | Yes |
|
|
|
| Yes | No |
|
|
|
| Yes | Yes |
|
|
|
BPX/SES | No | No |
|
|
|
PXM1E | Yes2 | Yes3 |
1.The AXSM/A term refers to the first release of the AXSM card, which is named AXSM. The AXSM/A term is often used to clarify that the reference is to the AXSM card and not the AXSM/B card.
2.Slot multicasting is supported in Release 4.0.15 and later.
3.Port multicasting is supported in Release 5.0 and later.
Slot multicasting or branching enables the PXM to branch an incoming P2MP connection to multiple service modules within the switch. Port multicasting allows a service module to branch an outgoing P2MP connection to multiple egress interfaces on that service module or to multiple channels on a port. When a service module does not support branching, the branching must be done at an upstream node that does support branching. To show how this works, this section introduces the PNNI farthest node branching feature.
| Cisco PNNI Network Planning Guide for MGX and SES Products, Release 5 |
Part Number |