Connecting Cisco ISDN PRI Network Modules to the Network
Channelized E1/ISDN PRI Balanced
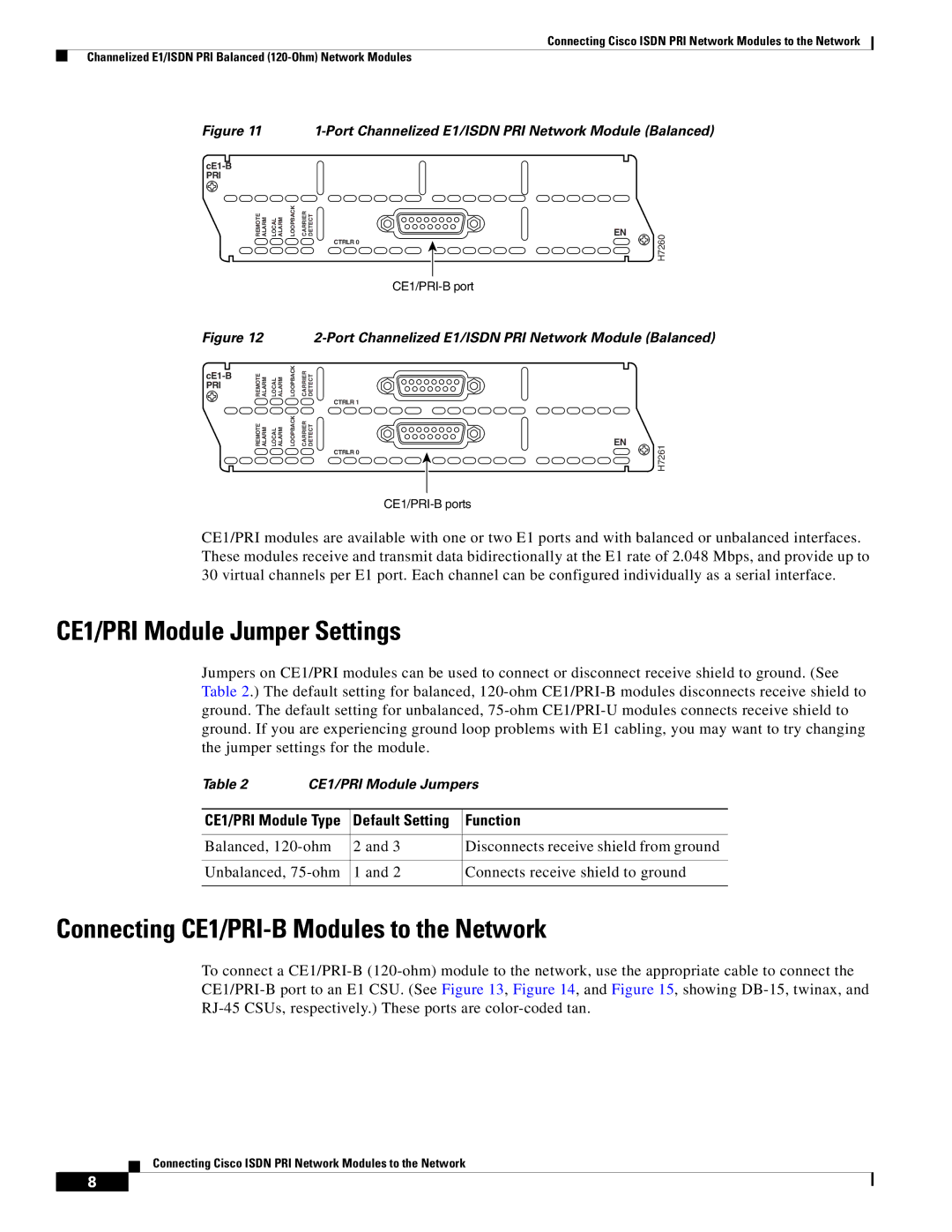
Figure 11 1-Port Channelized E1/ISDN PRI Network Module (Balanced)
REMOTE ALARM | LOCAL ALARM | LOOPBACK | CARRIER DETECT |
CTRLR 0
EN | H7260 |
|
Figure 12 2-Port Channelized E1/ISDN PRI Network Module (Balanced)
REMOTE | ALARM | LOCAL | ALARM | LOOPBACK | CARRIER | DETECT |
|
|
|
|
|
| CTRLR 1 |
REMOTE | ALARM | LOCAL | ALARM | LOOPBACK | CARRIER | DETECT |
CTRLR 0
EN | H7261 |
|
CE1/PRI modules are available with one or two E1 ports and with balanced or unbalanced interfaces. These modules receive and transmit data bidirectionally at the E1 rate of 2.048 Mbps, and provide up to 30 virtual channels per E1 port. Each channel can be configured individually as a serial interface.
CE1/PRI Module Jumper Settings
Jumpers on CE1/PRI modules can be used to connect or disconnect receive shield to ground. (See Table 2.) The default setting for balanced,
Table 2 | CE1/PRI Module Jumpers | ||
|
|
| |
CE1/PRI Module Type | Default Setting | Function | |
|
|
| |
Balanced, | 2 and 3 | Disconnects receive shield from ground | |
|
|
| |
Unbalanced, | 1 and 2 | Connects receive shield to ground | |
|
|
|
|
Connecting CE1/PRI-B Modules to the Network
To connect a
Connecting Cisco ISDN PRI Network Modules to the Network
8