Page
Contents
General Keys
Basic Definitions
Keys
Memory Keys
Special Keys
Function Keys
SCI Scientific Key
DRG Angle unit conversion key
Sin , cos , tan Sine, Cosine, Tangent Keys
Programming Keys USE in the PGM Mode only
Statistical Keys USE in the Stat Mode only
Arithmetic Mean Key
2ndF CAD Statistical Register Clear Key
Data , DEL Data Entry and Delete Key
2ndF σn Population Standard Deviation Key
Order of Operations
Accuracy and Capacity
Overflow / Error Conditions
Basic Calculation Including Parenthesis Calculations
Power Supply
Normal Calculations
Constant Calculations
Function Calculations
Memory Calculations
Sexagesimal ↔ Decimal conversion
Fraction Calculation
Trigonometric / Inverse Tri. Functions
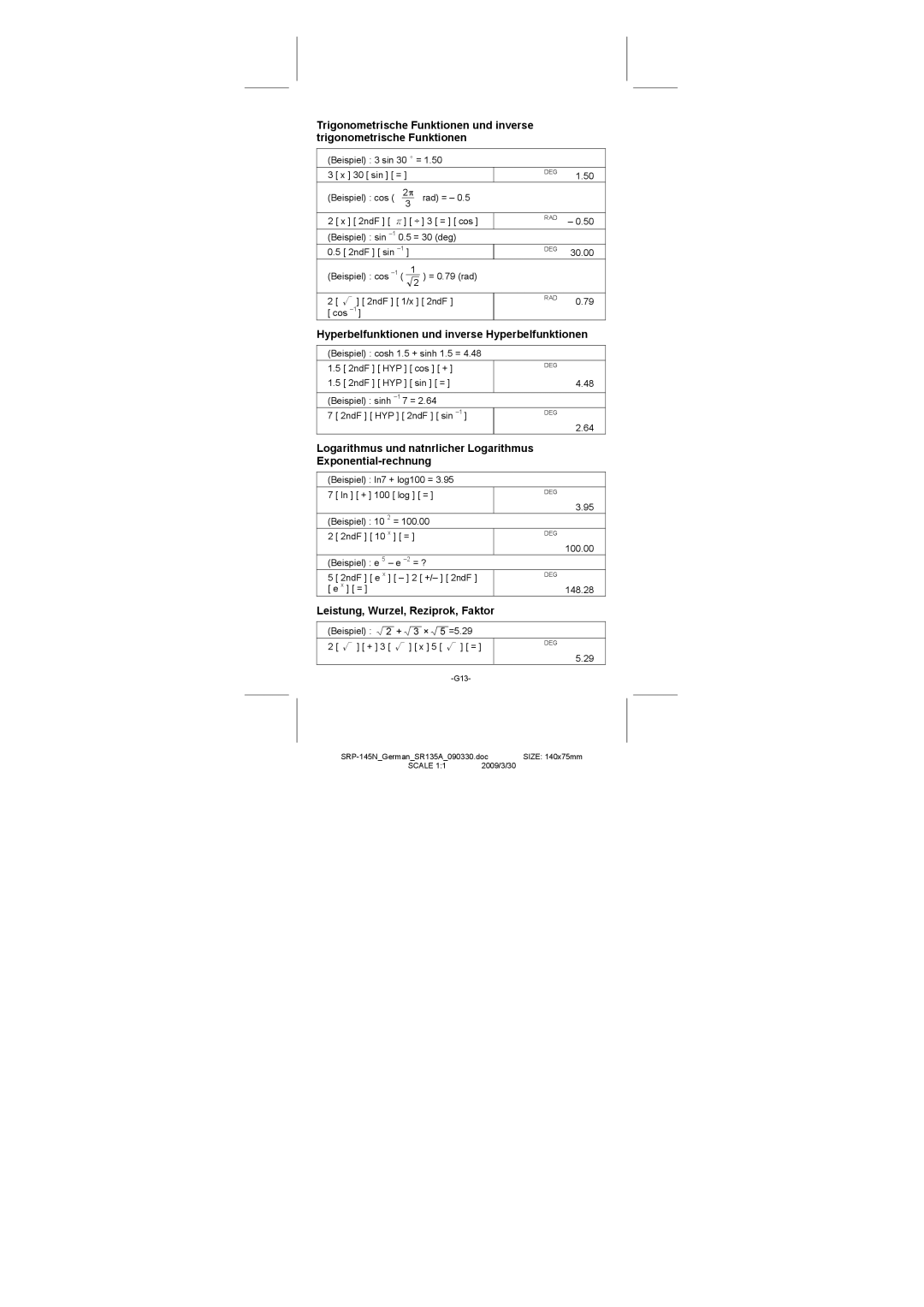
Hyperbolic Functions and Inverse Hyp. Functions
Power, Root, Reciprocals, Factorials
Standard Deviations
Common And Natural Logarithms / Exponentiations
Programming
E14 SRP-145NEnglishBlackSR135A090330.doc Size 140x75mm
→ Y
82 X Æ M
Definiciones Básicas
Calculo DE Funciones
Desviaciones Normales Programación
Definiciones Básicas
El teclado
Teclas DE Memoria
Teclas Especiales
Teclas CON Funciones Especificas
SCI Tecla para Ingeniería
DRG Tecla de Conversión de la Unidad del Ángulo
Sin , cos , tan teclas para Seno, coseno y tangente
2ndF 1/x Tecla reciproca
√ , x 2 Teclas para raíz cuadrada y cuadrados
2ndF 3√ Tecla de raíz cubica
2ndF x! Tecla factorial
LA Pantalla
Orden DE Operaciones
Exactitud & Capacidad
2n+1
Condiciones Erróneas
Incluyendo cálculos entre paréntesis
Suministro DE Energia
Cálculos Normales
Cálculos constantes
Calculo DE Funciones
Cálculos con Memoria
Conversion decimal ↔sexagesimal
Calculo Fraccionario
Hiperbólico / Funciones Inversas Hiperbólicas
Logarismos comunes y naturales / esponenciales
Desviaciones Normales
Programación
5000
→ Y
MR Kb x → k
Definições Básicas
Cálculos DA Função
Desviações Padrões Programação
Teclas Gerais
Definições Básicas
As Teclas
Teclas DE Memória
Teclas Especiais
Teclas DE Função
SCI Tecla Científica
DRG Tecla de conversão da unidade de Ângulo
Sin , cos , tan Teclas Seno, Coseno, Tangente
Teclas DE Programação Somente Para USO EM Modo PGM
Teclas Estatísticas Somente Para USO EM Modo Stat
Ordem DE Operações
Exatidão E Capacidade
≠ 2 π
Condições DE Excesso / Erro
Suprimento DE Energia
Cálculos Normais
Cálculo Básico Incluindo Cálculos entre Parênteses
Cálculos DA Função
Cálculos da Memória
Conversão Sexagesimal ↔ Decimal
Cálculo de Fração
Funções Trigonométricas / Inversas Tri
Funções Hiperbólicas e Inversas Hip
Logaritmos Comuns e Naturais / Exponenciações
Potência, Raíz, Recíprocas, Fatoriais
Desviações Padrões
Programação
P16
1610.51
P18
Grundlegendes
Funktionsberechnungen
Standardabweichungen Programmieren
Die Tastatur
Speichertasten
Sondertasten
Funktionstasten
2ndF 3√ Kubikwurzel
Log , 2ndF 10 x Normaler Logarithmus und Zehnerlogarithmus
√ , x 2 Quadratwurzel und Quadrat
2ndF 1/x Reziproker Wert
2ndF Halt Programmunterbrechnung
RUN Ausführen eines Programms
2ndF X Variablentaste
2ndF CAD Registerlöschtaste
Reihenfolge DER Rechenoperationen
Korrektheit UND Kapazität
Möglichkeit VON Overflows UND Fehlern
Stromversorgung
Übliche Rechnungen
Grundlegende Berechnungen Mit Klammerrechnung
Constant Calculations
Berechnung im Speicher
Funktionsberechnungen
Dezimal ↔ Sexagesimalberechnungen
Berechnung von Brüchen
Hyperbelfunktionen und inverse Hyperbelfunktionen
Leistung, Wurzel, Reziprok, Faktor
Standardabweichungen
Programmieren
G16
Beschreibung
G18
Definitions Fondamentales
Calculs DE Fonction
LA Variance Programmation
Definitions Fondamentales
Les Touches
EXP Touche Exposant
+ Touche d’Addition en Mémoire
Touches Spéciales Touches des Parenthèses
Touche 2ndF π
Touches DE Fonction
SCI Touche Ingénierie
DRG Touche de conversion d’unité d’angle
2ndF , 2ndF Touches Convertion Sexagésimale / Décimale
Touches Programmantes S’UTILISE Uniquement EN Mode PGM
Touches Statistiques S’EMPLOYE Uniquement EN Mode
’Affichage
Ordre DES Opérations
Précision DE Capacité
Surcharge / Conditions D’ERREUR
Calcul Simple Comprenant les Calculs avec Parenthèses
Source D’ALIMENTATION
Calculs Normaux
Les Calauls Constants
Calculs DE Fonction
Les Calculs avec Mémoires
Conversion Sexagésimal ↔ Décimale
Calcul de Fraction
Fonctions Trigonométriques / Inverses
Fonctions Hyperboliques et Fonctions Inverses
Logarithmes Communs et Naturels / Exponentiels
Puissance, Racine, Réciproque, Factoriel
LA Variance
Programmation
F16
RUN 1000
MR Kb xÆk
Indice
Tasti Generali
Definizioni Basiche
Tasti
Tasti DI Memoria
Tasti Speciali
Tasti DI Funzioni
SCI Tasto Scientifico
DRG Tasto per conversione dell’unità del Angolo
Sin , cos , tan Tasti Seno, Coseno, Tangente
Tasti DI Programmazione Solo Usare NEL Modo PGM
Tasti PER Statistiche Solo Usare NEL Modo Stat
Ordine DI Operazioni
Accuratezza E Capacità
Overflow / Condizioni DI Errore
Alimentazione
Calcoli Normali
Calcoli di Base Incluso Calcoli con Parentesi
Calcoli con Costanti
Conversione Sessagesimale ↔ Decimale
Calcoli DI Funzione
Calcoli con la Memoria
Calcolo di Frazione
Funzioni Trigonometriche / Tri. Inverse
Funzioni Iperboliche e Iperb. Inverse
Logaritmi Comuni e Naturali / Esponenziazioni
Deviazioni Standard
Potenza, Radice, Reciproco, Fattoriali
Programmazione
5000
Descrizione
27.33333333
Inhoud
Algemene Toetsen
Algemene Definities
De toetsen
Geheugentoetsen
Speciale Toetsen
De toets voor hoekconversie DRG
De toets voor het instellen van het decimaalteken 2ndF FIX
De wetenschappelijke toets SCI
Functietoetsen
De toets voor het berekenen van een machtsverheffing x y
De toets voor het berekenen van de 3de machtswortel 2ndF
De toets voor het berekenen van de faculteit 2ndF
De toets voor het berekenen van een machtswortel 2ndF y
Programmeertoetsen Enkel Voor Gebruik in DE PGM-MODUS
DE Statistische Toetsen Enkel Voor Gebruik in DE STAT-MODUS
De toets voor het berekenen van de som der waarden 2ndF Σx
De toets voor het berekenen van het wiskundig gemiddelde
Toets voor het berekenen van de som der kwadraten 2ndF Σx
De toets voor het weergeven van het aantal gegevens n
Volgorde VAN DE Bewerkingen
Nauwkeurigheid EN Capaciteit
Overflow / Foutmeldingen
Voeding
Normale Bewerkingen
Basisbewerkingen Inclusief bewerkingen met haakjes
Constante bewerkingen
Geheugenbewerkingen
Bewerkingen met breuken
Functiebewerkingen
Sexagesimale ↔ Decimale conversie
Trigonometrische / Inverse trigonometrische functies
Hyperbolische functies en inverse hyperbolische functies
Gewone en natuurlijke logaritmes / machtsverheffingen
Standaardafwijkingen
Programmeren
D16 SRP-145NDutchSR135A090330.doc Size 140x75mm
Beschrijving
978723404
Indhold
Generelle Taster
Grundlæggende Definitioner
Tasterne
Hukommelsestaster
Specialtaster
Funktionstaster
SCI Videnskabelig tast
DRG Tast til konvertering mellem vinkelenheder
Sin, cos, tan Sinus-, cosinus- og tangens-taster
Programmeringstaster Anvendes KUN I PGM-MODE
Statistiske Taster Anvendes KUN I STAT-MODE
Operationsrækkefølge
Nøjagtighed OG Kapacitet
Overløb / Fejltilstande
Strømforsyning
Normale Beregninger
Grundlæggende beregninger herunder parentesberegninger
Konstantberegninger
Hukommelsesberegninger
Brøkregning
Funktionsberegninger
Konvertering sexagesimal ↔ decimal
Trigonometriske / inverse trigonometriske funktioner
Hyperbolske og inverse hyperbolske funktioner
Opløftning, roduddragnings, reciprok værdi og fakultet
Standardafvigelser
Programmering
∑ x
Da15 SRP-145NDannishSR135A090330.doc Size 140x75mm
1610.51 Beskrivelse → Y
Da17 SRP-145NDannishSR135A090330.doc Size 140x75mm
Дисплей Порядок Выполнения Операций
Содержаниe
Основные Определения
Значений Переполнение / Ошибка Питание Обычные Расчеты
Основные Определения
Клавиши
Клавиши Ввода В Память
Специальные Клавиши
Функциональные Клавиши
SCI Научный режим
DRG Замена мер углов
Sin , cos , tan Клавиши синус, косинус, тангенс
2ndF 1/x Клавиша обратной величины
√ , x 2 Клавиши корня квадратного и квадрата
2ndF 3√ Клавиша корня кубического
2ndF x! Клавиша факториала
Клавиши Программирования Только В Режиме PGM
Клавиши Статистических Расчетов Только В Режиме Stat
2ndF Σx 2 Клавиша суммы квадратов
Дисплей
Порядок Выполнения Операций
2ndF Σx Клавиша суммы
Точность Расчетов И Допустимые Пределы Значений
Переполнение / Ошибка
Питание
Обычные Расчеты
Основные вычисления Включая расчеты с использованием скобок
Расчеты с использованием констант
Расчеты с использованием памяти
Расчеты с использованием дробей
Расчеты С Применением Функциональных Клавиш
Перевод шестидесятеричных чисел в десятичные
Тригонометрические и обратные Тригонометрические функции
Гиперболические и обратные гиперб. функции
Десятичные и натуральные логарифмы / Возведение в степень
Степень, корень квадратный, обратная величина, факториал
Стандартное Отклонение
Программирование
R16
Описание
R18 SRP-145NRussianSR135A090330.doc Size 140x75mm
Przedziały Przepełnienie I Błąd Zasilanie Obliczenia Zwykłe
Definicje Podstawowe
Wyświetlacz Kolejność Operacji
Funkcyjnych
Definicje Podstawowe
Klawisze
Klawisze Wprowadzania do Pamięci
Klawisze Specjalne
Klawisze Funkcyjne
SCI Tryb naukowy
DRG Konwersja jednostek miar kątów
Sin , cos , tan Klawisze sinus, cosinus, tangens
Klawize Programowania Wyłącznie W Trybie PGM
Klawisze Obliczeń Statystycznych Wyłącznie W Trybie Stat
Wyświetlacz
Kolejność Operacji
Dokładność Obliczeń Oraz Wprowadzane Przedziały
Przepełnienie I Błąd
Zasilanie
Obliczenia Zwykłe
Obliczenia wykorzystujące stałe
Obliczenia Z Wykorzystaniem Klawiszy Funkcyjnych
Obliczenia wykorzystujące pamięć
Konwersja sześćdziesiętnych liczb na dziesiętne
Działania na ułamkach
Funkcje hiperboliczne oraz odwrotne funkcje hiperboliczne
Logarytmy dziesiętne i naturalne / Potęgowanie
Potęga, pierwiastek, odwrotność, silnia
Odchylenie Standardowe
Programowanie
5000
2ndF PGM RUN 1000
Kb xÆk + MR = 2ndF Halt
Weee Mark