Page
Page
Cloud Infrastructure Concepts
User Services Overview
Getting More Information and Help
Concepts
Setting Up Networking for Users
Service Offerings
Steps to Provisioning Your Cloud Infrastructure
Working With Hosts 103
Working With Virtual Machines
Working With Storage 129
Working with Templates 113
Managing Networks and Traffic 147
Working with Usage 141
Page
System Reliability and High Availability 233
Tuning 249
Troubleshooting 251
Working with System Virtual Machines 229
Event Types 259 Alerts 261
Chapter
Getting More Information and Help
Additional Documentation Available
Citrix Knowledge Center Contacting Support
Page
Multiple Hypervisor Support
What Is CloudPlatform?
Concepts
What Can CloudPlatform Do?
Deployment Architecture Overview
Cloud Infrastructure Overview
Management Server Overview
More Information
Networking Overview
Page
Page
About Regions
Cloud Infrastructure Concepts
About Zones
Cloud Infrastructure Concepts
About Pods
About Clusters
About Primary Storage
About Hosts
About Physical Networks
About Secondary Storage
Basic Zone Network Traffic Types
Advanced Zone Network Traffic Types
Basic Zone Guest IP Addresses
Advanced Zone Guest IP Addresses
A zone that uses advanced networking
Advanced Zone Public IP Addresses
System Reserved IP Addresses
All zones
Page
Accounts, Users, and Domains
Accounts
Dedicating Resources to Accounts and Domains
How to Use Dedicated Hosts
Behavior of Dedicated Hosts, Clusters, Pods, and Zones
Configuring an Ldap Server
Using an Ldap Server for User Authentication
Adding an Ldap Server
Trust Store Trust Store Password
Removing an Ldap Configuration
Example Ldap Configuration Commands
Search Base
Active Directory
Query Filter
ApacheDS
Search User Bind DN
SSL Keystore Path and Password
Page
User Services Overview
Page
End Users UI Overview
User Interface
Supported Browsers
Log In to the UI
Logging In as the Root Administrator
Root Administrators UI Overview
Changing the Root Password
Using SSH Keys for Authentication
Creating an Instance from a Template that Supports SSH Keys
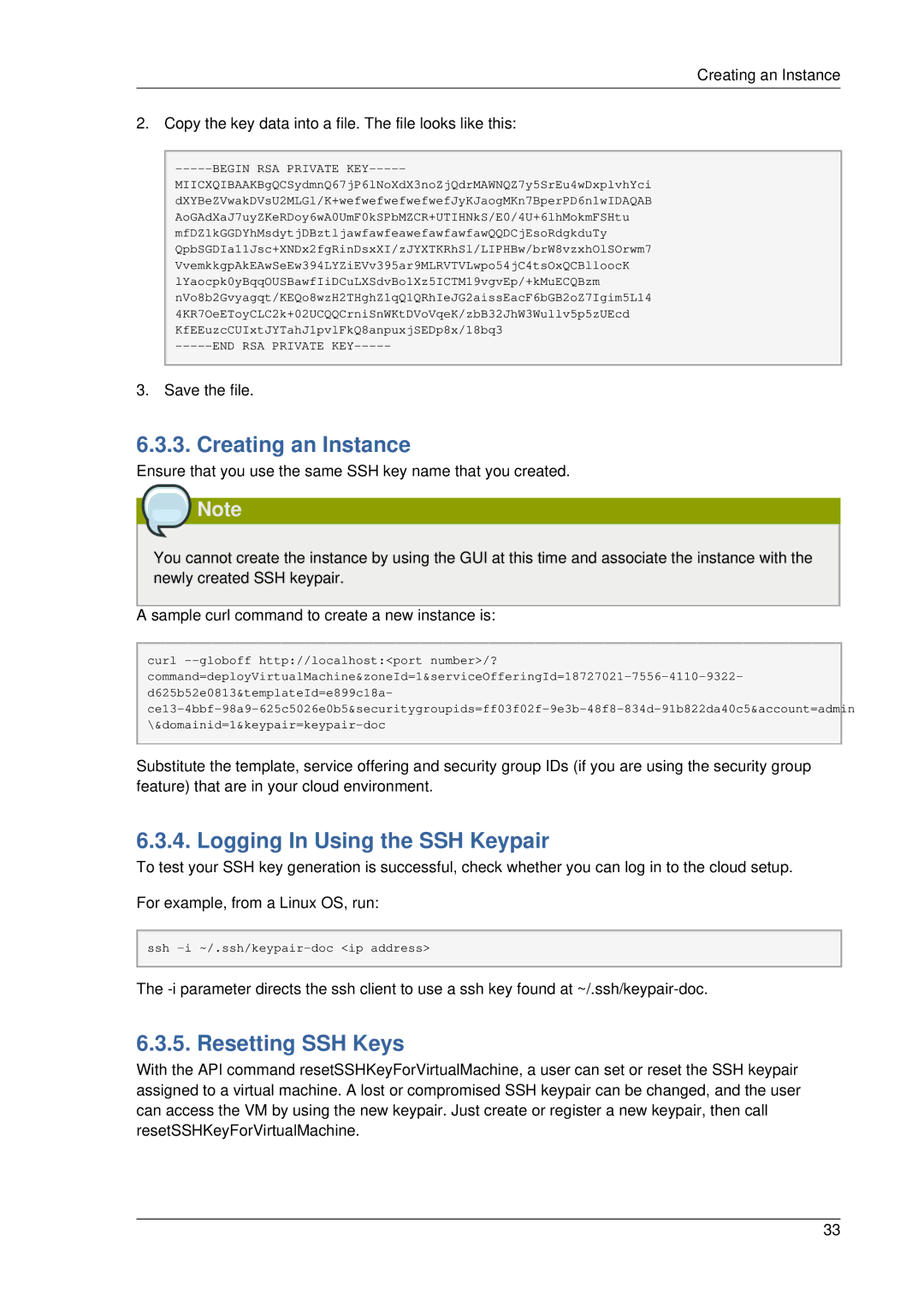
Creating the SSH Keypair
Output is something similar to what is given below
Resetting SSH Keys
Logging In Using the SSH Keypair
Creating an Instance
Page
Overview of Projects
Using Projects to Organize Users and Resources
Configuring Projects
Setting Up Invitations
Setting Project Creator Permissions
Setting Resource Limits for Projects
Adding Members to a Project
Creating a New Project
Sending Project Membership Invitations
Adding Project Members From the UI
Accepting a Membership Invitation
Suspending or Deleting a Project
Using the Project View
Page
Overview of Provisioning Steps
Steps to Provisioning Your Cloud Infrastructure
Adding Regions optional
First Region The Default Region
Adding a Region
Adding Third and Subsequent Regions
Deleting a Region
Create a Secondary Storage Mount Point for the New Zone
Adding a Zone
Prepare the System VM Template
Steps to Add a New Zone
Network Offering Description
Basic Zone Configuration
Steps to Provisioning Your Cloud Infrastructure
Page
Advanced Zone Configuration
Page
Steps to Provisioning Your Cloud Infrastructure
Page
NFS
Vmfs
Adding a Pod
Add Cluster KVM or XenServer
Adding a Cluster
Add Cluster OVM
VMware Cluster Size Limit
Add Cluster vSphere
Adding a vSphere Cluster
Steps to Provisioning Your Cloud Infrastructure
Page
Adding a Host XenServer, KVM, or OVM
Adding a Host
Requirements for XenServer, KVM, and OVM Hosts Warning
KVM Host Additional Requirements
Adding a XenServer, KVM, or OVM Host
Adding a Host vSphere
Adding Primary Storage
Adding Secondary Storage
Adding an NFS Secondary Staging Store for Each Zone
Initialize and Test
Steps to Provisioning Your Cloud Infrastructure
Compute and Disk Service Offerings
Service Offerings
Creating a New Compute Offering
Creating a New Disk Offering
Modifying or Deleting a Service Offering
System Service Offerings
Creating a New System Service Offering
For more information, see .7, Stopping and Starting VMs
Page
Page
Isolated Networks
Setting Up Networking for Users
Overview of Setting Up Networking for Users
About Virtual Networks
Individual
Network Service Providers
Network Service Providers Support Matrix
Runtime Allocation of Virtual Network Resources
ACL
Support Matrix for an Isolated Network Combination
Support Matrix for Shared Network Combination
Support Matrix for Basic Zone
Network Offerings
Creating a New Network Offering
Supported Services Description Isolated Shared
See Section Remote Access VPN
Changing the Network Offering on a Guest Network
Creating and Changing a Virtual Router Network Offering
Page
Page
About Working with Virtual Machines
Working With Virtual Machines
Best Practices for Virtual Machines
VM Lifecycle
Install Required Tools and Drivers
Monitor VMs for Max Capacity
Creating a VM from a template
Creating VMs
Creating a VM from an ISO
Configuring Usage of Linked Clones on VMware
Appending a Display Name to the Guest VM’s Internal Name
Accessing VMs
Assigning VMs to Hosts
Stopping and Starting VMs
Change Affinity Group for an Existing VM
Affinity Groups
Creating a New Affinity Group
Assign a New VM to an Affinity Group
View Members of an Affinity Group
Virtual Machine Snapshots for VMware
Delete an Affinity Group
Using VM Snapshots
Configuring VM Snapshots
Limitations on VM Snapshots
Changing the VM Name, OS, or Group
CPU and Memory Scaling for Running VMs
Changing the Service Offering for a VM
Limitations
Configuring Dynamic CPU and RAM Scaling
How to Dynamically Scale CPU and RAM
Updating Existing VMs
Moving VMs Between Hosts Manual Live Migration
Resetting the Virtual Machine Root Volume on Reboot
Deleting VMs
Recovering a Destroyed VM
Working with ISOs
Adding an ISO
Changing a VMs Base Image
Attaching an ISO to a VM
Page
102
Working With Hosts
Scheduled Maintenance and Maintenance Mode for Hosts
VCenter and Maintenance Mode
XenServer and Maintenance Mode
Working With Hosts
To take a server out of Maintenance Mode
Disabling and Enabling Zones, Pods, and Clusters
Removing Hosts
Removing XenServer and KVM Hosts
Re-Installing Hosts
Using Cisco UCS as Bare Metal Host CloudPlatform
Maintaining Hypervisors on Hosts
Associating a Profile with a UCS Blade
Registering a UCS Manager
Disassociating a Profile from a UCS Blade
Changing Host Password
Over-Provisioning and Service Offering Limits
Balloon Driver
Setting Over-Provisioning Ratios
Limitations on Over-Provisioning in XenServer and KVM
Requirements for Over-Provisioning
Vlan Provisioning
Service Offering Limits and Over-Provisioning
Adding Non Contiguous Vlan Ranges
Vlan Allocation Example
Assigning VLANs to Isolated Networks
Requirements for Templates
Default Template
Working with Templates
Creating Templates Overview
Creating a Template from an Existing Virtual Machine
Private and Public Templates
Working with Templates
Uploading Templates
Creating a Template from a Snapshot
Working with Templates
Creating a Windows Template
Exporting Templates
System Preparation for Windows Server 2008 R2
Working with Templates
Page
Working with Templates
System Preparation for Windows Server 2003 R2
Importing Amazon Machine Images
Create a grub entry in /boot/grub/grub.conf
Exit out of chroot
Converting a Hyper-V VM to a Template
Adding Password Management to Your Templates
Windows OS Installation
Linux OS Installation
Deleting Templates
128
Storage Overview
Working With Storage
Primary Storage
NFS support Local storage support Storage over-provisioning
Storage Tags
Working With Storage
Fiber Channel support
Changing the Secondary Storage IP Address
Maintenance Mode for Primary Storage
Secondary Storage
Best Practices for Secondary Storage
Changing Secondary Storage Servers
Working With Volumes
Creating a New Volume
Using Local Storage for Data Volumes
To Create a New Volume
Uploading an Existing Volume to a Virtual Machine
Hypervisor Disk Image Format
Attaching a Volume
VM Storage Migration
Detaching and Moving Volumes
Migrating a VM Root Volume to a New Storage Pool
Migrating a Data Volume to a New Storage Pool
Resizing Volumes
Working with Snapshots
Reset VM to New Root Disk on Reboot
Volume Deletion and Garbage Collection
To enable root disk reset on VM reboot
Volume Status
Incremental Snapshots and Backup
Automatic Snapshot Creation and Retention
VMware Volume Snapshot Performance
Snapshot Restore
Snapshot Job Throttling
Working with Usage
Configuring the Usage Server
Alerttypeusagesanityresult =
Working with Usage
Setting Usage Limits
Parameter Name Definition
Globally Configured Limits
Default Account Resource Limits
Per-Domain Limits
Guest Traffic
Managing Networks and Traffic
Networking in a Pod
Managing Networks and Traffic
Networking in a Zone
Advanced Zone Physical Network Configuration
Basic Zone Physical Network Configuration
Configuring Isolated Guest Network
Configure Public Traffic in an Advanced Zone
Configuring a Shared Guest Network
Limitation
Using Security Groups to Control Traffic to VMs
About Security Groups
Security Groups in Advanced Zones KVM Only
Adding a Security Group
Enabling Security Groups
Adding Ingress and Egress Rules to a Security Group
External Firewalls and Load Balancers
MPX
About Using a NetScaler Load Balancer
VPX
Configuring SNMPCommunity String on a Rhel Server
Initial Setup of External Firewalls and Load Balancers
Adding a Load Balancer Rule
Load Balancer Rules
Configuring AutoScale
Prerequisites
Configuration
Managing Networks and Traffic
Updating an AutoScale Configuration
Disabling and Enabling an AutoScale Configuration
Health Checks for Load Balancer Rules
Sticky Session Policies for Load Balancer Rules
Runtime Considerations
About Global Server Load Balancing
Global Server Load Balancing
Components of Gslb
How Gslb Works in CloudPlatform
Configuring Gslb
For more information, see Configuring a Gslb Virtual Server4
Enabling Gslb in NetScaler
Prerequisites and Guidelines
Adding a Gslb Rule
Assigning Load Balancing Rules to Gslb
Reconfiguring Networks in VMs
Using Multiple Guest Networks
Adding an Additional Guest Network
Removing a Network
Selecting the Default Network
Prerequisites
Adding a Network
Acquiring a New IP Address
Guest IP Ranges
Releasing an IP Address
Dedicating IP Address Ranges to an Account
Reserving Public IP Addresses and VLANs for Accounts
Gateway Netmask
Dedicating Vlan Ranges to an Account
Start IP End IP
IP Reservation Considerations
IP Reservation in Isolated Guest Networks
Best Practices
Configuring Multiple IP Addresses on a Single NIC
Reserving an IP Range
Assigning Additional IPs to a VM
Port Forwarding and StaticNAT Services Changes
Use Cases
Guidelines
Prerequisites and Guidelines
Multiple Subnets in Shared Network
Adding Multiple Subnets to a Shared Network
About Elastic IP
Managing Networks and Traffic
About Portable IP
Portable IPs
Acquiring a Portable IP
Configuring Portable IPs
Guidelines
Transferring Portable IP
Static NAT
Enabling or Disabling Static NAT
IP Forwarding and Firewalling
Configuring an Egress Firewall Rule
Egress Firewall Rules in an Advanced Zone
Allow
Configuring the Default Egress Policy
Deny
Firewall Rules
Port Forwarding
IP Load Balancing
Configuring Remote Access VPN
Remote Access VPN
DNS and Dhcp
Using Remote Access VPN with Windows
Setting Up a Site-to-Site VPN Connection
Using Remote Access VPN with Mac OS
Creating and Updating a VPN Customer Gateway Note
See .27, Configuring a Virtual Private Cloud
Managing Networks and Traffic
Page
Updating and Removing a VPN Customer Gateway
Creating a VPN gateway for the VPC
Cidr
Creating a VPN Connection Note
Managing Networks and Traffic
Restarting and Removing a VPN Connection
About Private Vlan
Isolation in Advanced Zone Using Private Vlan
Prerequisites
Creating a PVLAN-Enabled Guest Network
About Inter-VLAN Routing
Page
About Virtual Private Clouds
Configuring a Virtual Private Cloud
Major Components of a VPC
Connectivity Options for a VPC
Network Architecture in a VPC
VPC Network Considerations
Adding a Virtual Private Cloud
Adding Tiers
Managing Networks and Traffic
About Network ACL Lists
Configuring Network Access Control List
Creating ACL Lists
Creating an ACL Rule
Assigning a Custom ACL List to a Tier
Creating a Tier with Custom ACL List
Adding a Private Gateway to a VPC
See .27.5.2, ACL on Private Gateway
Source NAT on Private Gateway
Creating a Static Route
ACL on Private Gateway
Deploying VMs to VPC Tier and Shared Networks
Deploying VMs to the Tier
Blacklisting Routes
Acquiring a New IP Address for a VPC
Releasing an IP Address Alloted to a VPC
Enabling or Disabling Static NAT on a VPC
Load Balancing Public Traffic Public LB
Adding Load Balancing Rules on a VPC
Creating a Network Offering for Public LB
Creating a Public LB Rule
How Does Internal LB Work in VPC?
Load Balancing Tier-to-Tier traffic Internal LB
Enabling Internal LB on a VPC Tier
Creating an Internal LB Rule
Adding a Port Forwarding Rule on a VPC
TCP UDP
Removing Tiers
Editing, Restarting, and Removing a Virtual Private Cloud
Persistent Networks
Persistent Network Considerations
Creating a Persistent Guest Network
Console Proxy
Working with System Virtual Machines
System VM Template
Multiple System VM Support for VMware
Working with System Virtual Machines
Changing the Console Proxy SSL Certificate and Domain
Virtual Router
Configuring the Virtual Router
Secondary Storage VM
Upgrading a Virtual Router with System Service Offerings
Best Practices for Virtual Routers
Dedicated HA Hosts
HA-Enabled Virtual Machines
System Reliability and High Availability
HA for Management Server
Limiting the Rate of API Requests
Configuring the API Request Rate
Primary Storage Outage and Data Loss
Secondary Storage Outage and Data Loss
Limitations on API Throttling
236
Managing the Cloud
Using Tags to Organize Resources in the Cloud
About Configuration Parameters
Setting Configuration Parameters
Managing the Cloud
Setting Local Configuration Parameters
Setting Global Configuration Parameters
Granular Global Configuration Parameters
Cluster.cpu.allocated.capacity.disablThethr
Administrator Alerts
Changing the Database Configuration
Sending Alerts to External Snmp and Syslog Managers
Customizing Alerts with Global Configuration Settings
Snmp Alert Details
Syslog Alert Details
Configuring Snmp and Syslog Managers
Deleting an Snmp or Syslog Manager
Customizing the Network Domain Name
Stopping and Restarting the Management Server
User Data and Meta Data
Provisioning and Authentication API
CloudPlatform API
Allocators
CloudPlatform API
Set Database Buffer Pool Size
Tuning
Performance Monitoring
Increase Management Server Maximum Memory
Tuning
Configure XenServer dom0 Memory
Set and Monitor Total VM Limits per Host
Event Notification
Troubleshooting
Events
Event Logs
Standard Events
Troubleshooting
Long Running Job Events
Deleting and Archiving Events and Alerts
Event Log Queries
Working with Server Logs
Procedure
Permissions
Data Loss on Exported Primary Storage
Using cloud-bugtool
Symptom
Log Collection Utility cloud-bugtool
Cause
Recovering a Lost Virtual Router
Maintenance mode not working on vCenter
Solution
Unable to deploy VMs from uploaded vSphere template
Unable to power on virtual machine on VMware
Load balancer rules fail after changing network offering
Appendix A. Event Types
260
Appendix B. Alerts
Appendix B. Alerts