CY7C1266V18, CY7C1277V18 CY7C1268V18, CY7C1270V18
Delay Lock Loop (DLL)
These chips use a DLL that is designed to function between 120 MHz and the specified maximum clock frequency. The DLL may be disabled by applying ground to the DOFF pin. When the DLL is turned off, the device behaves in
the application note, DLL Considerations in QDRII/DDRII/QDRII+/DDRII+. The DLL can also be reset by slowing or stopping the input clocks K and K for a minimum of 30 ns. However, it is not necessary for the DLL to be reset to lock to the frequency you want. During power up, when the DOFF is tied HIGH, the DLL is locked after 2048 cycles of stable clock.
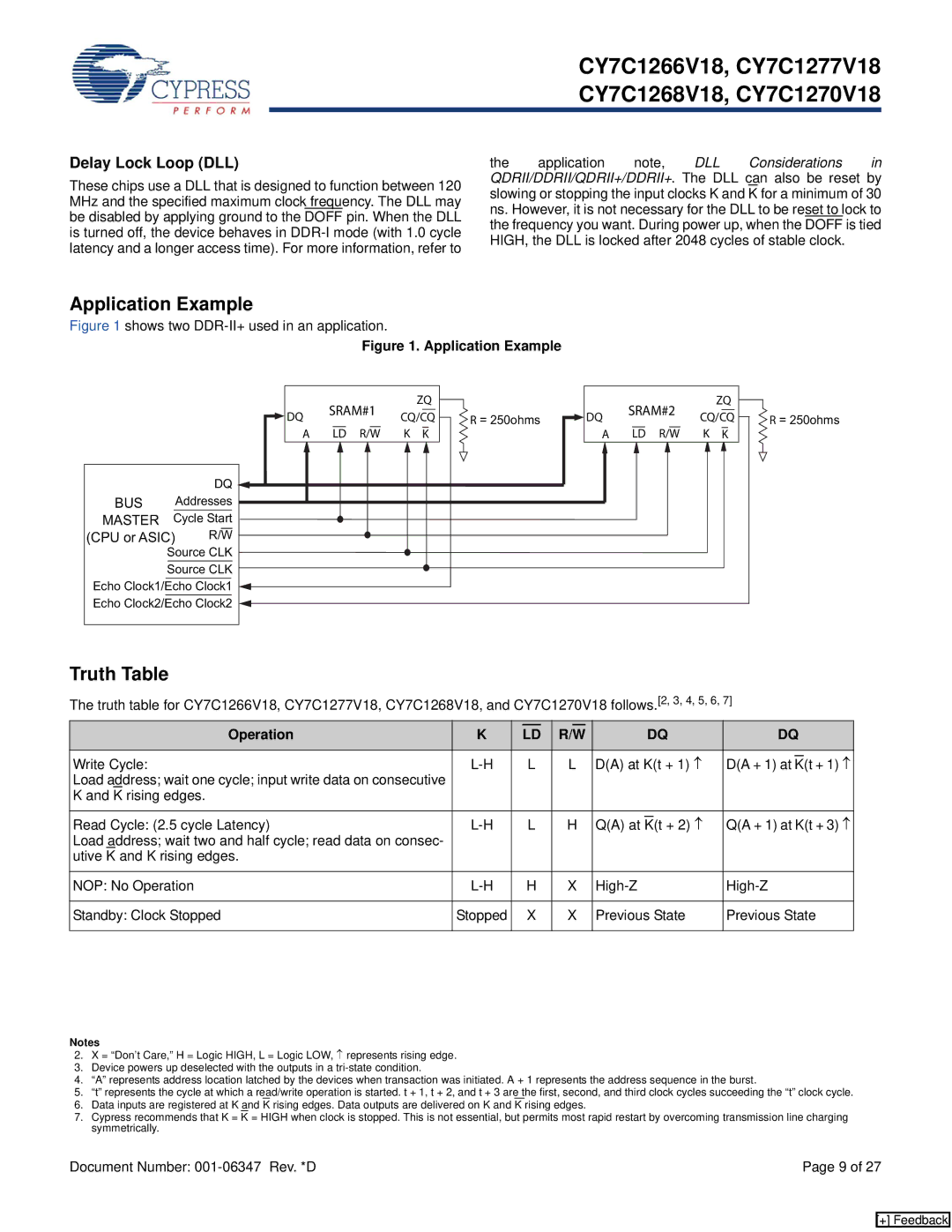
Application Example
Figure 1 shows two DDR-II+ used in an application.
Figure 1. Application Example
|
|
| SRAM#1 |
| ZQ |
|
| SRAM#2 |
| ZQ |
| ||
|
| DQ | CQ/CQ | R = 250ohms | DQ | CQ/CQ | R = 250ohms | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||
|
| A | LD | R/W | K | K |
| A | LD | R/W | K | K |
|
|
| DQ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
BUS |
| Addresses |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MASTER | Cycle Start |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
(CPU or ASIC) | R/W |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| Source CLK |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| Source CLK |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Echo Clock1/Echo Clock1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
Echo Clock2/Echo Clock2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
Truth Table
The truth table for CY7C1266V18, CY7C1277V18, CY7C1268V18, and CY7C1270V18 follows.[2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
Operation | K |
| LD | R/W |
| DQ | DQ | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Write Cycle: |
| L | L | D(A) at K(t + 1) ↑ | D(A + 1) at |
|
| ||||||
K(t + 1) ↑ | |||||||||||||
Load address; wait one cycle; input write data on consecutive |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
K and K rising edges. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||
Read Cycle: (2.5 cycle Latency) |
| L | H | Q(A) at |
|
| Q(A + 1) at K(t + 3) ↑ | ||||||
K(t + 2) ↑ | |||||||||||||
Load address; wait two and half cycle; read data on consec- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
utive K and K rising edges. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
NOP: No Operation |
| H | X | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Standby: Clock Stopped | Stopped |
| X | X | Previous State | Previous State | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Notes
2.X = “Don’t Care,” H = Logic HIGH, L = Logic LOW, ↑ represents rising edge.
3.Device powers up deselected with the outputs in a
4.“A” represents address location latched by the devices when transaction was initiated. A + 1 represents the address sequence in the burst.
5.“t” represents the cycle at which a read/write operation is started. t + 1, t + 2, and t + 3 are the first, second, and third clock cycles succeeding the “t” clock cycle.
6.Data inputs are registered at K and K rising edges. Data outputs are delivered on K and K rising edges.
7.Cypress recommends that K = K = HIGH when clock is stopped. This is not essential, but permits most rapid restart by overcoming transmission line charging symmetrically.
Document Number: | Page 9 of 27 |
[+] Feedback