C120-H007-05EN 47
4.4 Thermal Load and Cooling Capacities
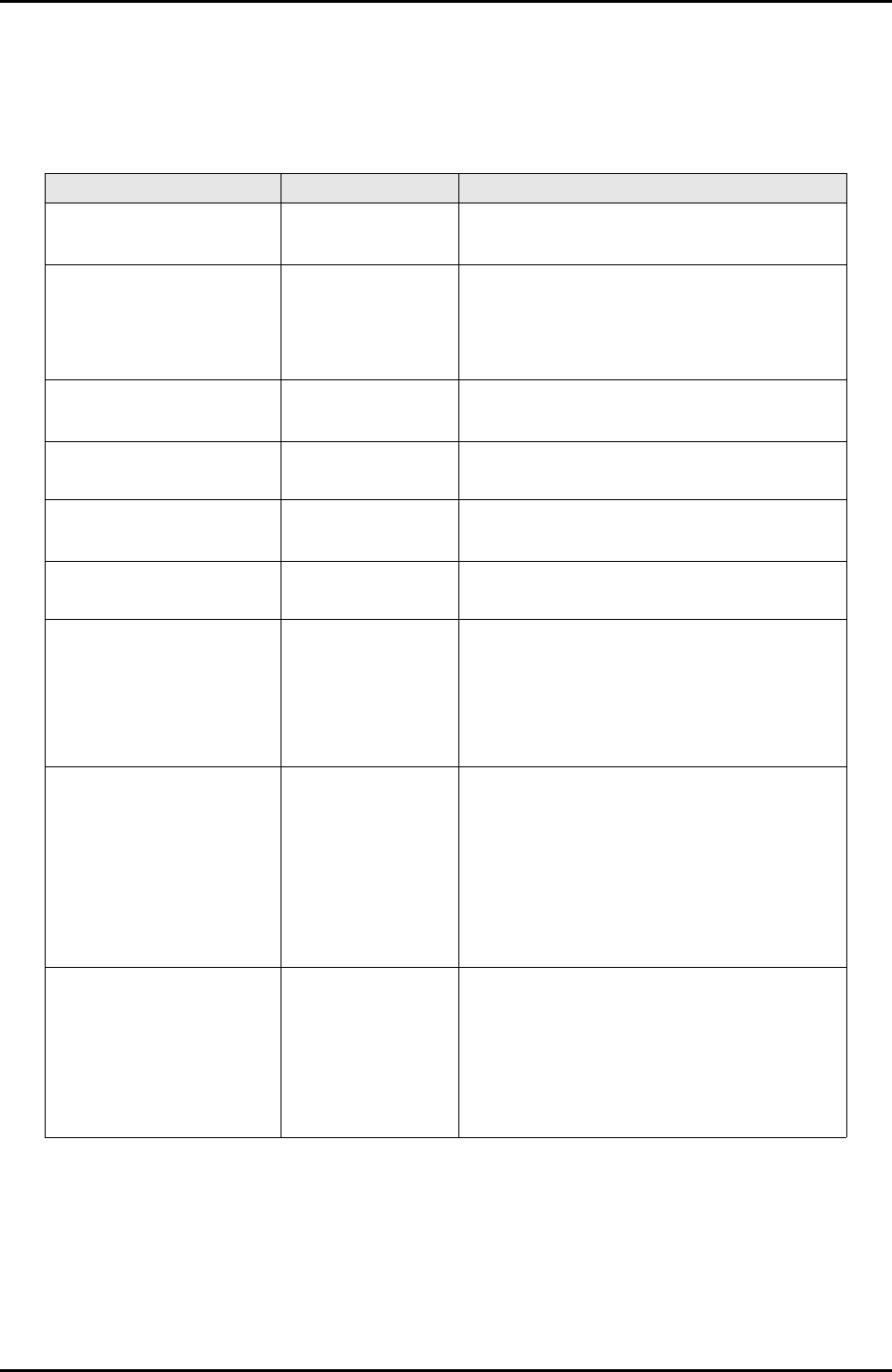
The values in the table involve certain characteristic curve and air-line diagram read errors.Table 4.6 Examples of typical air conditioner cooling capacity calculations (1/2)Item Calculated value Calculation method
Enthalpy of the air at the
conditioner inlet
i1=45.4 kJ/kg
(19.6 Btu/lb)
Determine the enthalpy at 24°C (75.2°F) and
45%RH from the air-line diagram
Enthalpy difference
between the air conditioner
coil inlet and the coil
surface
Δi=16.7 kJ/kg
(7.2 Btu/lb)
Determine the difference from typical air
conditioner characteristics.
Enthalpy on the air
conditioner coil surface
i2=28.7 kJ/kg
(12.4 Btu/lb)
Determine the enthalpy from the air-line
diagram.
Air conditioner bypass
factor
BF=0.095 Determine the bypass factor from typical air
conditioner characteristics.
Enthalpy of the air coming
out of the air conditioner
i3=30.3 kJ/kg
(13.1 Btu/lb)
Calculate the enthalpy by solving the bypass
factor relation BF= (i3 - i2) / (i1 - i2).
Temperature and humidity
at the inlet
24°C (75.2°F) 45% Setup condition
Enthalpy on the air
conditioner coil surface
9.7°C (49.5°F)
100%
Determine the temperature and humidity
from the point of intersection between the
enthalpy (i2) on the air conditioner coil
surface and 100% relative humidity in the
air-line diagram.
Temperature and humidity
of the air coming out of the
air conditioner
11.1°C (52°F) 92% Determine the temperature and humidity
from the point of intersection of a line
segment, between the status point at the
conditioner inlet and that on the air
conditioner coil surface, and the enthalpy of
the air coming out of the air conditioner in
the air-line diagram.
Air conditioner cooling
capacity
145.6 MJ/h
(138,029 Btu/h)
(i1 - i3) × Flow rate/Specific volume
=15.1 (kJ/kg) × 135 (m3/min) ×
60 (min/h) / 0.84 (m3/kg)
=6.5 (Btu/lb) × 4770 (ft3/min) ×
60 (min/h) / 13.5 (ft3/lb)