60 C120-H007-05EN
CHAPTER 5 Electromagnetic Environment and Static Electricity
5.1.2 Sources of magnetic fields and fault symptomsTable 5.1 lists the possible sources of magnetic fields and the associated display
screen faults.
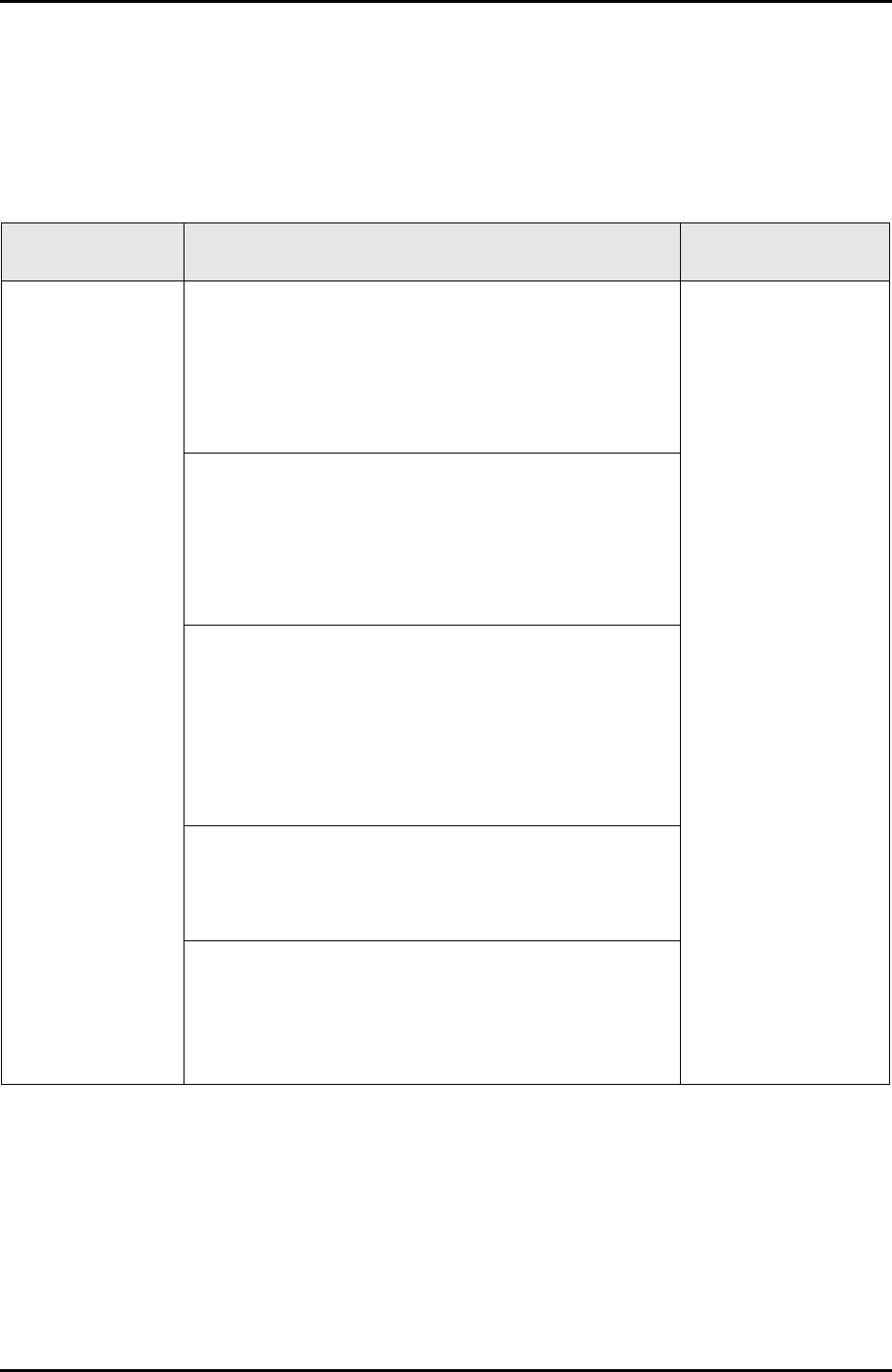
Table 5.1 Sources of magnetic fields and fault symptoms (1/2)
Magnetic field
component Source of magnetic field Fault symptom
AC magnetic field
components
1 Power supply facilities, such as an uninterruptible
power supply and a transformer, or any electrically
driven equipment, such as a motor: Magnetic fields are
generated by current flowing through the equipment.
Example: AC magnetic field of 8.2 μΤ at a point 4 m
(13 ft) away from a transformer rated at 100 kVA.
Fluctuating display
images
2 Indoor electrical connections: A separation of 2 m (7 ft)
from connections rated at 30 A or so will eliminate their
effects.
Example: AC magnetic field of 2.5 μΤ at a point 1 m (3
ft) away from a connection that is not enclosed in a steel
pipe.
3 High-voltage transmission lines, electric car overhead
lines
Example: A high-voltage transmission line rated at
about 280 A will affect the display images of displays
installed 5 m (16 ft) away with a magnetic field of 2.4
μΤ, but will not affect those of a display device installed
10 m (33 ft) away with only 0.6 μΤ
4 Adjacent equipment: Magnetic fields generated from
the adjacent equipment could exert adverse effects.
Example: AC magnetic field of 3 μΤ at a point 200 mm
(8 in.) away from a display device.
5 Mutual interference among display devices: Magnetic
fields generated from the deflection yoke in each device
may have an interfering effect.
Example: AC magnetic field of 3 μΤ at a point 200 mm
(8 in.) away from a display device.