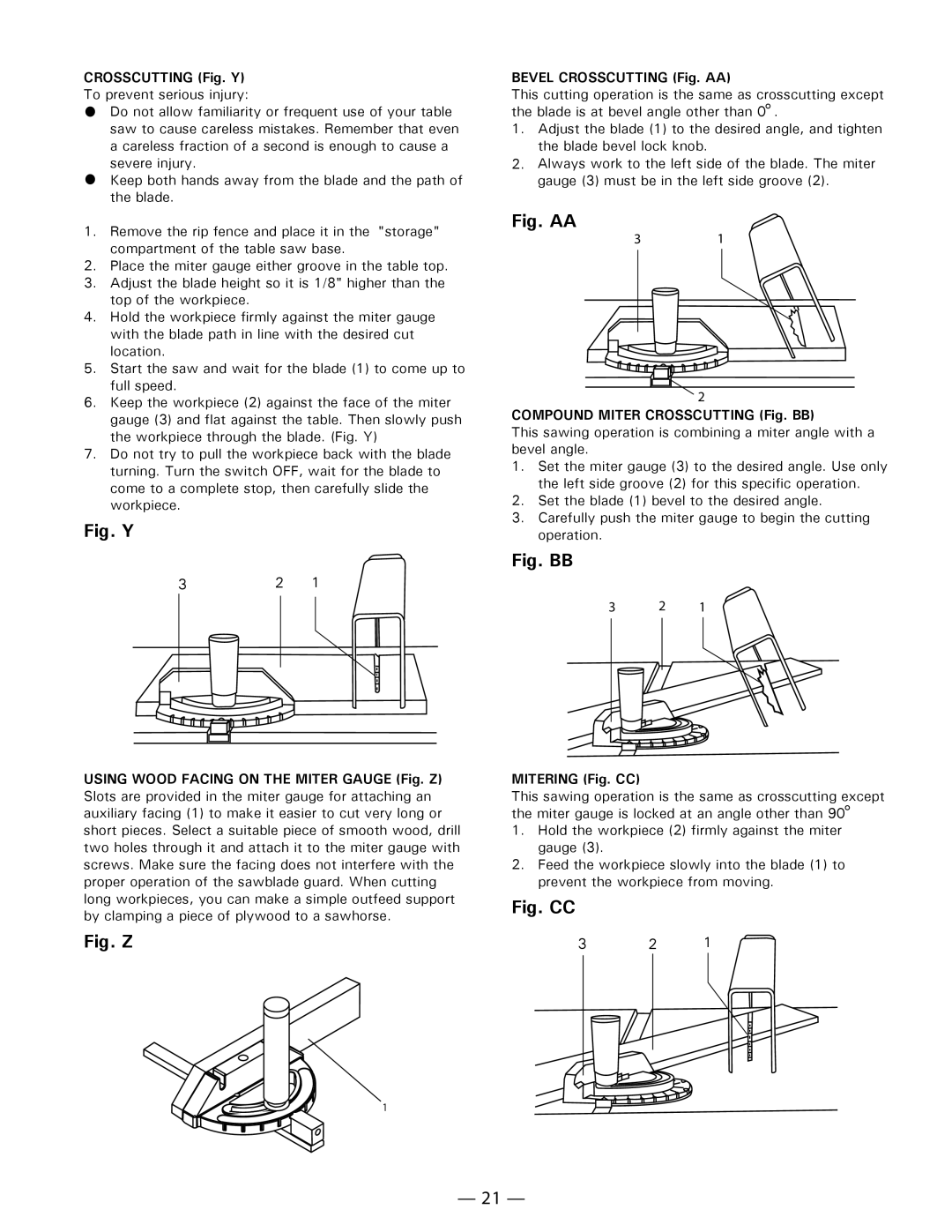
CROSSCUTTING (Fig. Y) To prevent serious injury:
Do not allow familiarity or frequent use of your table saw to cause careless mistakes. Remember that even a careless fraction of a second is enough to cause a severe injury.
Keep both hands away from the blade and the path of the blade.
1.Remove the rip fence and place it in the "storage" compartment of the table saw base.
2.Place the miter gauge either groove in the table top.
3.Adjust the blade height so it is 1/8" higher than the top of the workpiece.
4.Hold the workpiece firmly against the miter gauge with the blade path in line with the desired cut location.
5.Start the saw and wait for the blade (1) to come up to full speed.
6.Keep the workpiece (2) against the face of the miter gauge (3) and flat against the table. Then slowly push the workpiece through the blade. (Fig. Y)
7.Do not try to pull the workpiece back with the blade turning. Turn the switch OFF, wait for the blade to come to a complete stop, then carefully slide the workpiece.
Fig. Y
3 |
|
| 2 | 1 | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
USING WOOD FACING ON THE MITER GAUGE (Fig. Z) Slots are provided in the miter gauge for attaching an auxiliary facing (1) to make it easier to cut very long or short pieces. Select a suitable piece of smooth wood, drill two holes through it and attach it to the miter gauge with screws. Make sure the facing does not interfere with the proper operation of the sawblade guard. When cutting long workpieces, you can make a simple outfeed support by clamping a piece of plywood to a sawhorse.
Fig. Z
1
BEVEL CROSSCUTTING (Fig. AA)
This cutting operation is the same as crosscutting except the blade is at bevel angle other than 0![]() .
.
1.Adjust the blade (1) to the desired angle, and tighten the blade bevel lock knob.
2.Always work to the left side of the blade. The miter gauge (3) must be in the left side groove (2).
Fig. AA
31
2
COMPOUND MITER CROSSCUTTING (Fig. BB)
This sawing operation is combining a miter angle with a bevel angle.
1.Set the miter gauge (3) to the desired angle. Use only the left side groove (2) for this specific operation.
2.Set the blade (1) bevel to the desired angle.
3.Carefully push the miter gauge to begin the cutting operation.
Fig. BB
3 2 1
MITERING (Fig. CC)
This sawing operation is the same as crosscutting except the miter gauge is locked at an angle other than 90![]()
1.Hold the workpiece (2) firmly against the miter gauge (3).
2.Feed the workpiece slowly into the blade (1) to prevent the workpiece from moving.
Fig. CC
3 2 1
— 21 —