Disaster Tolerance and Recovery in a Serviceguard Cluster
Disaster Tolerant Architecture Guidelines
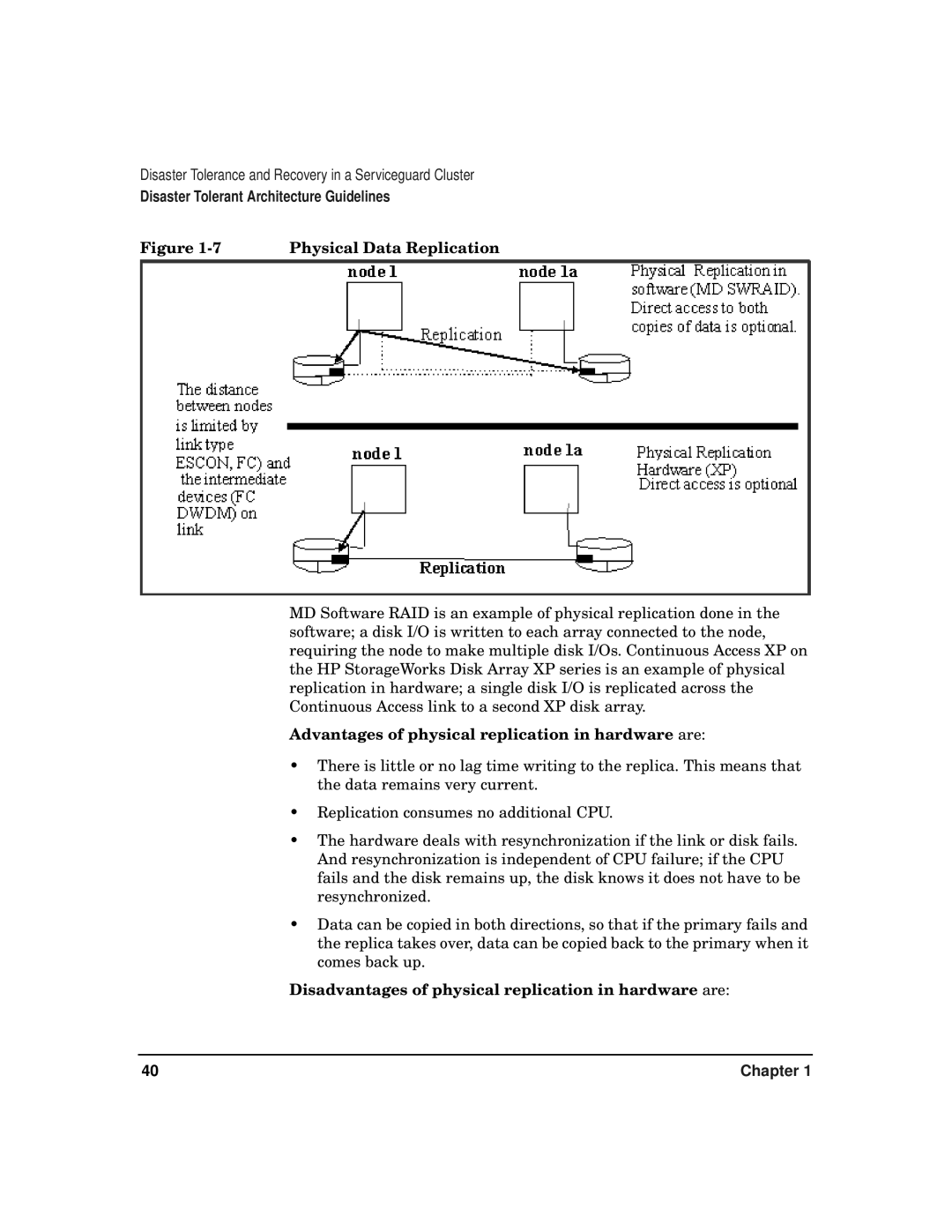
Figure | Physical Data Replication |
MD Software RAID is an example of physical replication done in the software; a disk I/O is written to each array connected to the node, requiring the node to make multiple disk I/Os. Continuous Access XP on the HP StorageWorks Disk Array XP series is an example of physical replication in hardware; a single disk I/O is replicated across the Continuous Access link to a second XP disk array.
Advantages of physical replication in hardware are:
•There is little or no lag time writing to the replica. This means that the data remains very current.
•Replication consumes no additional CPU.
•The hardware deals with resynchronization if the link or disk fails. And resynchronization is independent of CPU failure; if the CPU fails and the disk remains up, the disk knows it does not have to be resynchronized.
•Data can be copied in both directions, so that if the primary fails and the replica takes over, data can be copied back to the primary when it comes back up.
Disadvantages of physical replication in hardware are:
40 | Chapter 1 |