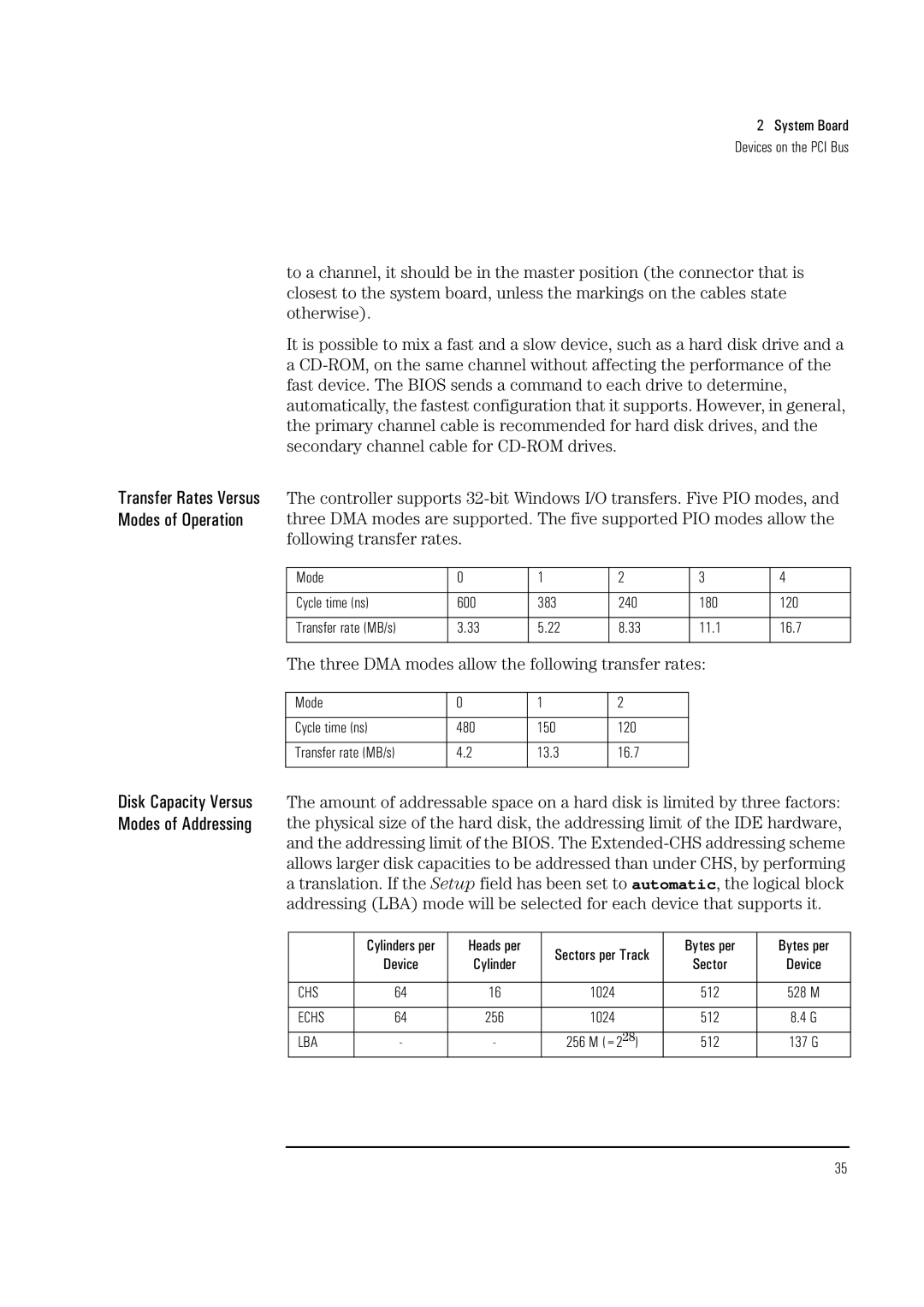
Vectra VL 5/xxx 5 specifications
The HP Vectra VL 5/xxx was a series of desktop personal computers introduced by Hewlett-Packard in the mid-1990s. These machines were designed for both business and professional environments, making them suitable for a range of applications from basic office tasks to more demanding computing needs. This series played a significant role in HP's efforts to strengthen its market presence in the PC sector during a time when competition was intensifying.One of the standout features of the HP Vectra VL 5/xxx line was its versatility. The series included various configurations designated by the '5/xxx' nomenclature, which indicated different performance levels and specifications. The performance was driven primarily by Intel Pentium processors, widely acclaimed for their reliability and efficiency. This allowed users to choose a model that suited their specific requirements, whether for everyday tasks or more resource-intensive applications.
In addition to its strong processing capabilities, the Vectra VL 5/xxx featured advanced graphics support, which was critical for visual applications and presentations. Many units in this series came equipped with onboard graphics capabilities that supported a range of resolutions, enhancing the user experience in both standard office environments and more creative settings.
Storage options were another highlight of the HP Vectra VL 5/xxx series. The machines typically featured a variety of hard drive configurations, allowing for ample data storage. Some models included the option for expanding storage through additional hard drives or external devices. Coupled with considerable RAM options, these machines ensured smooth multitasking and efficient performance across various applications.
Connectivity was also a core aspect of the Vectra VL 5/xxx. The systems typically included multiple USB ports, parallel and serial ports, and integrated networking capabilities. This made it easy for businesses to integrate the Vectra machines into their existing infrastructure, facilitating seamless interaction with peripherals and networks.
In terms of design, the HP Vectra VL 5/xxx series presented a robust yet compact form factor, which was ideal for office environments with limited space. Additionally, HP emphasized the reliability and serviceability of these machines, which included easy access to internal components for maintenance and upgrades, thereby extending the product life cycle.
Overall, the HP Vectra VL 5/xxx line offered a balanced combination of performance, flexibility, and reliability, making it a solid choice for organizations looking to leverage computing power for a range of professional applications. The series embodied HP's commitment to delivering quality and innovation in the ever-evolving landscape of personal computing.