Page
Page
Page
Page
Contents
Appendix. Notices 155
Important Safety Information
About this manual
Dynamic Configure To Order CTO
FRU Identification for CTO, CMV, and GAV products
Using eSupport
Important information about replacing RoHS compliant FRUs
Related Web URLs are
Safety information
General safety
Electrical safety
Hardware Maintenance Manual
Safety inspection guide
Handling electrostatic discharge-sensitive devices
Grounding requirements
Safety notices multi-lingual translations
To Connect To Disconnect
Do not
Safety information
Hardware Maintenance Manual
Safety information
≥18 kg 37 lbs ≥32 kg 70.5 lbs ≥55 kg 121.2 lbs
Perigo
Para Conectar Para Desconectar
Cuidado
Cuidado
Hardware Maintenance Manual
Safety information
Hardware Maintenance Manual
Safety information
Hardware Maintenance Manual
Connexion Déconnexion
Ne pas
≥18 kg 37 lbs ≥32 kg 70.5 lbs ≥55 kg 121.2 lbs
Vorsicht
Achtung
Arbeitsschutzrichtlinien beim Anheben der Maschine beachten
Safety information
Hardware Maintenance Manual
Safety information
Pericolo
Per collegarsi Per scollegarsi
Attenzione
Prestare attenzione nel sollevare l’apparecchiatura
Safety information
Hardware Maintenance Manual
Safety information
Peligro
No debe
Adopte procedimientos seguros al levantar el equipo
Access IBM program
General information
Additional information resources
Specifications
Select Start Options Set Power-On Self-Test to Enhanced
General Checkout
Problem determination tips
Green Yellow Power LED Diagnostic LED Action
General Checkout
Hardware Maintenance Manual
Diagnostics using PC-Doctor for DOS
Starting PC-Doctor from the Rescue and Recovery workspace
Starting PC-Doctor from a diagnostic diskette or CD-ROM
Diagnostics program download
Navigating through the diagnostics programs
Running diagnostics tests
Test selection
Test results
Fixed disk advanced test Fdat
Fixed-Disk Tests
Destructive versus non-destructive testing
Quick and Full erase hard drive
Viewing the test log
Using the Setup Utility
Starting the Setup Utility program
Viewing and changing settings
Exiting from the Setup Utility program
Password considerations
User Password
Administrator Password
IDE Drive User Password
Setting, changing, and deleting a password
Using Security Profile by Device
Diskette Drive Access
IDE controller
Advanced settings
Selecting a startup device
Selecting a temporary startup device
Changing the startup device sequence
Symptom-to-FRU Index
Hard disk drive boot error
Power Supply Errors
Error FRU/Action
Make sure the power cord is attached to a working
Diagnostic error codes
Hardware Maintenance Manual
Diagnostic Error Code FRU/Action 001-027-XXX Run Setup
001-034-XXX Reboot the system
001-039-XXX Flash the system. See Flash update
001-040-XXX Power-off/on system and re-test
Hardware Maintenance Manual
Symptom-to-FRU Index
Diagnostic Error Code FRU/Action 005-031-XXX Video cable
005-032-XXX Video card, if installed
005-036-XXX Video card, if installed
005-038-XXX Video card, if installed
It is connected and/or enabled
011-027-XXX Run Setup, enable port
006-196-XXX Press F3 to review the log file
006-197-XXX If a component is called out, make sure
014-027-XXX Run Setup, enable port
011-196-XXX Press F3 to review the log file
011-197-XXX Make sure the component that is called
011-198-XXX If a component is called out, make sure
015-027-XXX Flash the system. See Flash update
014-195-XXX Information only
014-196-XXX Press F3 to review the log file
014-197-XXX Make sure the component that is called
015-040-XXX Run setup and check for conflicts
018-0XX-XXX Riser card, if installed
015-035-XXX Remove USB devices and re-test
015-036-XXX System board
018-197-XXX Make sure the component that is called
018-198-XXX If a component is called out, make sure
018-199-XXX
018-250-XXX PCI card
025-00X-XXX IDE signal cable 025-01X-XXX
025-027-XXX IDE signal cable
025-02X-XXX IDE signal cable 025-03X-XXX
020-199-XXX
030-00X-XXX Scsi signal cable 030-01X-XXX
030-027-XXX Scsi signal cable
030-03X-XXX Scsi signal cable 030-04X-XXX
025-199-XXX
035-0XX-XXX RAID signal cable
030-199-XXX
035-000-XXX No action
035-195-XXX Information only
071-04X-XXX Run Setup
071-02X-XXX
071-03X-XXX Speakers
071-195-XXX Information only
086-040-XXX Run Setup
080-197-XXX Make sure the component that is called
080-198-XXX If a component is called out, make sure
080-199-XXX
089-198-XXX Flash the system. See Flash update
086-198-XXX If a component is called out, make sure
086-199-XXX
089-000-XXX No action
Diagnostic Error Code FRU/Action 170-0XX-XXX Flash system
170-199-XXX See Undetermined problems on
170-250-XXX Power supply 170-251-XXX
170-195-XXX Information only
175-199-XXX See Undetermined problems on
185-278-XXX Assure Asset Security Enabled
175-198-XXX If a component is called out, make sure
175-250-XXX Check fans 175-251-XXX
CD-ROM Drive error
Check power supply voltages
Hi-Capacity Cartridge Drive error
Keyboard error
Modem error
Remove the Modem and re-test the system
Beep symptoms
Beeps Description
Symptom-to-FRU Index
No-beep symptoms
Symptom/Error FRU/Action
Post error codes
Post Error Code FRU/Action
201
210
211
1962
5962
Miscellaneous error messages
See Power Supply Errors on
If network administrator is using
Display
Printer
Undetermined problems
Locating connectors on the front
Replacing FRUs
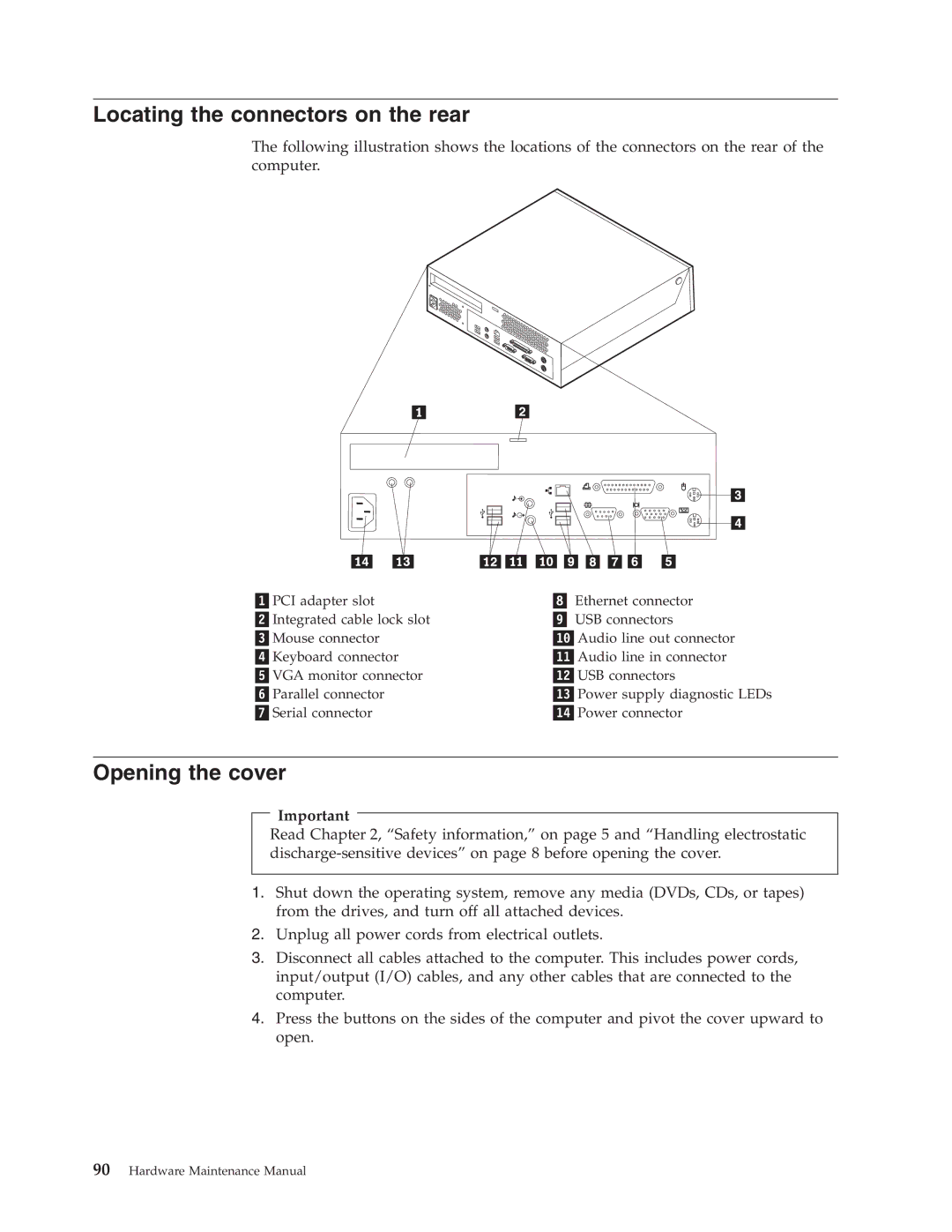
Locating the connectors on the rear
Opening the cover
Locating components
Identifying parts on the system board
Removing and replacing a memory module
Removing and replacing a PCI adapter
Removing and replacing the battery
Replacing FRUs
Removing and replacing the power supply
Removing and replacing the system board
Hardware Maintenance Manual
Replacing FRUs
Removing and replacing the microprocessor
Microprocessor Thermal grease
Removing and replacing an optical drive
Removing and replacing a hard disk drive
Completing the FRU replacement
FRU lists
Machine Type
Item # FRUs
19K1568
26K5427
ACJ ADJ
FRUs listed in the following table are not illustrated
33F8354
Keyboards Standard PS/2 Black
Windows XP Home Recovery CDs
Keyboards Productivity USB, no hub
Windows XP Pro Recovery CDs
Power Cords
4AG ARG 1BA 1BT 1BV
Machine Type
DVD-ROM 8x/24x models CTO 40Y8787
FRUs listed in the following table are not illustrated
Keyboards Standard PS/2 Black
US/UK/AP/TH models CTO
PO models CTO-G
FRU# CRU
Machine Type
DVD-ROM/CD-RW Combo Drive 24x24x24x8x models CTO 40Y8783
Mouse, PS/2 2-button Blackmodels CTO 24P0383
Keyboards Standard PS/2 Black
39J6267 Hardware Maintenance Manual
US/UK/AP/TH models 99U 99L 99G 99M 99A 99Q 99T 99H
Power Cord EMEA, LA models 99S 99P 99L 99D 99Y 99G
Machine Type
DVD-ROM 8x/24x models 71G 73G CTO 40Y8787
FRUs listed in the following table are not illustrated
Keyboards Standard PS/2 Black
US/UK/AP/TH models CTO-U CTO-G
GR models 71G 72G 73G 74G 75G CTO-G 76G 77G 13G
Machine Type
CTO A4S A4Y
FRUs listed in the following table are not illustrated
Keyboards Standard PS/2 Black
US/UK/AP/TH models A3U CTO-U CTO-G A5U 14U 26U
CS models 23C 30R4777 HK models 24B 27K6746
FRU# CRU
Machine Type
DVD-ROM 8x/24x models CTO 40Y8787
FRUs listed in the following table are not illustrated
Keyboards Standard PS/2 Black
US/UK/AP/TH models CTO 11A 11Q 11T 11U 11H
Power Cords
Hardware Maintenance Manual
Additional Service Information
Bios levels
Flash update procedures
Updating flashing Bios from a diskette or CD-ROM
Updating flashing Bios from your operating system
Recovering from a POST/BIOS update failure
Power management
Automatic configuration and power interface Acpi Bios
Automatic Power-On features
Recovering software using the Rescue and Recovery program
Starting the Rescue and Recovery workspace
Hardware Maintenance Manual
Appendix. Notices
155
Television output notice
Trademarks
Page
Part Number 19R2387