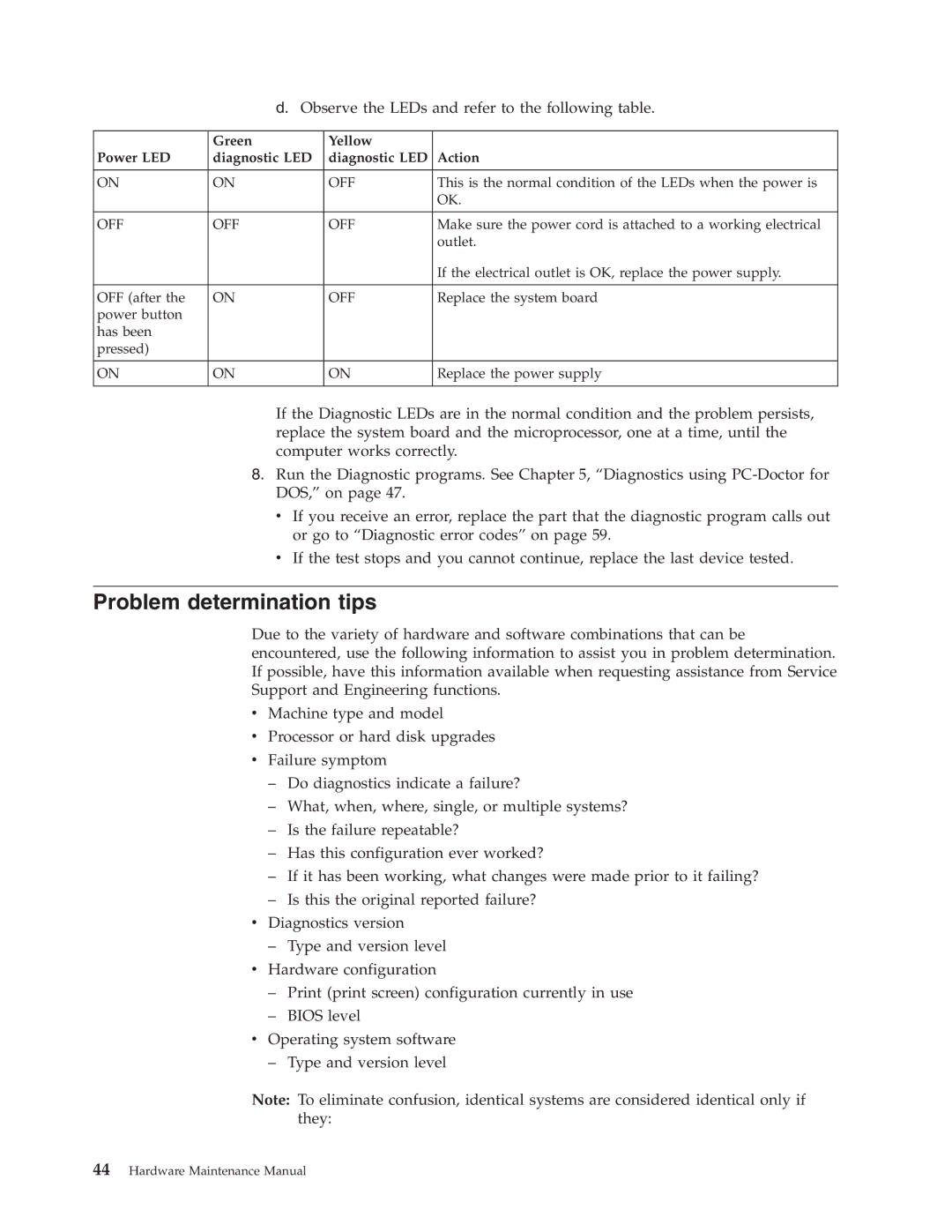
8089, 8086, 8087, 8090, 8094 specifications
The Lenovo 8088, 8094, 8090, 8087, and 8086 series represent a significant portion of the historical legacy of computing, particularly in the realm of personal computers and microprocessors. Each of these models showcases unique features and technologies that contributed to the evolution of computing during their time.Starting with the Lenovo 8088, this microprocessor was an enhancement of the earlier Intel 8086, designed primarily for use in IBM-compatible PCs. Its 16-bit processor architecture was notably capable of handling 8-bit data bus interactions, which made it more versatile for various applications. The 8088 had a maximum clock speed of 4.77 MHz, providing sufficient computational power for its time. One of the key features was its support for segmented memory, which allowed for more efficient memory management by dividing memory into segments for code, data, and stack.
The Lenovo 8094, while less commonly mentioned, often refers to IBM’s PS/2 line that utilized advanced features for the time. It supported VGA graphics, a significant improvement in visual output that opened new possibilities for graphical user interfaces. The 8094 also hosted a more sophisticated input/output system that allowed for better compatibility and connectivity with peripherals.
Moving to the Lenovo 8090, this model was part of the PS/2 portfolio, noted for its improved hardware architecture. It provided an upgraded interface for keyboard and mouse, which enhanced user interaction. With further support for high-density floppy disks and better memory access speeds, the 8090 paved the way for more efficient personal computing experiences.
The Lenovo 8087 was an auxiliary processor that brought floating-point arithmetic capabilities to the 8086 series. This coprocessor greatly expanded the computing power of the CPU by handling complex mathematical computations, which was especially useful in engineering and scientific applications. The 8087 allowed for more precise calculations than the basic integer math natively supported by earlier processors.
Finally, the Lenovo 8086, iconic in its own right, was a groundbreaking microprocessor that introduced the x86 architecture. It operated at clock speeds ranging from 5 to 10 MHz and was one of the first to support 16-bit data types fully. Its capabilities shaped software development and computer programming and established a foundation for the PC compatibles we know today.
In summary, the evolution from the Lenovo 8088 through to the 8086 helped shape modern computing paradigms by introducing features that improved performance, efficiency, and user experience, paving the way for the vast technological advancements seen in contemporary computing devices.