general information
![]()
![]() NOTICE
NOTICE
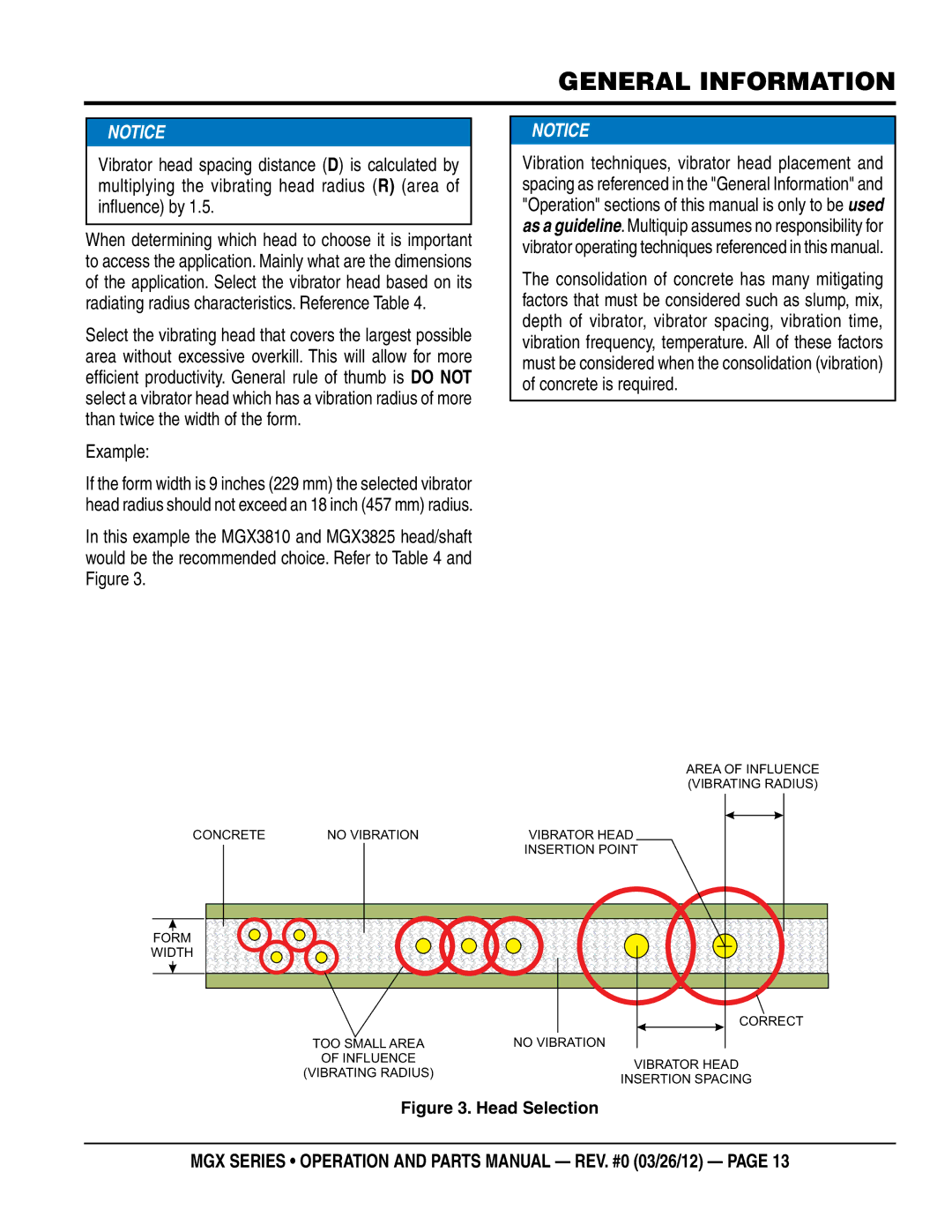
Vibrator head spacing distance (D) is calculated by multiplying the vibrating head radius (R) (area of influence) by 1.5.
When determining which head to choose it is important to access the application. Mainly what are the dimensions of the application. Select the vibrator head based on its radiating radius characteristics. Reference Table 4.
Select the vibrating head that covers the largest possible area without excessive overkill. This will allow for more efficient productivity. General rule of thumb is DO NOT select a vibrator head which has a vibration radius of more than twice the width of the form.
Example:
If the form width is 9 inches (229 mm) the selected vibrator head radius should not exceed an 18 inch (457 mm) radius.
In this example the MGX3810 and MGX3825 head/shaft would be the recommended choice. Refer to Table 4 and Figure 3.
![]() NOTICE
NOTICE
Vibration techniques, vibrator head placement and spacing as referenced in the "General Information" and "Operation" sections of this manual is only to be used as a guideline. Multiquip assumes no responsibility for vibrator operating techniques referenced in this manual.
The consolidation of concrete has many mitigating factors that must be considered such as slump, mix, depth of vibrator, vibrator spacing, vibration time, vibration frequency, temperature. All of these factors must be considered when the consolidation (vibration) of concrete is required.
AREA OF INFLUENCE (VIBRATING RADIUS)
CONCRETE | NO VIBRATION |
|
|
| |||
VIBRATOR HEAD |
| ||||||
|
|
|
|
| INSERTION POINT |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
FORM
WIDTH
|
|
| CORRECT | |
TOO SMALL AREA | NO VIBRATION | |||
OF INFLUENCE | VIBRATOR HEAD | |||
(VIBRATING RADIUS) | ||||
INSERTION SPACING | ||||
| ||||
Figure 3. Head Selection
mgx Series • operation and parts manual — rev. #0 (03/26/12) — page 13