3.GRAPHICAL COMPONENTS
Windows and panes
The display layouts are hierarchically organised. The layouts are built using components called windows and panes.
screen | Screen is the topmost display component, |
| corresponding to the entire pixel area of the |
| physical screen. |
window | Window is a component that has no parent except |
| the screen. Typically a window fills up the entire |
| screen, but there are also smaller (temporary) |
| windows that take up only a part of the screen, |
| leaving other parts of the screen visible around |
| themselves. |
| Each application runs in a window of it's own. |
| Applications can also use other temporary windows. |
pane | Pane means a |
| window). |
| A window may contain many panes, and each pane |
| may contain further |
| level component that cannot have a sub- |
| component, can be called an element. |
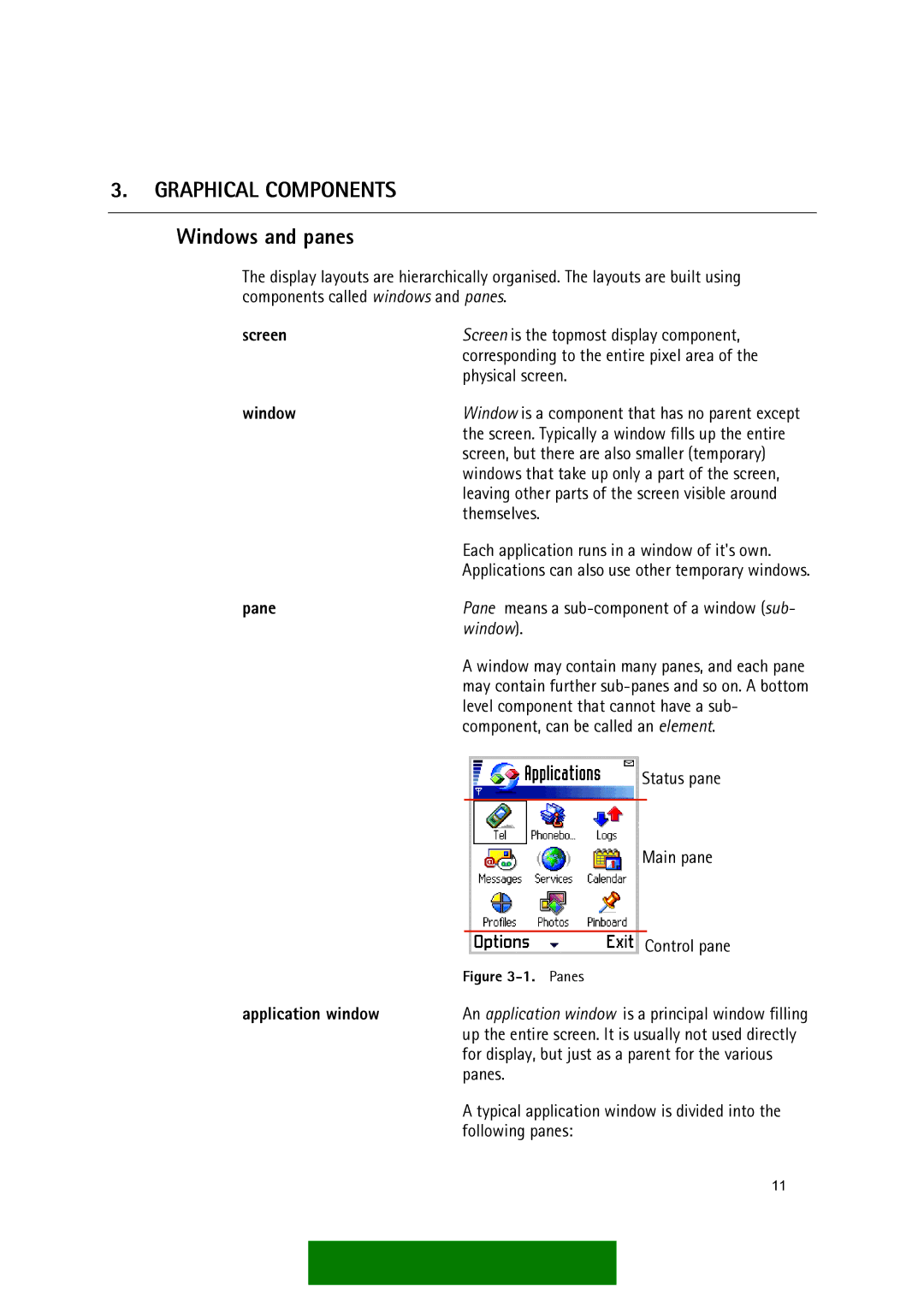
| Status pane |
Main pane
|
|
| Control pane |
|
| Figure | |
application window | An application window is a principal window filling | ||
|
| up the entire screen. It is usually not used directly | |
|
| for display, but just as a parent for the various | |
|
| panes. | |
|
| A typical application window is divided into the | |
|
| following panes: | |
|
| 11 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|