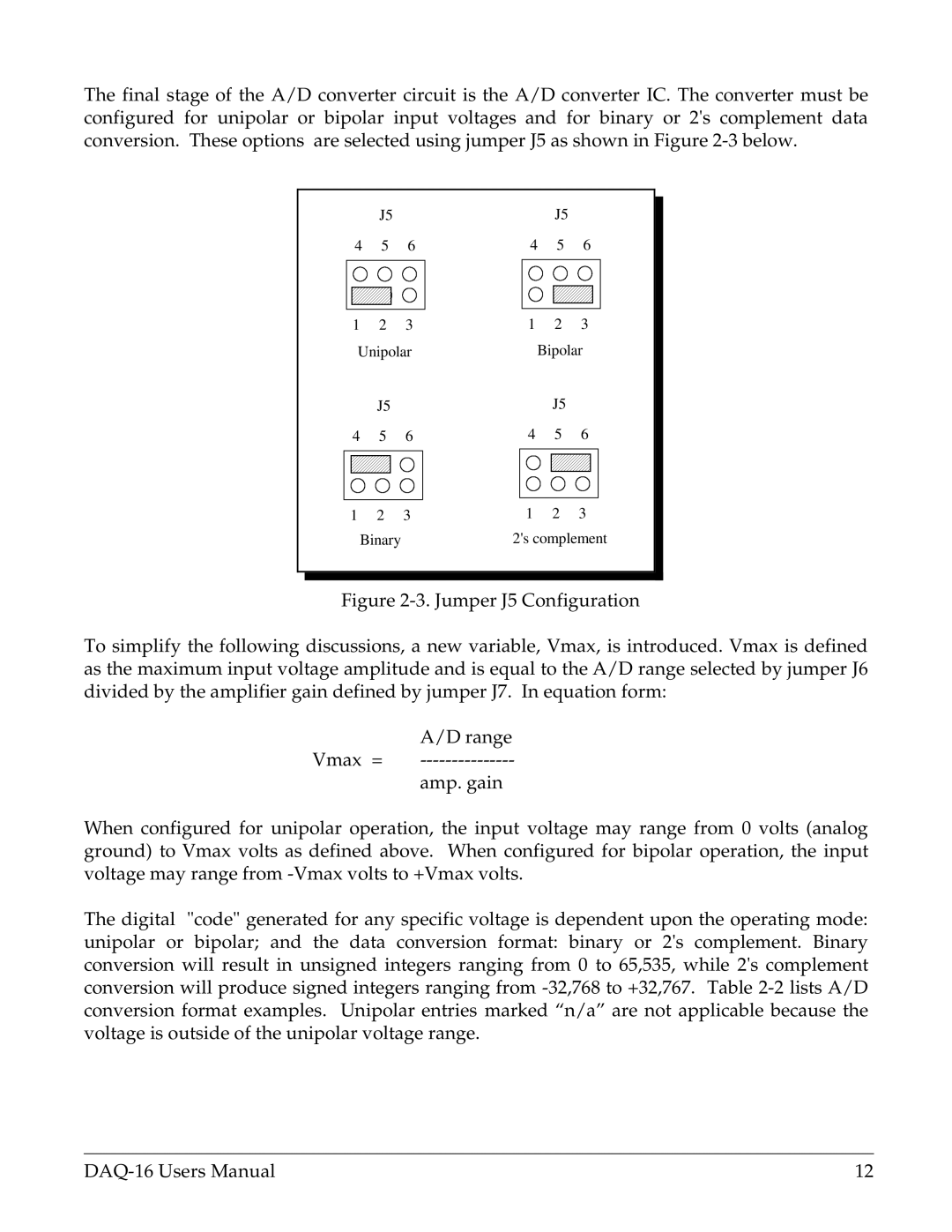
The final stage of the A/D converter circuit is the A/D converter IC. The converter must be configured for unipolar or bipolar input voltages and for binary or 2's complement data conversion. These options are selected using jumper J5 as shown in Figure
|
| J5 |
|
|
| J5 |
|
| |
4 | 5 |
| 6 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 | 2 |
| 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| |||
| Unipolar |
|
| Bipolar | ||||||
|
| J5 |
|
|
|
| J5 |
|
| |
4 | 5 |
| 6 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Binary |
| 2's complement | ||
Figure 2-3. Jumper J5 Configuration
To simplify the following discussions, a new variable, Vmax, is introduced. Vmax is defined as the maximum input voltage amplitude and is equal to the A/D range selected by jumper J6 divided by the amplifier gain defined by jumper J7. In equation form:
A/D range Vmax = ---------------
amp. gain
When configured for unipolar operation, the input voltage may range from 0 volts (analog ground) to Vmax volts as defined above. When configured for bipolar operation, the input voltage may range from -Vmax volts to +Vmax volts.
The digital "code" generated for any specific voltage is dependent upon the operating mode: unipolar or bipolar; and the data conversion format: binary or 2's complement. Binary conversion will result in unsigned integers ranging from 0 to 65,535, while 2's complement conversion will produce signed integers ranging from -32,768 to +32,767. Table 2-2 lists A/D conversion format examples. Unipolar entries marked “n/a” are not applicable because the voltage is outside of the unipolar voltage range.
12 |