Barracuda ES.2 SAS
ST31000640SS ST3750630SS ST3500620SS
Page
Performance characteristics
Reliability specifications
Physical/electrical specifications
General description
Interface requirements
Defect and error management
Installation
Seagate Technology Support Services
Barracuda ES.2 SAS Product Manual, Rev
Scope
Barracuda ES.2 SAS Product Manual, Rev. G
Standards, compliance and reference documents
Standards
Electromagnetic compatibility
Electromagnetic susceptibility
Compliance
Reference documents
Barracuda ES.2 SAS Product Manual, Rev. G
General description
Barracuda ES.2 drive illustration
Standard features
Media description
Performance
Reliability
Programmable drive capacity
Factory-installed options
Formatted capacities
Barracuda ES.2 SAS Product Manual, Rev. G
Performance characteristics
Internal drive characteristics
Access time
Seek performance
Start/stop time
Format command execution time minutes
General performance characteristics
Caching write data
Prefetch/multi-segmented cache control
Cache operation
Prefetch operation
Reliability specifications
Error rates
Recoverable Errors
Unrecoverable Errors
Reliability and service
Seek errors
Interface errors
Preventive maintenance
4 S.M.A.R.T
Controlling S.M.A.R.T
Performance impact
Reporting control
Thermal monitor
Temperature Log Page 0Dh
Predictive failures
State of the drive prior to testing
DST failure definition
Implementation
Invoking DST
Product warranty
Short test Function Code 001b
Extended test Function Code 010b
Log page entries
Shipping
Product repair and return information
Barracuda ES.2 SAS Product Manual, Rev. G
Physical/electrical specifications
AC power requirements
DC power requirements
ST31000640SS DC power requirements
ST3750630SS DC power requirements
ST3500620SS DC power requirements
General DC power requirement notes
Power sequencing
Conducted noise immunity
Current profiles
Typical ST31000640SS drive +5V and +12V current profiles
Power dissipation
Typical ST3500620SS drive +5V and +12V current profiles
Barracuda ES.2 SAS Product Manual, Rev. G
Temperature a. Operating
Environmental limits
Relative humidity
Effective altitude sea level a. Operating
Shock and vibration
Shock
Package size Packaged/product weight Drop height
Air cleanliness
Vibration a. Operating-normal
Acoustics
Corrosive environment
See Section Barracuda ES.2 SAS Product Manual, Rev. G
Mechanical specifications
Physical dimensions
Drive error recovery procedures
Defect and error management
Drive internal defects/errors
108.29
Media Pre-Scan
SAS system errors
Background Media Scan
Deferred Auto-Reallocation
Idle Read After Write
Installation
Drive orientation
Cooling
Air flow
Drive mounting
Grounding
Barracuda ES.2 SAS Product Manual, Rev. G
SAS features
Interface requirements
Dual port support
Command name Command code Supported
Scsi commands supported
Commands supported by Barracuda ES.2 SAS family drives
Commands supported by Barracuda ES.2 SAS family drives
Commands supported by Barracuda ES.2 SAS family drives
Commands supported by Barracuda ES.2 SAS family drives
Barracuda ES.2 SAS inquiry data Bytes Data hex
Mode Sense data
Inquiry data
Page
2.1 ST31000640SS Mode Sense data
Mode Pages
2.2 ST3750630SS Mode Sense data
2.3 ST3500620SS Mode Sense data
Miscellaneous operating features and conditions
Miscellaneous features
Supported Feature or condition
Miscellaneous status
SAS physical interface
Datum B
Physical characteristics
Connector requirements
Pin Signal name Signal type
Electrical description
Pin descriptions
SAS pin descriptions
Signal characteristics
Power
SAS transmitters and receivers
Ready LED Out
LED drive signal
Differential signals
General interface characteristics
Eye masks Eye masks overview
Receive eye mask
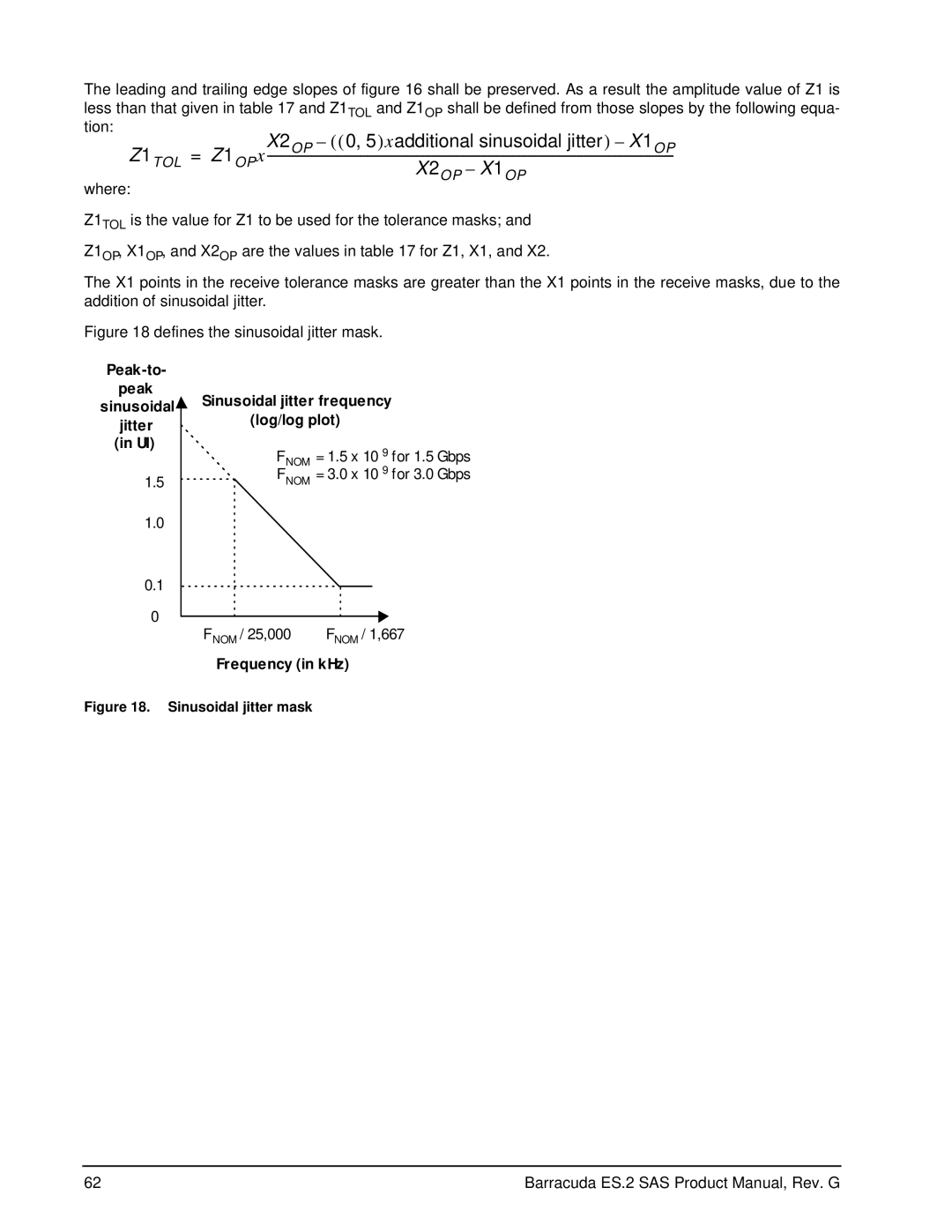
Jitter tolerance masks
Absolute amplitude
Normalized time in UI
Peak-to
Sinusoidal
Jitter
Frequency in kHz
Transmitter signal characteristics
Signal characteristica Units Gbps
Receiver signal characteristics
Signal characteristic Units Gbps
Maximum allowable jitter
Gbps m, n Deterministic jitterq
Impedance specifications
Receiver jitter tolerance
Compliant jitter test pattern Cjtpat
Impedance requirements Sheet 1
Electrical TxRx connections
Transmitter characteristics
Impedance requirements Sheet 2
= -5,437dB
Shows the zero-length test load
Receiver characteristics
Barracuda ES.2 SAS Product Manual, Rev. G