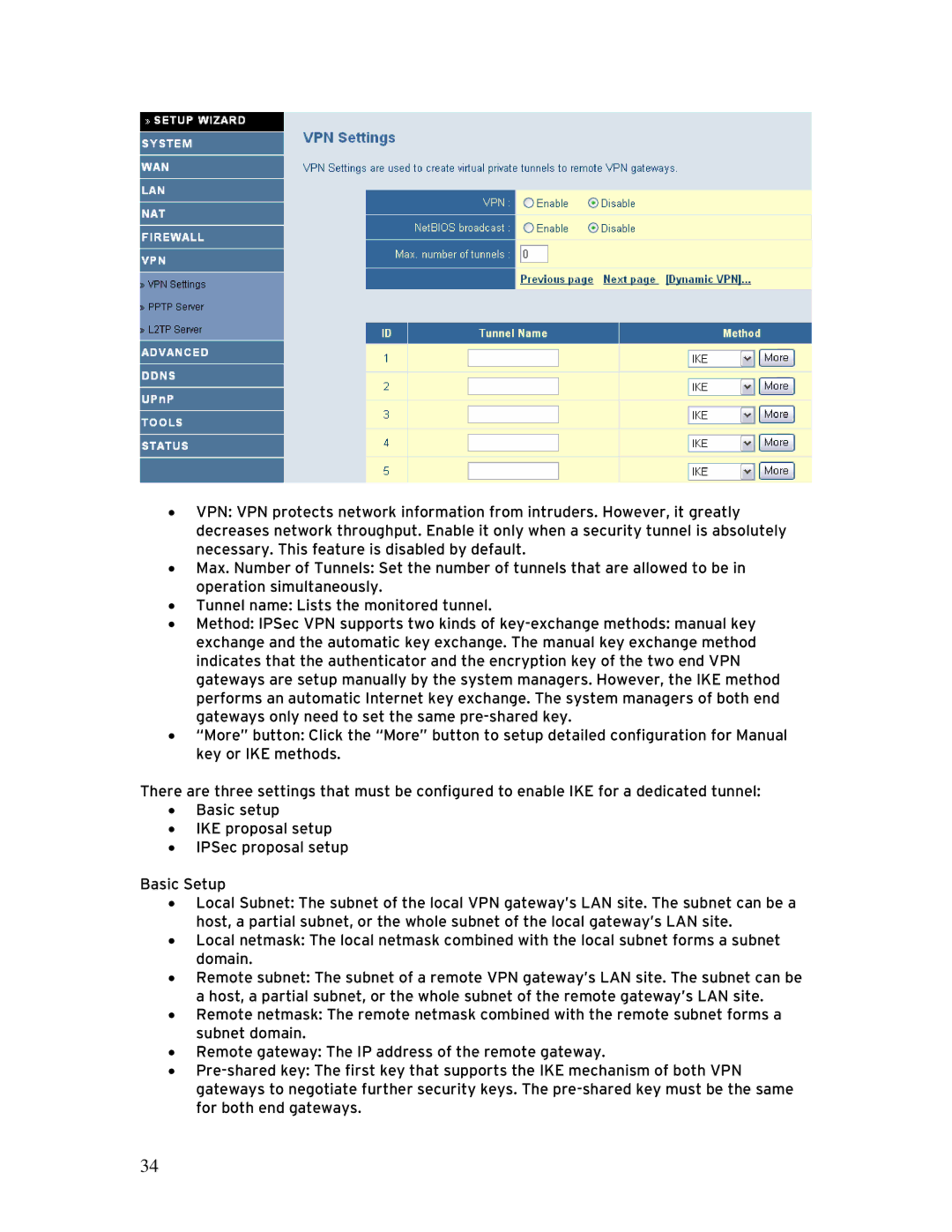
•VPN: VPN protects network information from intruders. However, it greatly decreases network throughput. Enable it only when a security tunnel is absolutely necessary. This feature is disabled by default.
•Max. Number of Tunnels: Set the number of tunnels that are allowed to be in operation simultaneously.
•Tunnel name: Lists the monitored tunnel.
•Method: IPSec VPN supports two kinds of
•“More” button: Click the “More” button to setup detailed configuration for Manual key or IKE methods.
There are three settings that must be configured to enable IKE for a dedicated tunnel:
•Basic setup
•IKE proposal setup
•IPSec proposal setup
Basic Setup
•Local Subnet: The subnet of the local VPN gateway’s LAN site. The subnet can be a host, a partial subnet, or the whole subnet of the local gateway’s LAN site.
•Local netmask: The local netmask combined with the local subnet forms a subnet domain.
•Remote subnet: The subnet of a remote VPN gateway’s LAN site. The subnet can be a host, a partial subnet, or the whole subnet of the remote gateway’s LAN site.
•Remote netmask: The remote netmask combined with the remote subnet forms a subnet domain.
•Remote gateway: The IP address of the remote gateway.
•
34