Solving Double Inequalities
The solution to a system of two inequalities in one variable consists of all values of the variable that make each inequality in the system true. A system f (x) ≥ a, f (x) ≤ b, where the same expression appears on both inequalities, is commonly referred to as a “double” inequality and is often written in the form a ≤ f (x) ≤ b. Be certain that both inequality signs are pointing in the same direction and that the double inequality is only used to indicate an expression in x “trapped” in between two values. Also a must be less than or equal to b in the inequality a ≤ f (x) ≤ b or b ≥ f (x) ≥ a.
Example
Solve a double inequality, using graphical techniques.
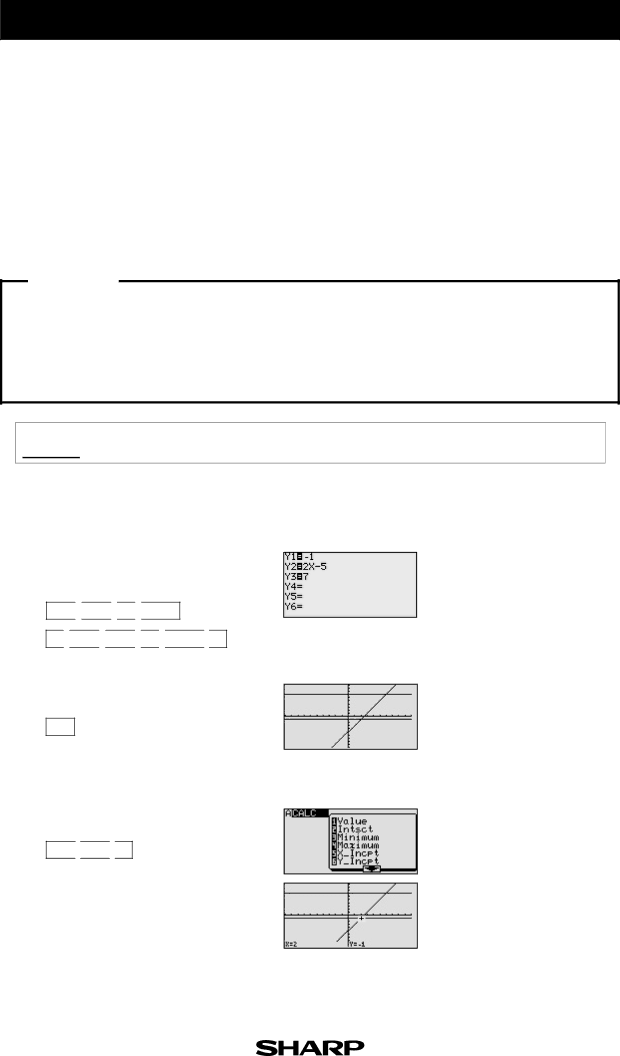
2x - 5 ≥ -1
2x -5 ≤ 7
Before There may be differences in the results of calculations and graph plotting depending on the setting. Starting Return all settings to the default value and delete all data.
Step & Key Operation | Display | Notes |
1Enter y =
Y= ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() 1
1 ![]()
![]() ENTER
ENTER
2 ![]()
![]() X/
X/![]() /T/n
/T/n![]()
![]() —
— ![]()
![]() 5
5 ![]()
![]() ENTER
ENTER ![]()
![]() 7
7
The “double” inequality given can also be written to
2View the lines.
GRAPH
3Find the point of intersection.
2nd F ![]()
![]() CALC
CALC ![]()
![]() 2
2
y = 2x - 5 and
y =