The Receiver bar graph is visible on the right side (green). This indicates that the fault is ahead of the operator in the direction of the
When the bar graph is visible on the left side (red), the fault has been passed and is now behind the operator.
Move back, inserting the frame every few inches, until the bar graph returns to the green side. Turn the frame ninety degrees to the cable path. The fault is located beneath the center of the frame when the bar graph changes from one side to the other.
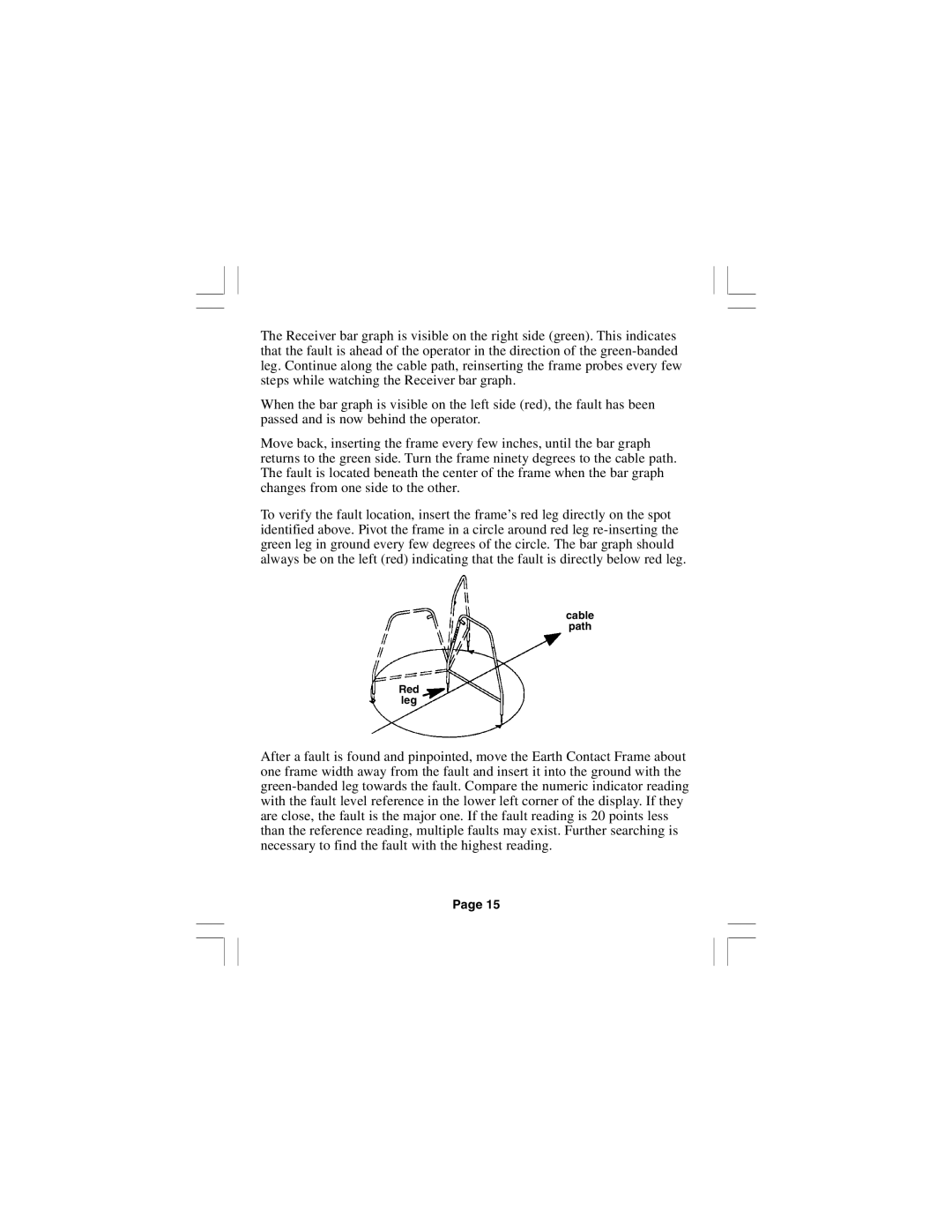
To verify the fault location, insert the frame’s red leg directly on the spot identified above. Pivot the frame in a circle around red leg
cable path
Red leg
After a fault is found and pinpointed, move the Earth Contact Frame about one frame width away from the fault and insert it into the ground with the
Page 15