DBM16 Interfacing
This section will show some general examples of how to interface the DBM16 I/O lines to external devices. Caution must be taken not to exceed the DBM16 specifications, failure to do so could result in damage to the DBM16 and will void the warranty.
Before connecting the DBM16 to the SDD16 module and connecting any external device to the DBM16 determine which I/O lines on the SDD16 module are inputs and which are outputs. Once the inputs and outputs are known, set the jumpers on the DBM16 accordingly. Refer to Figure C.2.
Figure C.2 - DBM16 Outline Drawing
Inputs
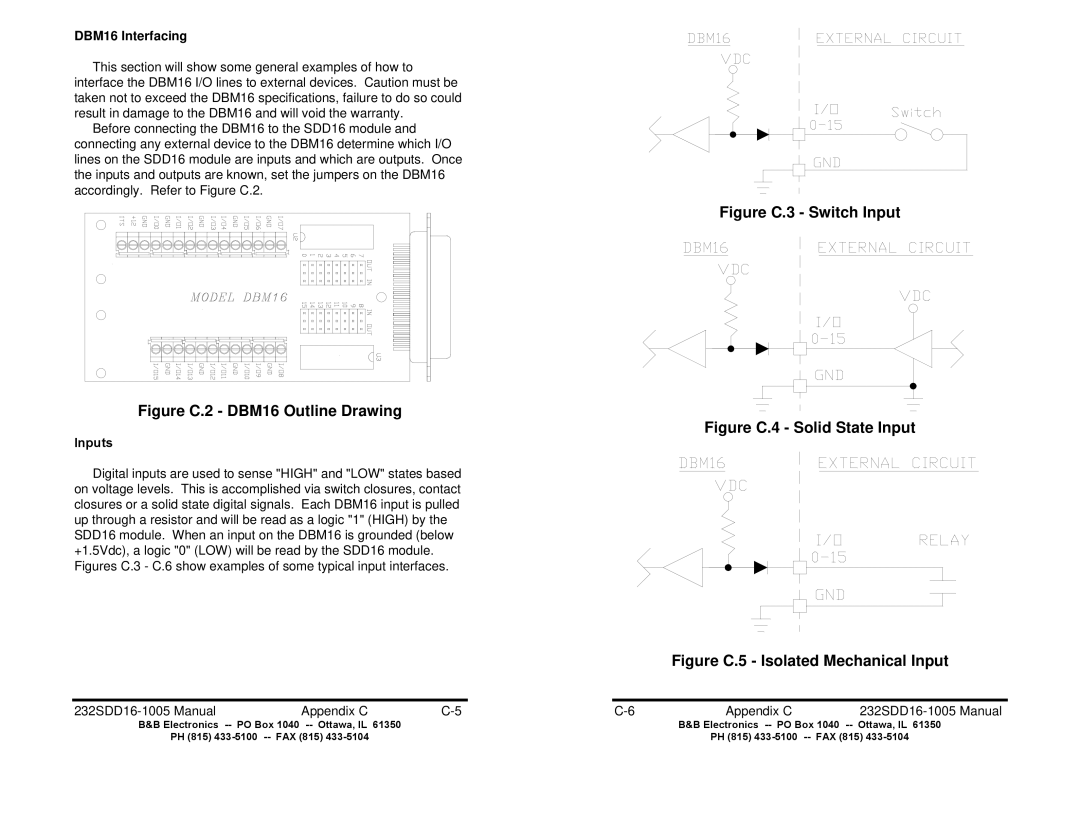
Digital inputs are used to sense "HIGH" and "LOW" states based on voltage levels. This is accomplished via switch closures, contact closures or a solid state digital signals. Each DBM16 input is pulled up through a resistor and will be read as a logic "1" (HIGH) by the SDD16 module. When an input on the DBM16 is grounded (below +1.5Vdc), a logic "0" (LOW) will be read by the SDD16 module. Figures C.3 - C.6 show examples of some typical input interfaces.
Appendix C |
Figure C.3 - Switch Input
Figure C.4 - Solid State Input
Figure C.5 - Isolated Mechanical Input
Appendix C |
B&B Electronics | B&B Electronics |
PH (815) | PH (815) |