BM2610995777 10/03 10/7/03 4:51 PM Page 10
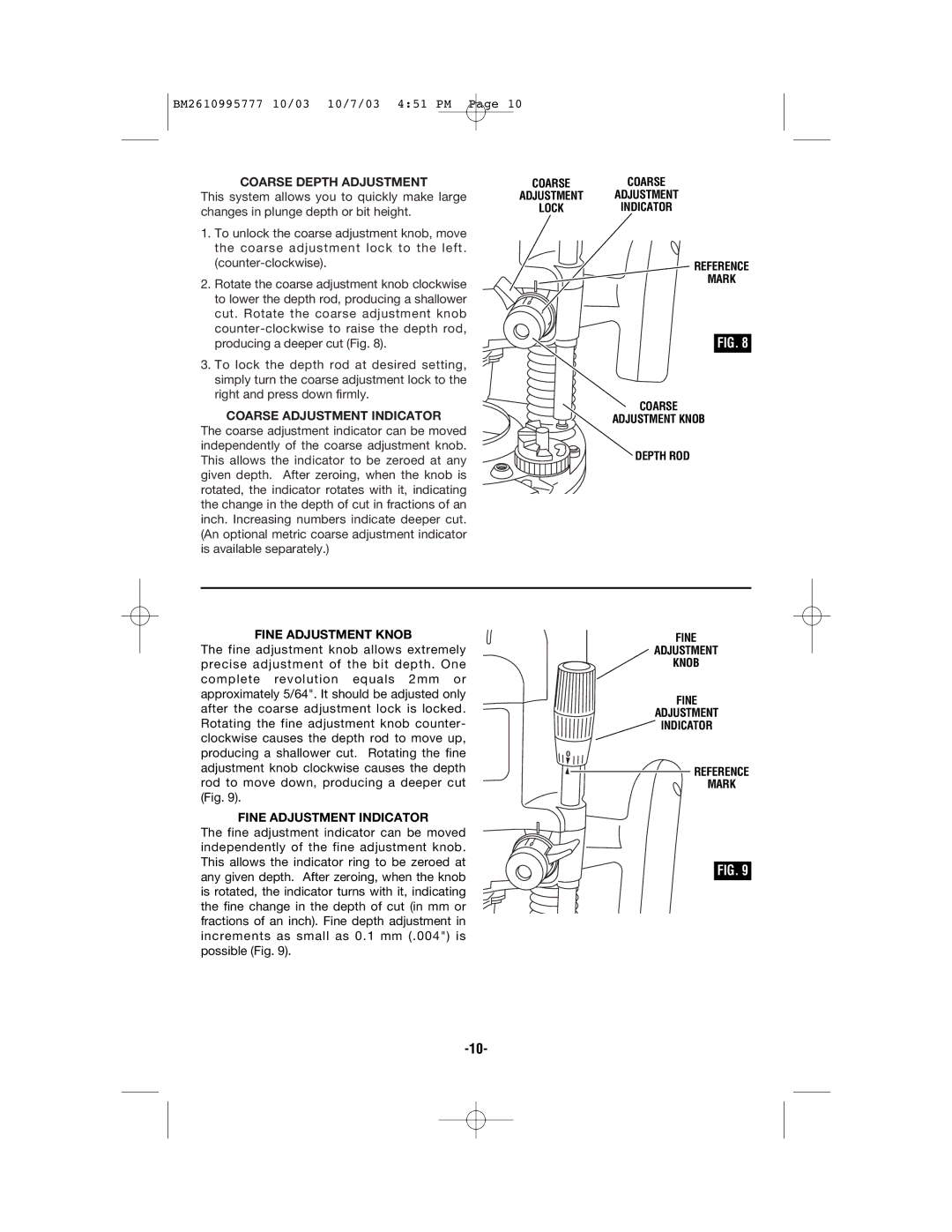
COARSE DEPTH ADJUSTMENT
This system allows you to quickly make large changes in plunge depth or bit height.
1.To unlock the coarse adjustment knob, move the coarse adjustment lock to the left.
2.Rotate the coarse adjustment knob clockwise to lower the depth rod, producing a shallower cut. Rotate the coarse adjustment knob
3.To lock the depth rod at desired setting, simply turn the coarse adjustment lock to the right and press down firmly.
COARSE ADJUSTMENT INDICATOR
The coarse adjustment indicator can be moved independently of the coarse adjustment knob. This allows the indicator to be zeroed at any given depth. After zeroing, when the knob is rotated, the indicator rotates with it, indicating the change in the depth of cut in fractions of an inch. Increasing numbers indicate deeper cut. (An optional metric coarse adjustment indicator is available separately.)
COARSE | COARSE |
ADJUSTMENT | ADJUSTMENT |
LOCK | INDICATOR |
REFERENCE
MARK
FIG. 8
COARSE
ADJUSTMENT KNOB
DEPTH ROD
FINE ADJUSTMENT KNOB | FINE | |
The fine adjustment knob allows extremely | ADJUSTMENT | |
precise adjustment of the bit depth. One | KNOB | |
complete revolution equals 2mm or |
| |
approximately 5/64". It should be adjusted only | FINE | |
after the coarse adjustment lock is locked. | ||
ADJUSTMENT | ||
Rotating the fine adjustment knob counter- | ||
INDICATOR | ||
clockwise causes the depth rod to move up, |
| |
producing a shallower cut. Rotating the fine | 0 | |
adjustment knob clockwise causes the depth | REFERENCE | |
rod to move down, producing a deeper cut | ||
MARK | ||
(Fig. 9). |
| |
FINE ADJUSTMENT INDICATOR |
| |
The fine adjustment indicator can be moved |
| |
independently of the fine adjustment knob. |
| |
This allows the indicator ring to be zeroed at | FIG. 9 | |
any given depth. After zeroing, when the knob | ||
| ||
is rotated, the indicator turns with it, indicating |
| |
the fine change in the depth of cut (in mm or |
| |
fractions of an inch). Fine depth adjustment in |
| |
increments as small as 0.1 mm (.004") is |
| |
possible (Fig. 9). |
|