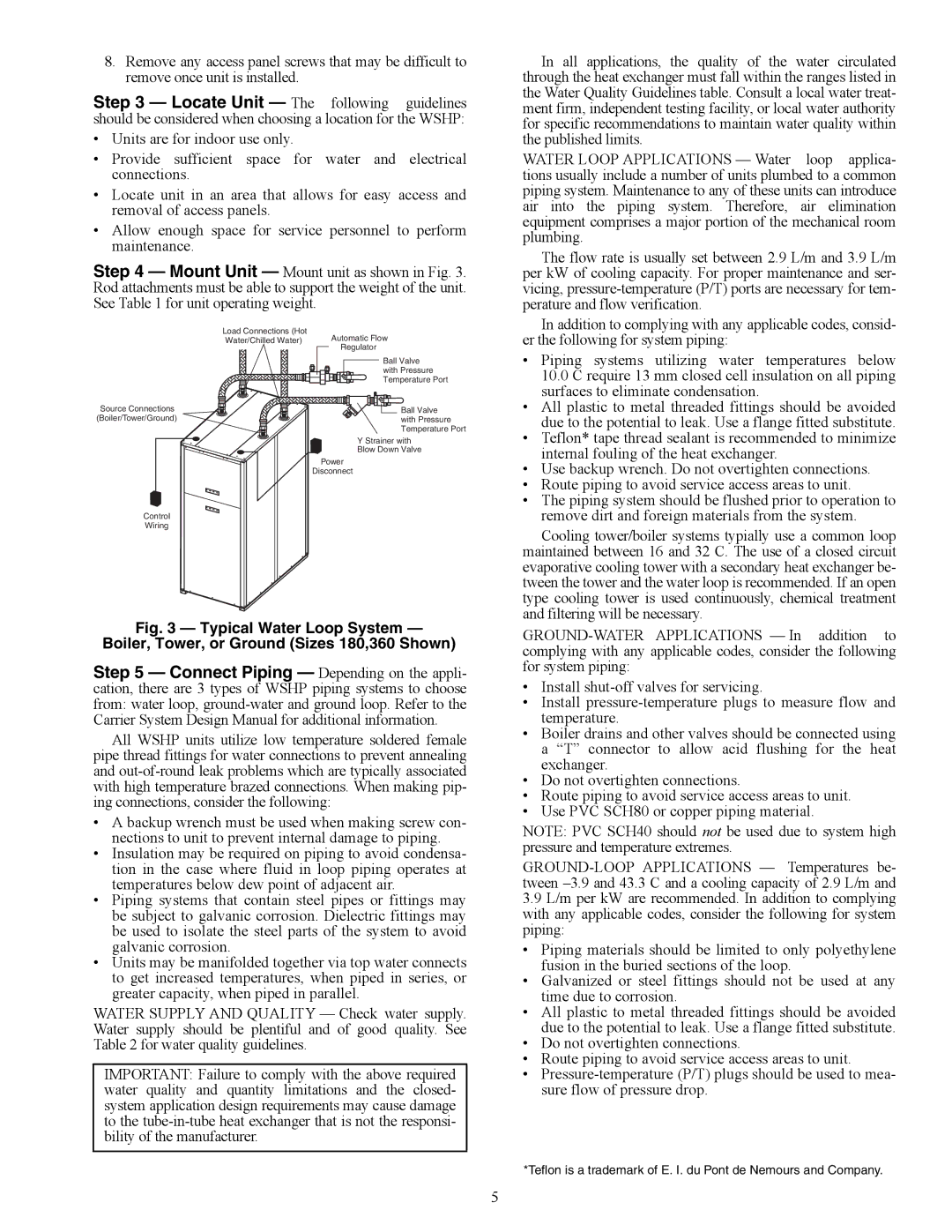
50PSW036-360 specifications
The Carrier 50PSW036-360 is a highly efficient and reliable rooftop unit designed for commercial applications. It combines advanced technologies and innovative features to provide optimal indoor comfort while ensuring energy savings and ease of operation. Its robust construction and numerous functionalities make the 50PSW036-360 an ideal choice for various building types, from retail spaces to office complexes.One of the main features of the Carrier 50PSW036-360 is its efficient cooling and heating capabilities. It employs state-of-the-art scroll compressors, which deliver consistent performance and lower noise levels while consuming less energy compared to conventional compressors. This translates into significant energy savings, making it a cost-effective solution for businesses aiming to reduce their operational expenses.
The unit is equipped with a range of advanced technologies, including Carrier’s EcoBlue™ technology, which optimizes airflow and enhances energy efficiency. This technology helps achieve higher SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) ratings, allowing users to benefit from lower utility bills without sacrificing comfort. Additionally, the unit comes with smart control options, enabling users to easily manage and monitor temperature settings, fan speeds, and energy consumption through intuitive interfaces.
The Carrier 50PSW036-360 also emphasizes versatility and adaptability. It has a compact design that makes it easy to install on rooftops, while its extensive selection of options, such as electric heat and economizers, allows it to be configured to meet various application requirements. Its advanced filtration system ensures high indoor air quality by removing dust, allergens, and other pollutants, which is essential for maintaining a healthy indoor environment.
Durability is another characteristic that sets the Carrier 50PSW036-360 apart. The unit is constructed using high-quality materials designed to withstand the rigors of outdoor environments. This ensures longevity and reliability, making it an excellent long-term investment for businesses.
In summary, the Carrier 50PSW036-360 is a top-of-the-line rooftop unit, ideal for commercial applications. Its blend of energy efficiency, advanced technologies, and robust construction makes it a preferred choice for maintaining optimal indoor climate conditions. With its versatility, durability, and ease of use, this system ensures comfort for occupants while helping businesses achieve their sustainability goals.