Chapter 4 Configuring the ISA and ISM
IPSec Example
outbound esp sas:
spi: 0x20890A6F(545852015) transform:
slot: 0, conn id: 27, crypto map:
sa timing: remaining key lifetime (k/sec): (4607999/90)
IV size: 8 bytes
replay detection support: Y outbound ah sas:
For a detailed description of the information displayed by the show commands, refer to the “IP Security and Encryption” chapter of the Security Command Reference publication.
IPSec Example
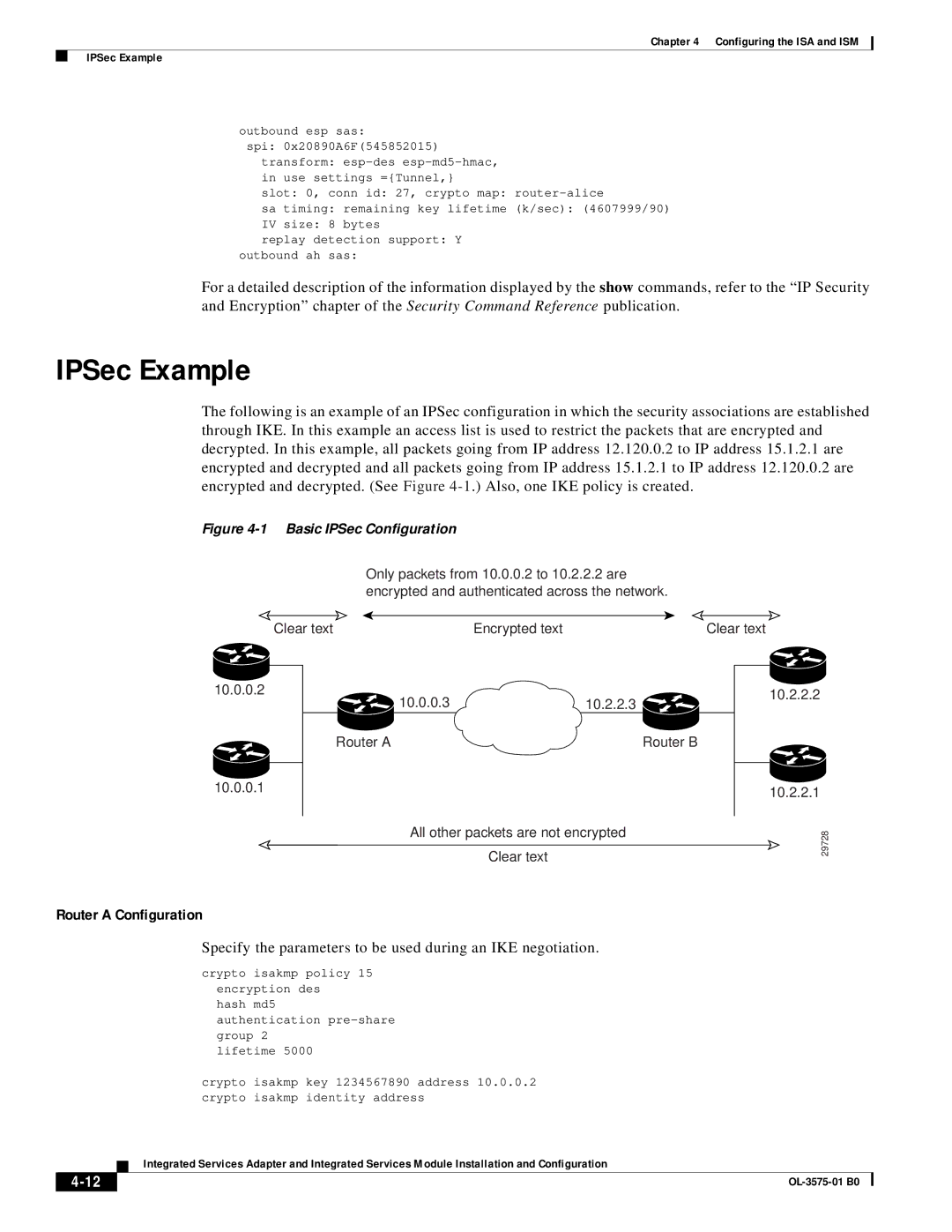
The following is an example of an IPSec configuration in which the security associations are established through IKE. In this example an access list is used to restrict the packets that are encrypted and decrypted. In this example, all packets going from IP address 12.120.0.2 to IP address 15.1.2.1 are encrypted and decrypted and all packets going from IP address 15.1.2.1 to IP address 12.120.0.2 are encrypted and decrypted. (See Figure
Figure 4-1 Basic IPSec Configuration
Only packets from 10.0.0.2 to 10.2.2.2 are encrypted and authenticated across the network.
Clear text | Encrypted text |
10.0.0.2 |
|
10.0.0.3 | 10.2.2.3 |
Router A | Router B |
10.0.0.1
All other packets are not encrypted
Clear text
Clear text
10.2.2.2
10.2.2.1
29728
Router A Configuration
Specify the parameters to be used during an IKE negotiation.
crypto isakmp policy 15 encryption des
hash md5
authentication
lifetime 5000
crypto isakmp key 1234567890 address 10.0.0.2 crypto isakmp identity address
| Integrated Services Adapter and Integrated Services Module Installation and Configuration |