R F I D A N D T H E A D V A N T A G E R F I D P R I N T E R
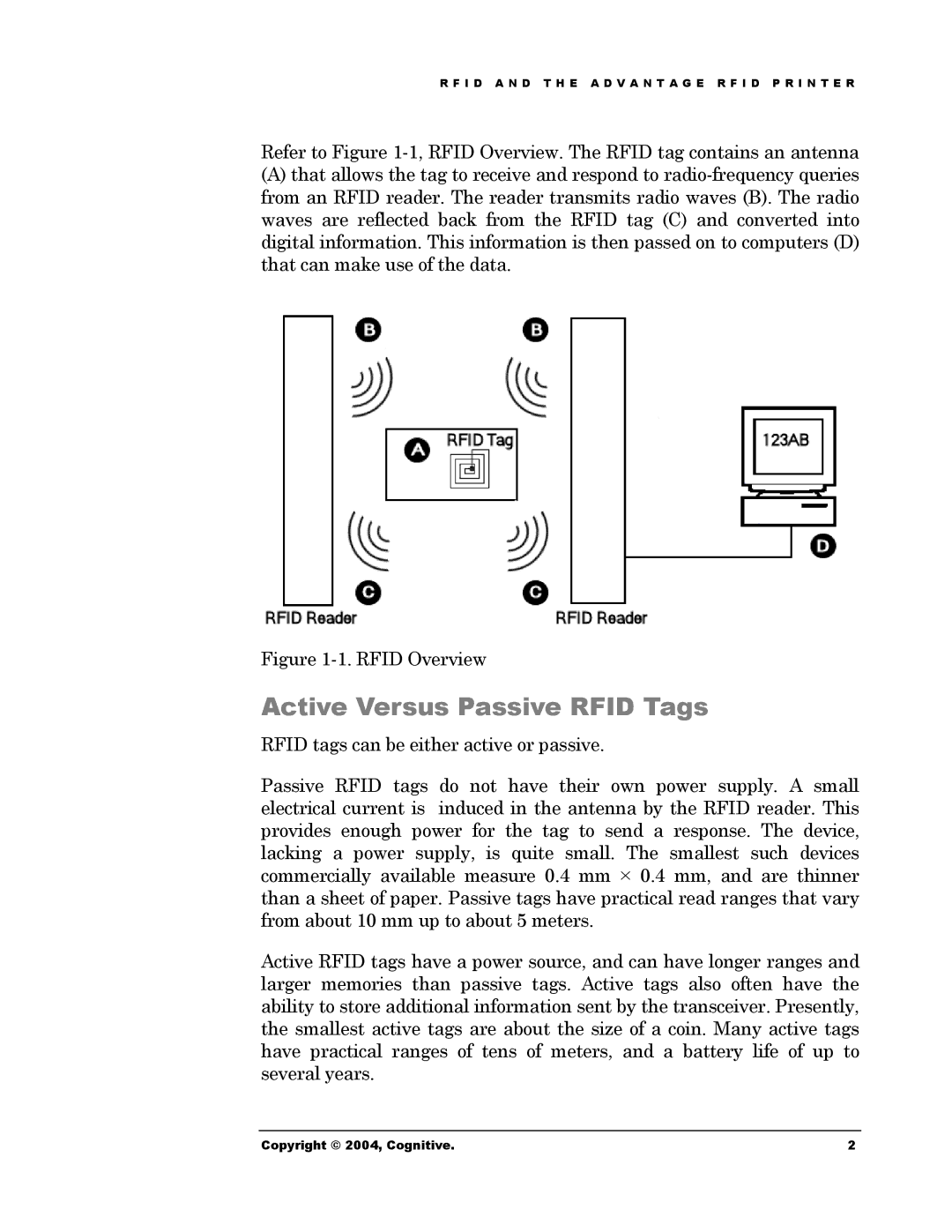
Refer to Figure
(A)that allows the tag to receive and respond to
Figure 1-1. RFID Overview
Active Versus Passive RFID Tags
RFID tags can be either active or passive.
Passive RFID tags do not have their own power supply. A small electrical current is induced in the antenna by the RFID reader. This provides enough power for the tag to send a response. The device, lacking a power supply, is quite small. The smallest such devices commercially available measure 0.4 mm × 0.4 mm, and are thinner than a sheet of paper. Passive tags have practical read ranges that vary from about 10 mm up to about 5 meters.
Active RFID tags have a power source, and can have longer ranges and larger memories than passive tags. Active tags also often have the ability to store additional information sent by the transceiver. Presently, the smallest active tags are about the size of a coin. Many active tags have practical ranges of tens of meters, and a battery life of up to several years.
Copyright © 2004, Cognitive. | 2 |