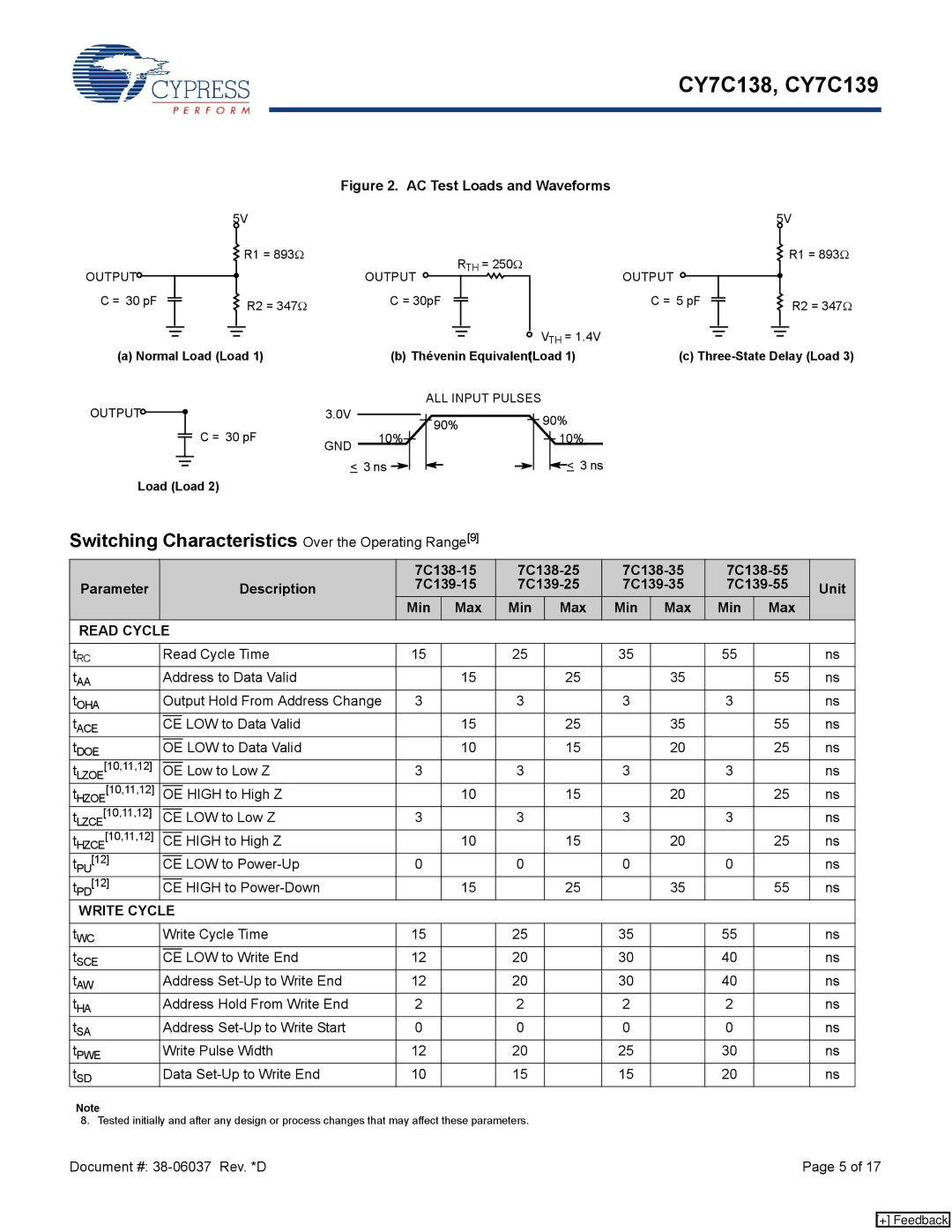
CY7C138, CY7C139 specifications
The Cypress CY7C139 and CY7C138 are advanced static random-access memory (SRAM) components that have garnered attention in the field of digital electronics due to their high performance and reliability. These SRAMs are designed to meet the demanding needs of a variety of applications, ranging from telecommunications to automotive systems and consumer electronics.The CY7C139 is a 128K x 8 bit static RAM, while the CY7C138 is a 256K x 8 bit SRAM, offering flexible memory solutions for designers. Both devices utilize a fast access time, typically around 10 to 15 nanoseconds, allowing quick data retrieval essential for high-speed applications. This remarkable speed is complemented by low power consumption, making them suitable for battery-operated devices and other applications where efficiency is paramount.
One of the key features of the CY7C139 and CY7C138 is their asynchronous operation, which enables them to provide high-speed data access without the need for a clock signal. This characteristic simplifies system design and enhances performance, as users can write to and read from the memory without waiting for synchronization. The devices support standard CMOS interface levels, which facilitate integration into a diverse range of digital systems.
Additionally, these SRAMs have been designed with a low standby current, making them particularly effective for low-power applications. The devices also include a robust input/output structure that ensures reliable signal integrity under various operating conditions. Their built-in data retention capability allows the SRAMs to retain stored data even during power failures, a critical feature in many systems that require data preservation.
Both CY7C139 and CY7C138 SRAMs support a wide range of temperature and voltage ranges, making them suitable for industrial and automotive environments. They are packaged in industry-standard configurations, allowing for easy integration into existing designs.
In summary, the Cypress CY7C139 and CY7C138 SRAMs provide high-speed, low-power memory solutions suitable for various applications. Their asynchronous operation, low standby current, and robust performance characteristics make them a preferred choice for engineers looking to enhance system efficiency and reliability. These features make the CY7C139 and CY7C138 indispensable components in modern digital electronic designs.