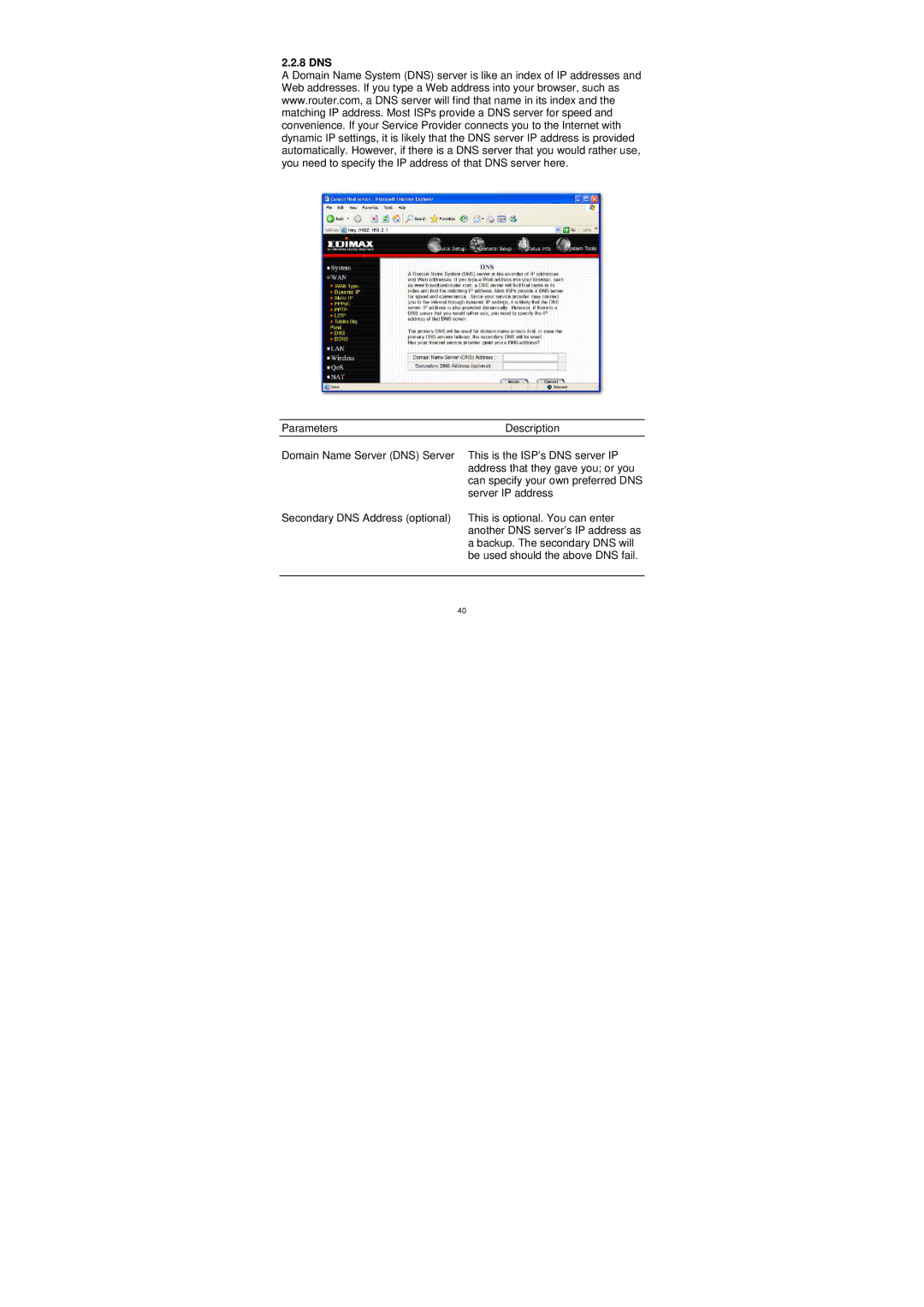
2.2.8 DNS
A Domain Name System (DNS) server is like an index of IP addresses and Web addresses. If you type a Web address into your browser, such as www.router.com, a DNS server will find that name in its index and the matching IP address. Most ISPs provide a DNS server for speed and convenience. If your Service Provider connects you to the Internet with dynamic IP settings, it is likely that the DNS server IP address is provided automatically. However, if there is a DNS server that you would rather use, you need to specify the IP address of that DNS server here.
Parameters | Description |
Domain Name Server (DNS) Server | This is the ISP’s DNS server IP |
| address that they gave you; or you |
| can specify your own preferred DNS |
| server IP address |
Secondary DNS Address (optional) | This is optional. You can enter |
| another DNS server’s IP address as |
| a backup. The secondary DNS will |
| be used should the above DNS fail. |
|
|
| 40 |