APPENDIX B. FLOW CONTROL
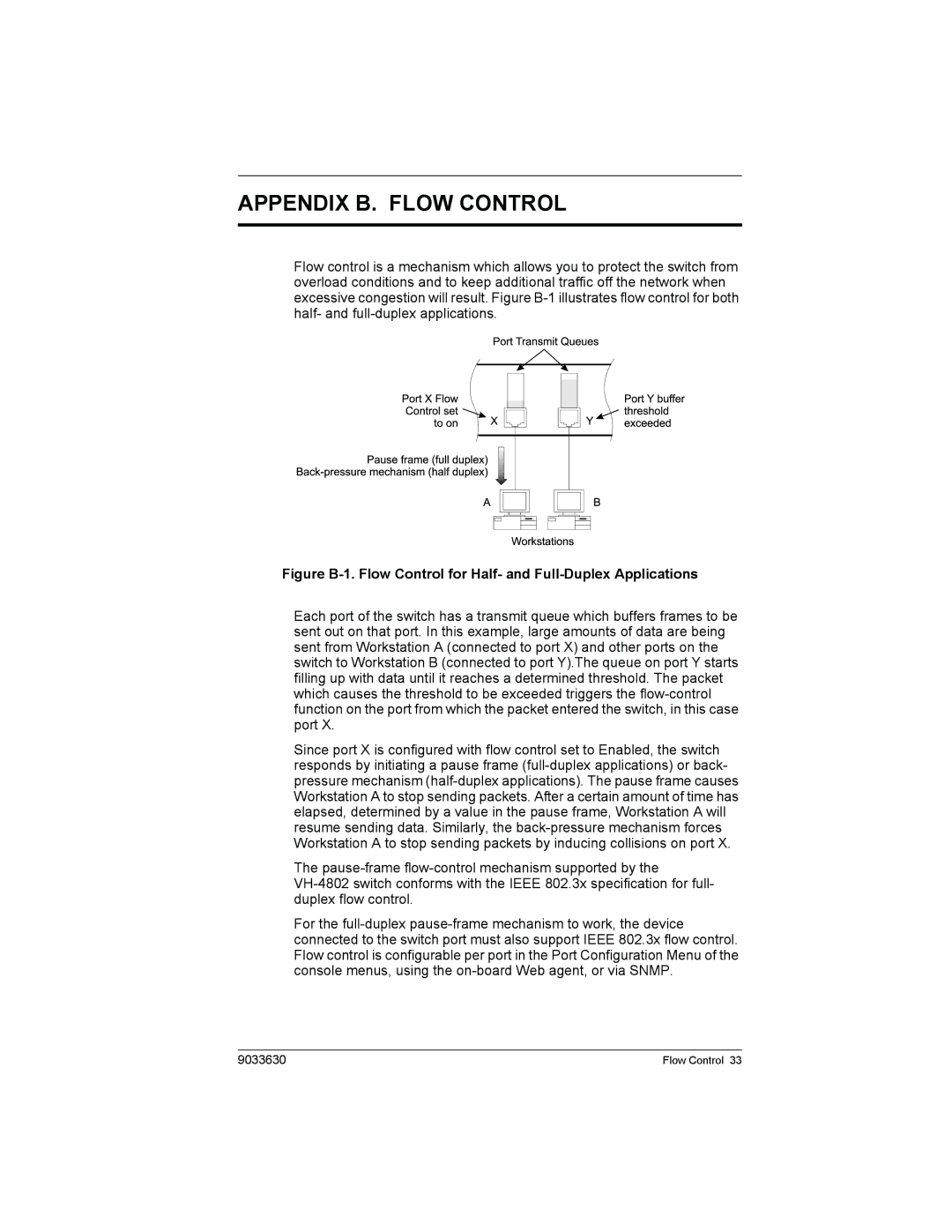
Flow control is a mechanism which allows you to protect the switch from overload conditions and to keep additional traffic off the network when excessive congestion will result. Figure
Figure B-1. Flow Control for Half- and Full-Duplex Applications
Each port of the switch has a transmit queue which buffers frames to be sent out on that port. In this example, large amounts of data are being sent from Workstation A (connected to port X) and other ports on the switch to Workstation B (connected to port Y).The queue on port Y starts filling up with data until it reaches a determined threshold. The packet which causes the threshold to be exceeded triggers the
Since port X is configured with flow control set to Enabled, the switch responds by initiating a pause frame
The
For the
9033630 | Flow Control 33 |