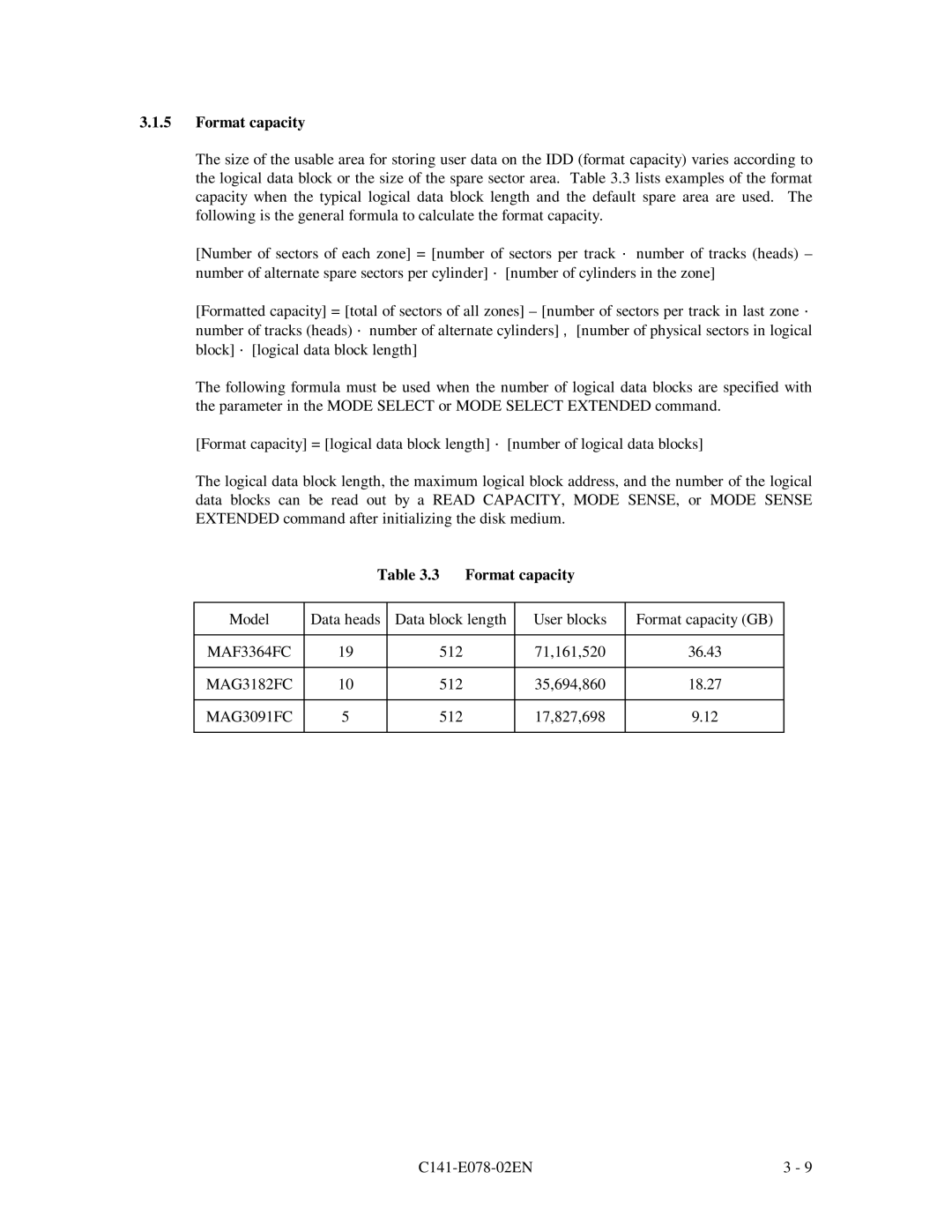
MAG3182FC, MAF3364FC, MAG3091FC specifications
Fujitsu has established itself as a leading provider of storage solutions, with a robust lineup that includes the MAG3182FC, MAG3091FC, and MAF3364FC hard drives. These models cater to the needs of enterprise and data center environments, focusing on reliability, performance, and advanced technology.The Fujitsu MAG3182FC is a Fibre Channel hard drive designed for high-speed data transfer and optimal storage performance. With a capacity of 18.2 GB, it is built for applications requiring rapid access to data. The drive operates at a spindle speed of 10,000 RPM, ensuring quick data retrieval and low latency. It features a 2 Gbps Fibre Channel interface, which allows for fast communication between the drive and the server, making it ideal for environments that demand high throughput, such as transaction processing and database management.
Next in line is the Fujitsu MAG3091FC. This model takes the capabilities of its predecessor a step further with a capacity of 9.1 GB and similar 10,000 RPM speed. The MAG3091FC is also equipped with a 2 Gbps Fibre Channel interface, providing the same high-performance connectivity. Its reliability is enhanced with advanced error correction and a design that minimizes the risk of data loss, making it suitable for mission-critical applications where uptime is essential.
Lastly, the Fujitsu MAF3364FC hard drive is tailored for enterprise-level operations, featuring a capacity of 36.4 GB. It utilizes a 10,000 RPM spindle speed and is built with the same 2 Gbps Fibre Channel interface, ensuring swift access to stored data. The MAF3364FC stands out for its improved data integrity features, including sophisticated error correction codes and a robust design that enhances durability. Its higher capacity combined with fast access times makes it a versatile choice for data-intensive applications and large-scale storage solutions.
All three drives incorporate Fujitsu's commitment to innovation, featuring technologies like S.M.A.R.T (Self-Monitoring, Analysis, and Reporting Technology) for predictive failure analysis. They are designed to operate in demanding environments, ensuring that businesses can rely on them for consistent performance and data protection. In summary, the Fujitsu MAG3182FC, MAG3091FC, and MAF3364FC represent a powerful collection of enterprise-grade hard drives, providing advanced features and technologies that meet the rigorous demands of modern data storage needs.