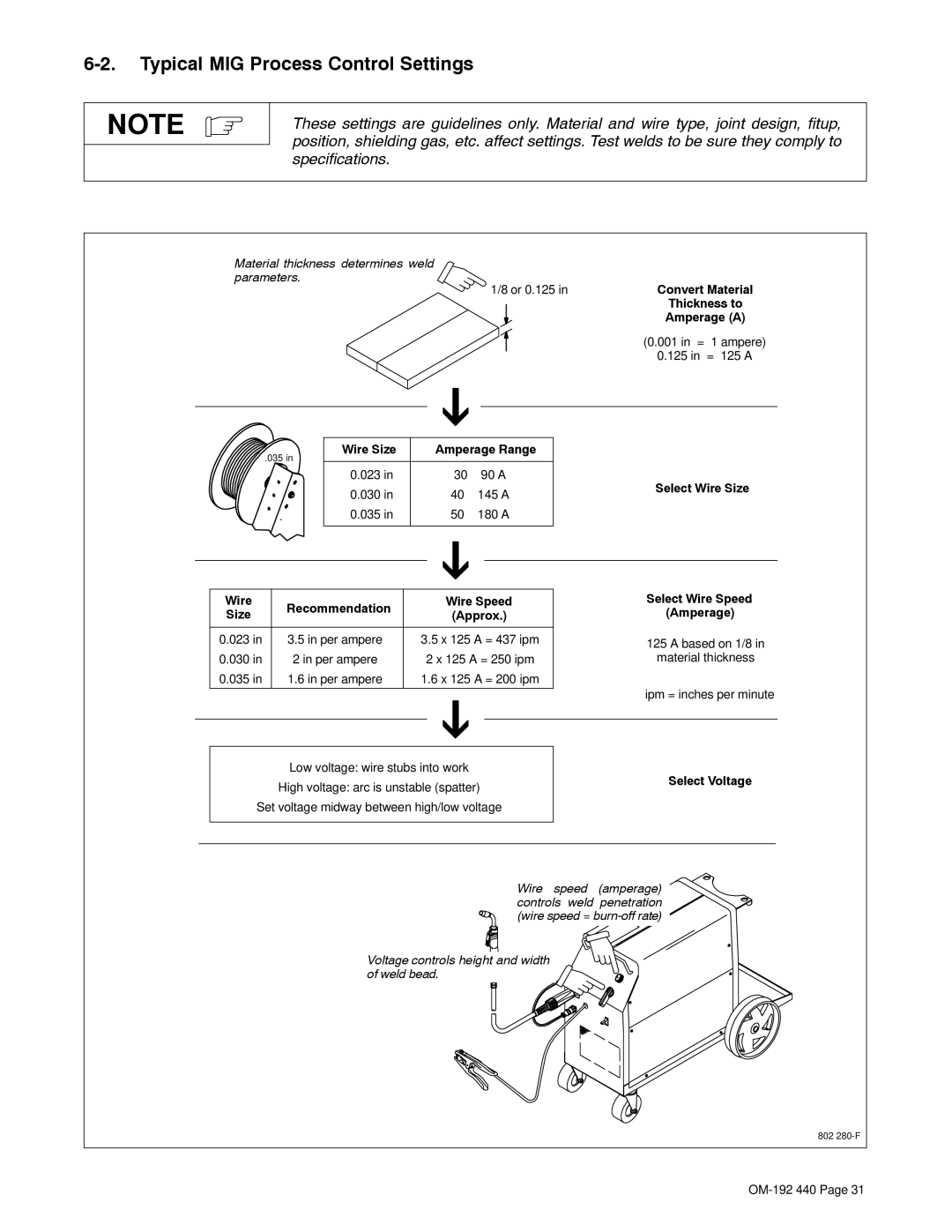
6-2. Typical MIG Process Control Settings
NOTE
These settings are guidelines only. Material and wire type, joint design, fitup, position, shielding gas, etc. affect settings. Test welds to be sure they comply to specifications.
Material thickness determines weld parameters.
![]() 1/8 or 0.125 inConvert Material
1/8 or 0.125 inConvert Material
Thickness to
Amperage (A)
(0.001 in = 1 ampere)
0.125 in = 125 A
.035 in
Wire Size | Amperage Range | ||
|
|
|
|
0.023 in |
| 30 − 90 A | |
0.030 in | 40 − 145 A | ||
0.035 in | 50 − 180 A | ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Select Wire Size
|
| Wire | Recommendation |
| Wire Speed | Select Wire Speed | ||||
|
| Size |
| (Approx.) | (Amperage) | |||||
|
|
|
| |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 0.023 in | 3.5 in per ampere | 3.5 x 125 A = 437 ipm | 125 A based on 1/8 in | |||||
|
| 0.030 in | 2 in per ampere | 2 x 125 A = 250 ipm | material thickness | |||||
|
| 0.035 in | 1.6 in per ampere | 1.6 x 125 A = 200 ipm |
|
| ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ipm = inches per minute | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Low voltage: wire stubs into work | Select Voltage | ||||||
|
|
| High voltage: arc is unstable (spatter) | |||||||
|
|
|
|
| ||||||
|
| Set voltage midway between high/low voltage |
|
| ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Wire speed (amperage) controls weld penetration (wire speed =
Voltage controls height and width of weld bead. ![]()
802