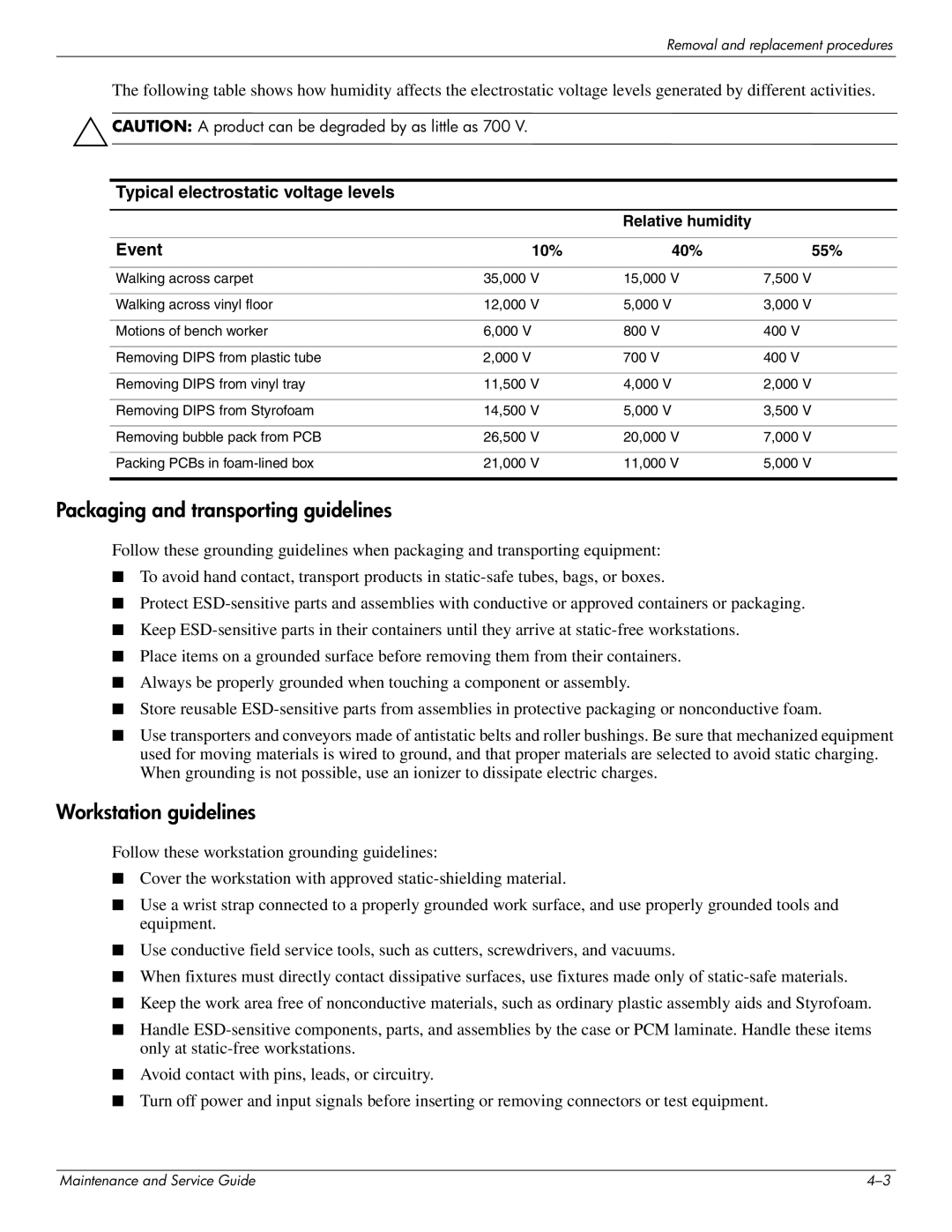
4410t Mobile specifications
The HP 4410t Mobile is a versatile mobile workstation designed to meet the demands of professionals who require both power and portability. It combines a sleek design with robust performance capabilities, making it an ideal choice for users who need reliable computing on the go.At the heart of the HP 4410t is its powerful Intel Core processor. Available in various configurations, this processor ensures smooth multitasking and efficient performance. With options for different generations, users can select a model that best fits their computing requirements. The laptop's memory capacity can be expanded, allowing for more applications to run simultaneously, which is a crucial feature for professionals in design, engineering, and technical fields.
The display of the HP 4410t is another standout feature. It boasts a 14-inch HD display that provides crisp visuals and vibrant colors, making it ideal for design work and presentations. The anti-glare technology ensures that users can work comfortably even in brightly lit environments. This feature is particularly beneficial for professionals who spend extended hours in front of their screens.
In terms of storage, the HP 4410t offers a range of options, including solid-state drives (SSDs) that provide faster data access speeds compared to traditional hard drives. This enhances the overall responsiveness of the system, allowing users to boot up quickly and load applications with minimal delay.
Connectivity is also a strong point for the HP 4410t. It includes multiple USB ports, including USB 3.0 for high-speed device connections, HDMI for video output, and Ethernet for wired networking. This range of ports ensures that users can connect to various peripherals and networks seamlessly.
The HP 4410t is built with durability in mind. It features a robust chassis designed to withstand the rigors of mobile use. The spill-resistant keyboard and reinforced hinges are testament to its longevity and reliability.
Moreover, security is a priority in the HP 4410t. It comes equipped with features such as a fingerprint reader and advanced encryption options, ensuring that sensitive data remains protected.
Finally, the mobility of the HP 4410t is enhanced by its lightweight design and long battery life, making it an excellent choice for professionals who are frequently on the move. In summary, the HP 4410t Mobile combines power, performance, and portability, making it a reliable workstation for anyone needing high-performance computing while on the go.