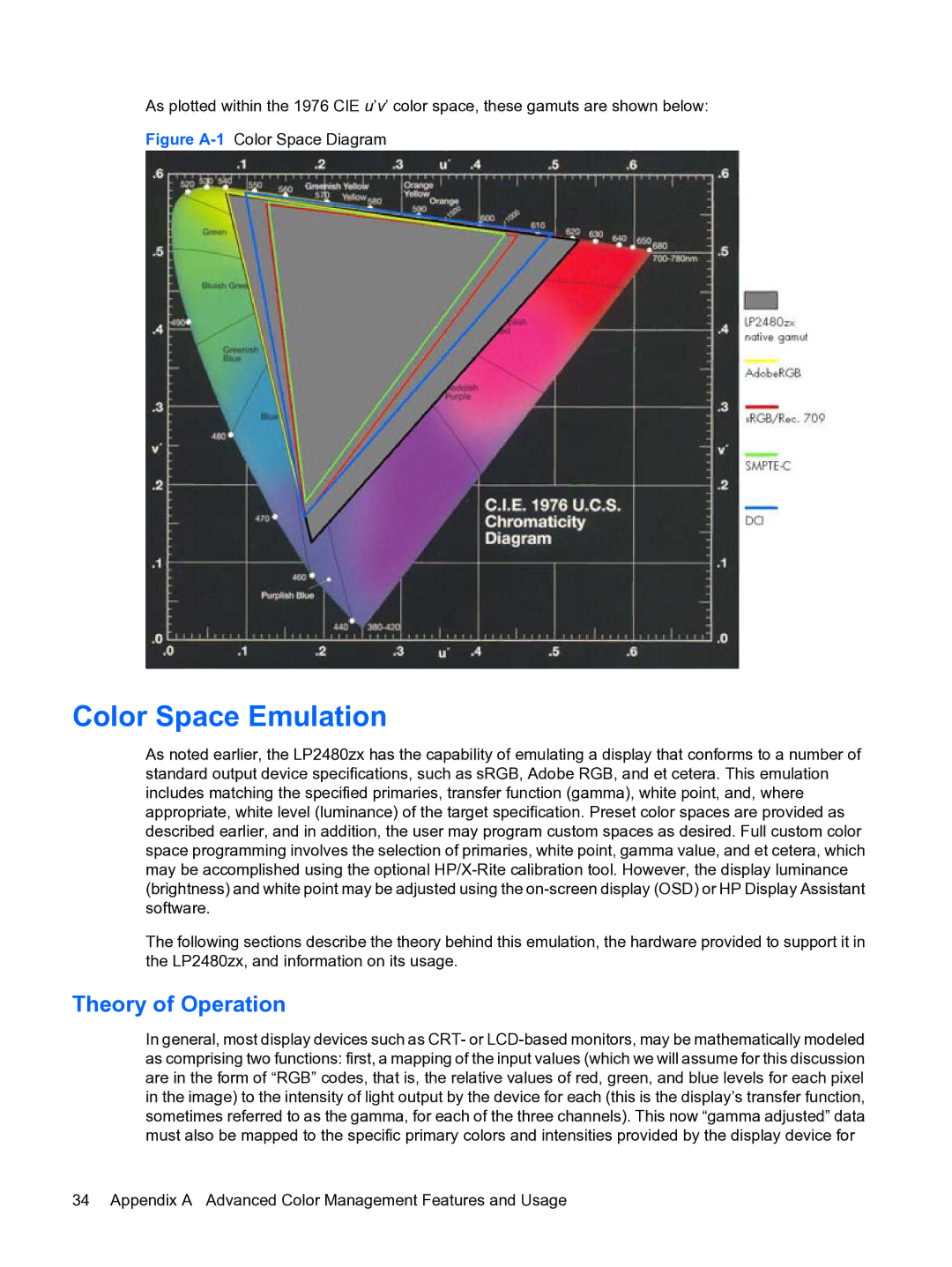
As plotted within the 1976 CIE u’v’ color space, these gamuts are shown below:
Figure A-1 Color Space Diagram
Color Space Emulation
As noted earlier, the LP2480zx has the capability of emulating a display that conforms to a number of standard output device specifications, such as sRGB, Adobe RGB, and et cetera. This emulation includes matching the specified primaries, transfer function (gamma), white point, and, where appropriate, white level (luminance) of the target specification. Preset color spaces are provided as described earlier, and in addition, the user may program custom spaces as desired. Full custom color space programming involves the selection of primaries, white point, gamma value, and et cetera, which may be accomplished using the optional
The following sections describe the theory behind this emulation, the hardware provided to support it in the LP2480zx, and information on its usage.
Theory of Operation
In general, most display devices such as CRT- or
34 Appendix A Advanced Color Management Features and Usage