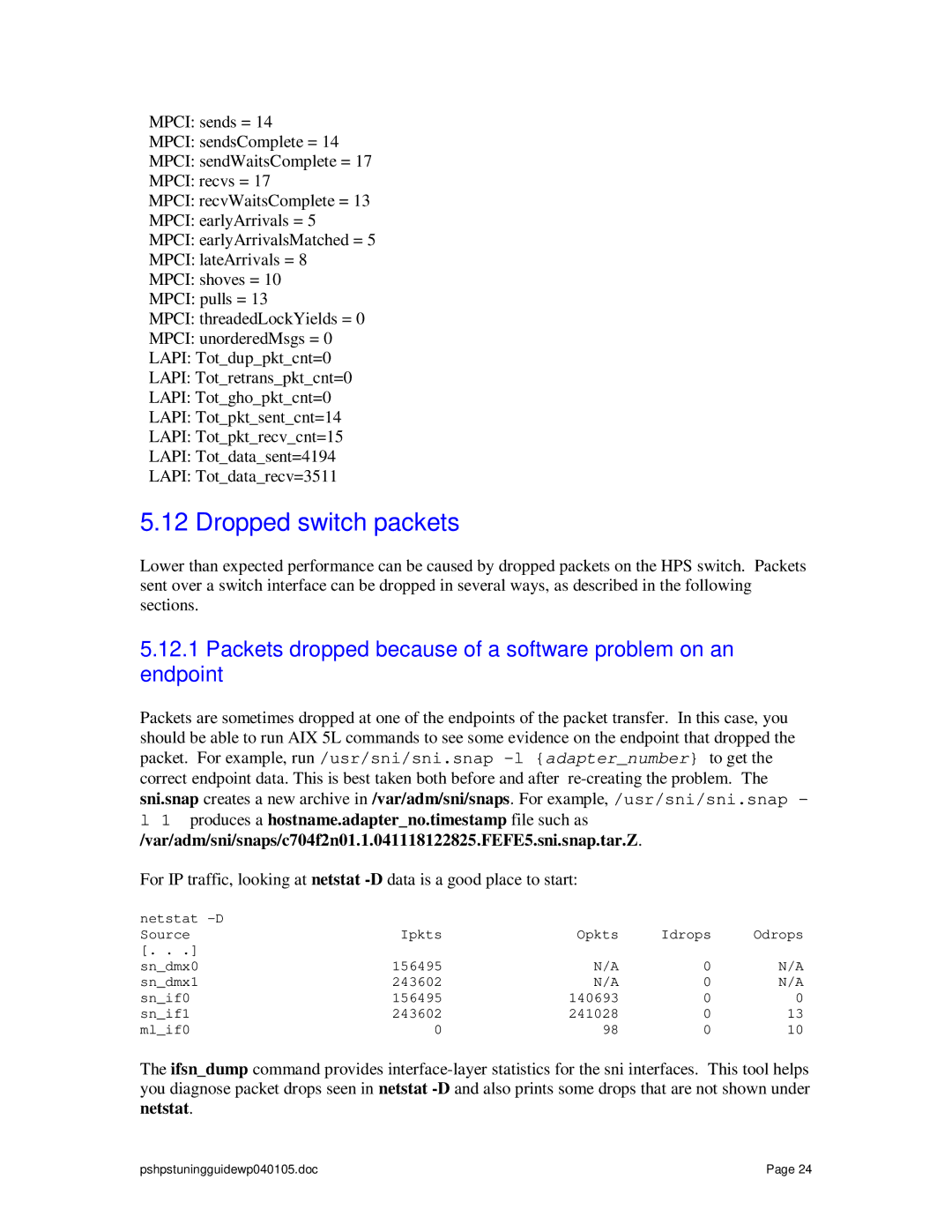
MPCI: sends = 14
MPCI: sendsComplete = 14
MPCI: sendWaitsComplete = 17
MPCI: recvs = 17
MPCI: recvWaitsComplete = 13
MPCI: earlyArrivals = 5
MPCI: earlyArrivalsMatched = 5
MPCI: lateArrivals = 8
MPCI: shoves = 10
MPCI: pulls = 13
MPCI: threadedLockYields = 0
MPCI: unorderedMsgs = 0
LAPI: Tot_dup_pkt_cnt=0
LAPI: Tot_retrans_pkt_cnt=0
LAPI: Tot_gho_pkt_cnt=0
LAPI: Tot_pkt_sent_cnt=14
LAPI: Tot_pkt_recv_cnt=15
LAPI: Tot_data_sent=4194
LAPI: Tot_data_recv=3511
5.12 Dropped switch packets
Lower than expected performance can be caused by dropped packets on the HPS switch. Packets sent over a switch interface can be dropped in several ways, as described in the following sections.
5.12.1Packets dropped because of a software problem on an endpoint
Packets are sometimes dropped at one of the endpoints of the packet transfer. In this case, you should be able to run AIX 5L commands to see some evidence on the endpoint that dropped the packet. For example, run /usr/sni/sni.snap
l1 produces a hostname.adapter_no.timestamp file such as /var/adm/sni/snaps/c704f2n01.1.041118122825.FEFE5.sni.snap.tar.Z.
For IP traffic, looking at netstat
netstat |
|
|
|
|
Source | Ipkts | Opkts | Idrops | Odrops |
[. . .] |
|
|
|
|
sn_dmx0 | 156495 | N/A | 0 | N/A |
sn_dmx1 | 243602 | N/A | 0 | N/A |
sn_if0 | 156495 | 140693 | 0 | 0 |
sn_if1 | 243602 | 241028 | 0 | 13 |
ml_if0 | 0 | 98 | 0 | 10 |
The ifsn_dump command provides
pshpstuningguidewp040105.doc | Page 24 |