PLL IC
The PLL circuit provides stable oscillation of the transmit frequency and receive 1st LO frequency. The PLL output frequency is controlled by the divided ratio
The applied signals are divided at the prescaler and programmable counter according to the control signals (“SSO,” “PLST” and "SCK”) from the CPU. The divided signal is
The phase difference is output from pin 4 as a pulse type signal after being passed through the internal charge pump. The output signal is converted into the DC voltage (lock voltage) by passing through the loop filter (Q8, Q9). The lock voltage is applied to the variable capacitors (D10 and D13 of RX VCO1, D8 and D9 of RX VCO2, D14 and D17 of TX VCO), and locked to keep the VCO frequency constant.
If the oscillated signal drifts, its phase changes from that of the reference frequency, causing a lock voltage change to compensate for the drift in the VCO oscillating frequency.
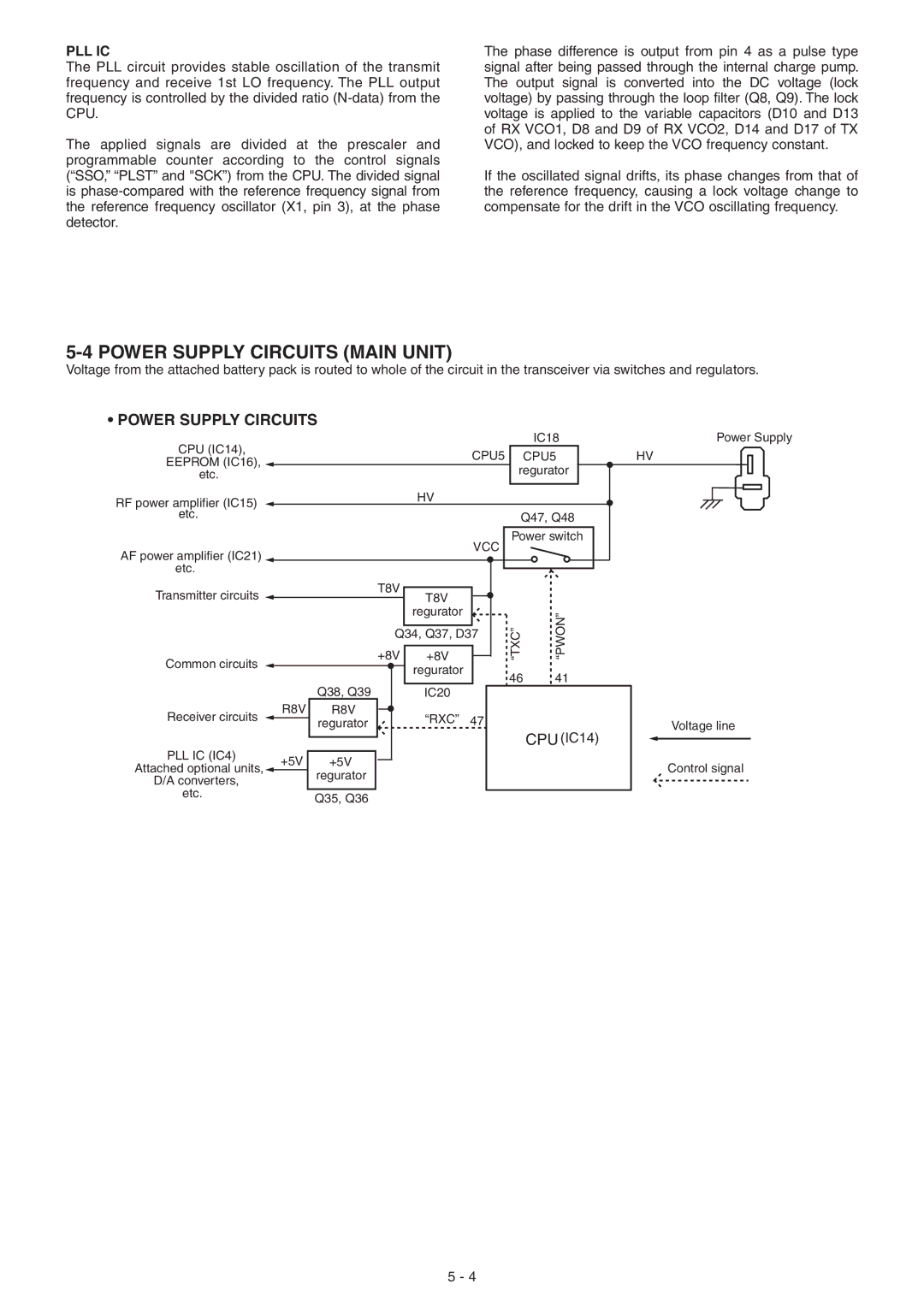
5-4 POWER SUPPLY CIRCUITS (MAIN UNIT)
Voltage from the attached battery pack is routed to whole of the circuit in the transceiver via switches and regulators.
• POWER SUPPLY CIRCUITS |
| |
CPU (IC14), | CPU5 | |
EEPROM (IC16), | ||
| ||
etc. |
| |
RF power amplifier (IC15) | HV | |
| ||
etc. |
| |
AF power amplifier (IC21) | VCC | |
| ||
etc. |
|
T8V
Transmitter circuits ![]() T8V regurator
T8V regurator
IC18
CPU5 regurator
Q47, Q48
Power switch
Power Supply
HV
Common circuits |
| |
Receiver circuits | R8V | |
| ||
PLL IC (IC4) | +5V | |
Attached optional units, | ||
| ||
D/A converters, |
| |
etc. |
|
Q38, Q39
R8V regurator
+5V regurator
Q35, Q36
Q34, Q37, D37
+8V | +8V |
regurator
IC20 “RXC” 47
“TXC” | “PWON” |
46 | 41 |
CPU (IC14)
Voltage line
Control signal
5 - 4