4-1-5 AF AMPLIFIER CIRCUIT (MAIN AND FRONT UNITS)
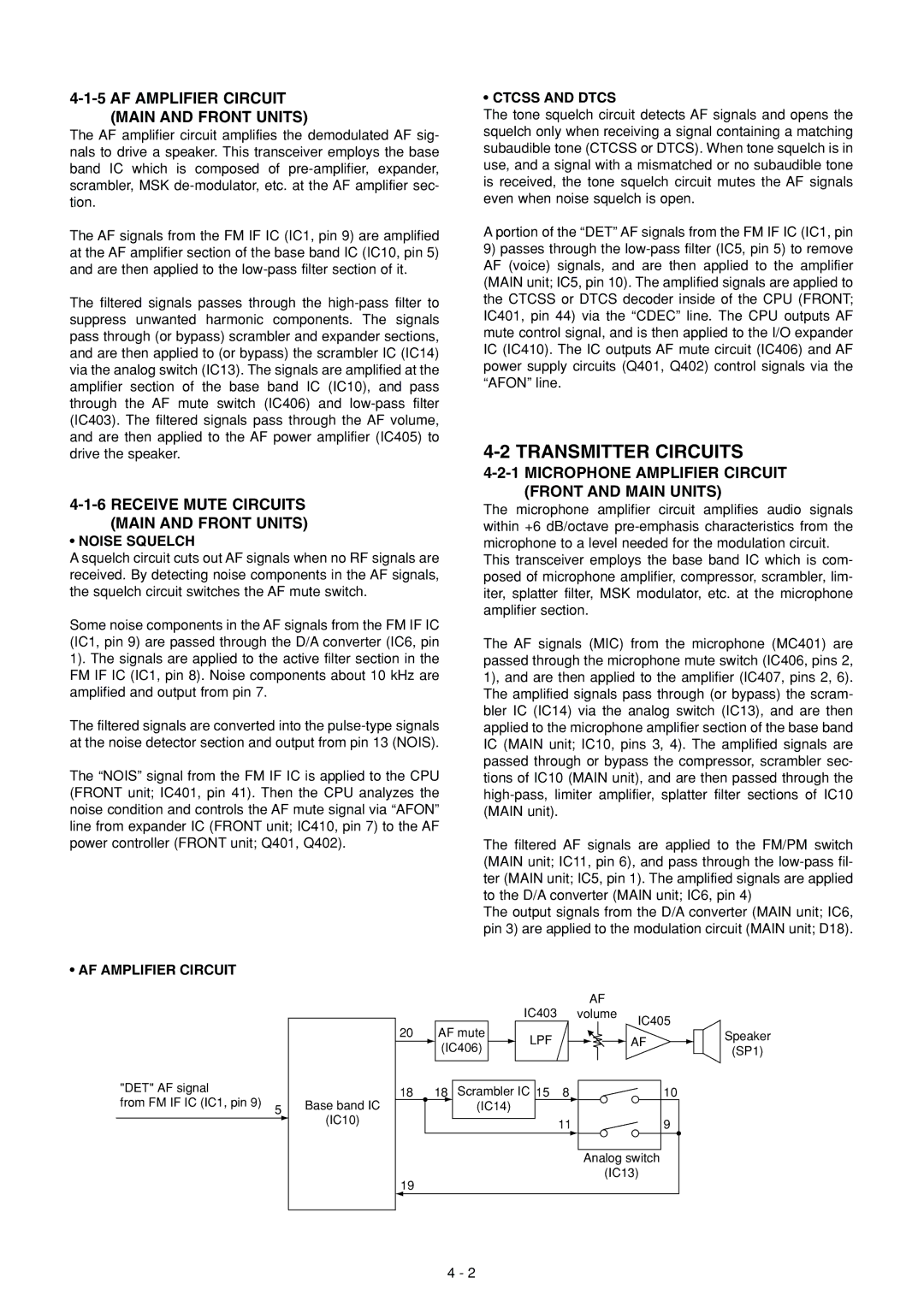
The AF amplifier circuit amplifies the demodulated AF sig- nals to drive a speaker. This transceiver employs the base band IC which is composed of
The AF signals from the FM IF IC (IC1, pin 9) are amplified at the AF amplifier section of the base band IC (IC10, pin 5) and are then applied to the
The filtered signals passes through the
4-1-6 RECEIVE MUTE CIRCUITS (MAIN AND FRONT UNITS)
•NOISE SQUELCH
A squelch circuit cuts out AF signals when no RF signals are received. By detecting noise components in the AF signals, the squelch circuit switches the AF mute switch.
Some noise components in the AF signals from the FM IF IC (IC1, pin 9) are passed through the D/A converter (IC6, pin 1). The signals are applied to the active filter section in the FM IF IC (IC1, pin 8). Noise components about 10 kHz are amplified and output from pin 7.
The filtered signals are converted into the
The “NOIS” signal from the FM IF IC is applied to the CPU (FRONT unit; IC401, pin 41). Then the CPU analyzes the noise condition and controls the AF mute signal via “AFON” line from expander IC (FRONT unit; IC410, pin 7) to the AF power controller (FRONT unit; Q401, Q402).
•CTCSS AND DTCS
The tone squelch circuit detects AF signals and opens the squelch only when receiving a signal containing a matching subaudible tone (CTCSS or DTCS). When tone squelch is in use, and a signal with a mismatched or no subaudible tone is received, the tone squelch circuit mutes the AF signals even when noise squelch is open.
A portion of the “DET” AF signals from the FM IF IC (IC1, pin
9)passes through the
4-2 TRANSMITTER CIRCUITS
4-2-1 MICROPHONE AMPLIFIER CIRCUIT (FRONT AND MAIN UNITS)
The microphone amplifier circuit amplifies audio signals within +6 dB/octave
This transceiver employs the base band IC which is com- posed of microphone amplifier, compressor, scrambler, lim- iter, splatter filter, MSK modulator, etc. at the microphone amplifier section.
The AF signals (MIC) from the microphone (MC401) are passed through the microphone mute switch (IC406, pins 2, 1), and are then applied to the amplifier (IC407, pins 2, 6). The amplified signals pass through (or bypass) the scram- bler IC (IC14) via the analog switch (IC13), and are then applied to the microphone amplifier section of the base band IC (MAIN unit; IC10, pins 3, 4). The amplified signals are passed through or bypass the compressor, scrambler sec- tions of IC10 (MAIN unit), and are then passed through the
The filtered AF signals are applied to the FM/PM switch (MAIN unit; IC11, pin 6), and pass through the
The output signals from the D/A converter (MAIN unit; IC6, pin 3) are applied to the modulation circuit (MAIN unit; D18).
•AF AMPLIFIER CIRCUIT
"DET" AF signal
from FM IF IC (IC1, pin 9)
5
Base band IC
(IC10)
|
| IC403 | AF |
|
|
|
| volume | IC405 |
| |
20 | AF mute |
|
|
| |
LPF |
| AF | Speaker | ||
| (IC406) |
| (SP1) | ||
|
|
|
| ||
18 | 18 Scrambler IC 15 8 |
| 10 |
| |
| (IC14) |
|
|
|
|
|
| 11 |
| 9 |
|
Analog switch
(IC13)
19
4 - 2