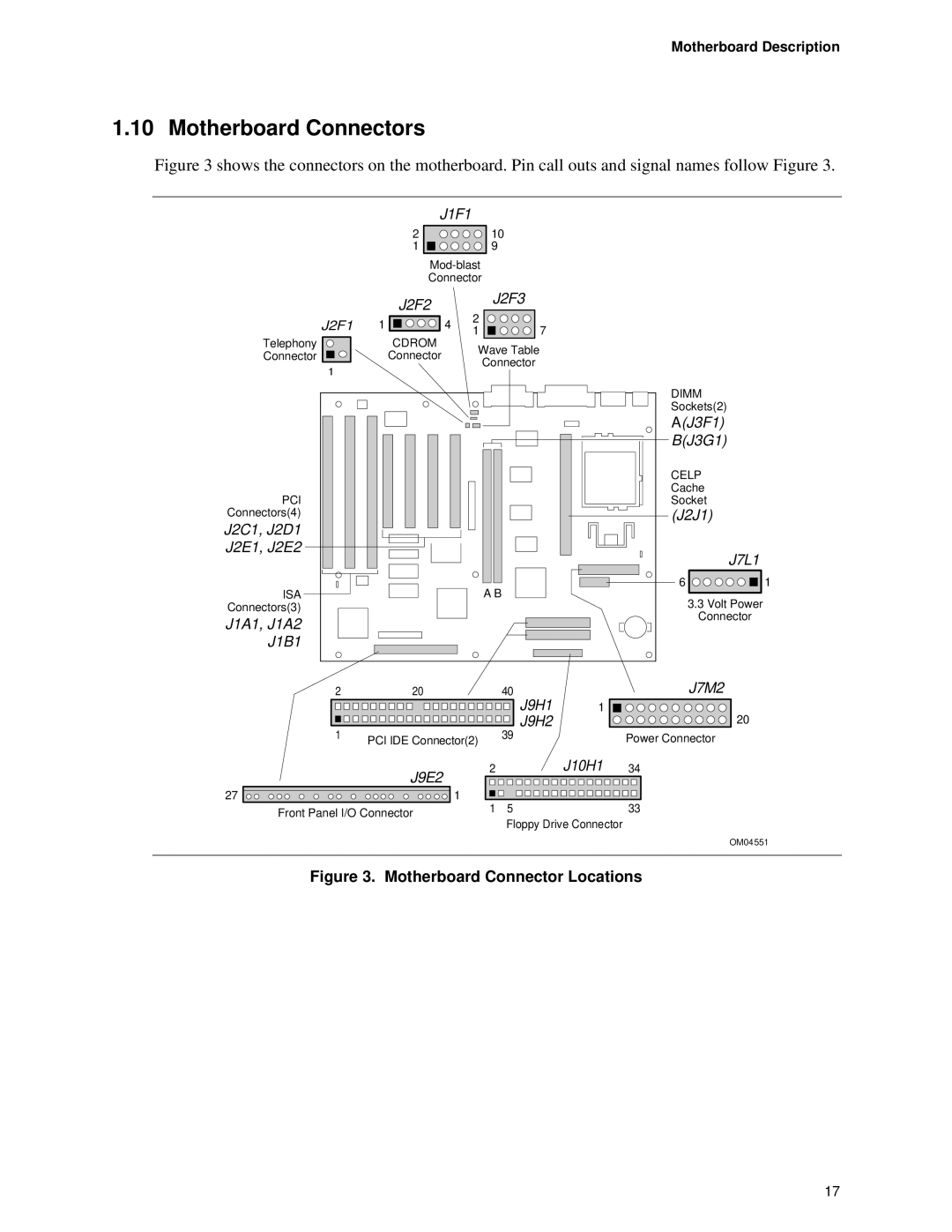
TE430VX specifications
The Intel TE430VX was a landmark product in the realm of computing during the early 1990s. This microprocessor, part of Intel's line of Pentium processors, was primarily aimed at the burgeoning market for personal and business computing.One of the main features of the Intel TE430VX was its 32-bit architecture, which allowed for a significant increase in processing power compared to its predecessors. The 32-bit data bus enabled the handling of larger amounts of data simultaneously, enhancing overall system performance. The TE430VX was capable of executing instructions at clock speeds ranging from 60 MHz to 66 MHz, which was quite impressive for its time. This processing power made it suitable not only for everyday computing tasks but also for more demanding applications such as graphic design and gaming.
The TE430VX also incorporated advanced technologies such as pipelining, which allowed it to execute multiple instructions in a single clock cycle. This feature contributed to improved performance and responsiveness, making the user experience smoother. The microprocessor supported a variety of RAM types, including EDO (Extended Data Out) RAM, which further enhanced its performance by reducing memory access times.
Another characteristic that set the TE430VX apart was its compatibility with a wide range of operating systems, including DOS, Windows, and various UNIX variants. This flexibility ensured that users could run their preferred software without compatibility issues, making it a versatile choice for home and business environments alike.
The integration of a built-in memory controller also simplified motherboard design, reducing the overall cost of systems utilizing the TE430VX. This chip also supported advanced graphics options, allowing users to experience better multimedia performance through dedicated graphics cards.
Power consumption was another consideration in the design of the TE430VX. It was engineered to operate efficiently while maintaining good performance, an important factor for long-term sustainability in computing environments.
In summary, the Intel TE430VX was a significant advancement in microprocessor technology during the early 1990s. Its 32-bit architecture, pipelining capabilities, compatibility with multiple operating systems, and efficient power consumption contributed to its reputation as a reliable choice for both personal and professional use, solidifying Intel's position as a leader in the computing landscape.