UX-A7DVD
Consists of CA-UXA7DVD and SP-UXA7DVD
UX-A7DVD
Important for Laser Products
Precautions
Introduction
Contents
Main Unit
Location of the Buttons and Controls
Main unit
Display window on the electronic swing panel
Display window
Remote Control
See pages in parentheses for details
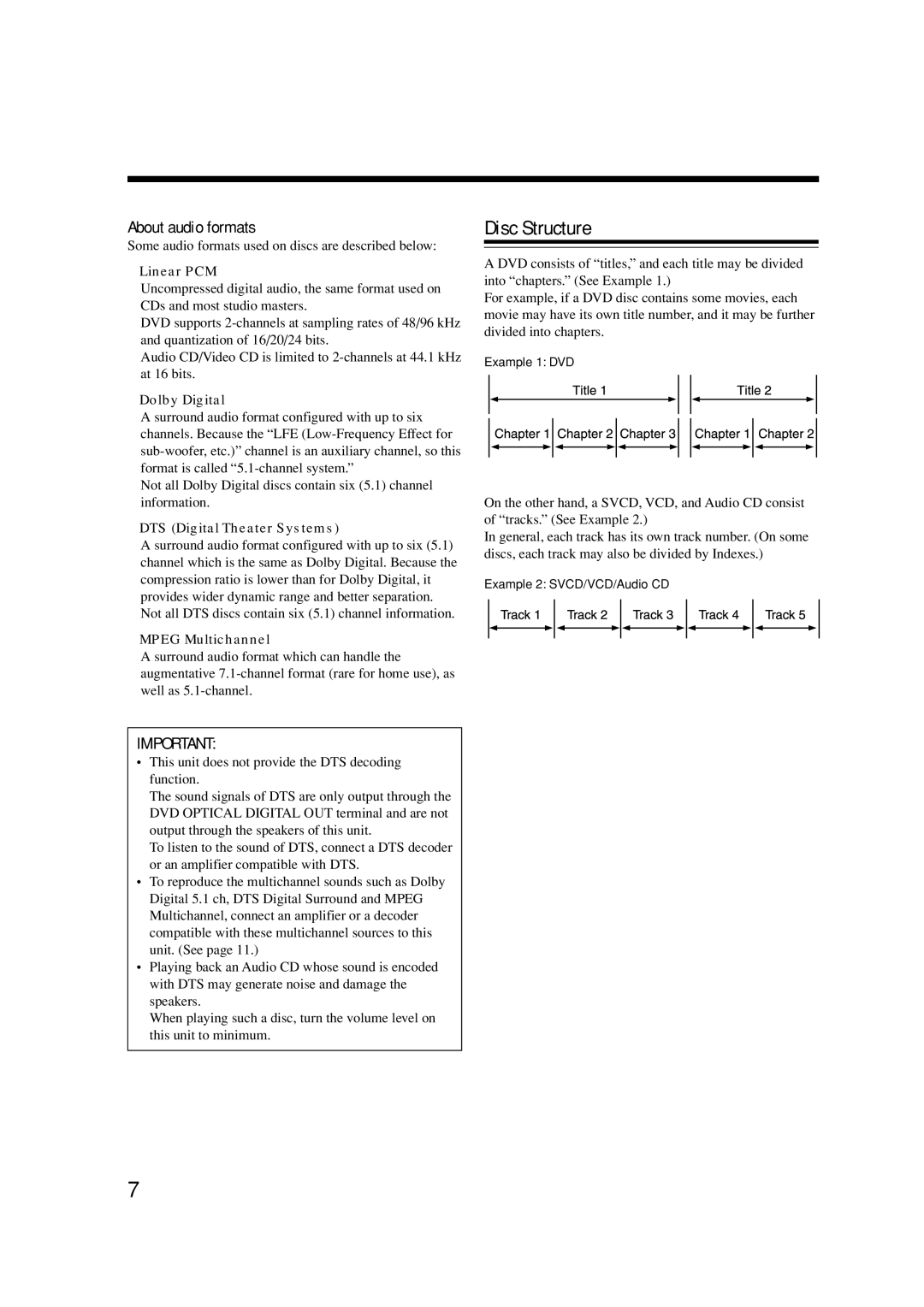
About Discs
Playable Disc Types
Disc Structure
About audio formats
Getting Started
Putting the Batteries into the Remote Control
Connecting Antennas
Unpacking
AM antenna
Connecting Speakers
You can connect the speakers using the speaker cords
To connect an outdoor AM antenna
To select the color system
Connecting a TV
To remove the speaker grilles
Speaker grilles are removable as illustrated below
Connecting Other Equipment
Adjusting the Voltage Selector
To connect analog audio equipment
Setting the DVD Player
Go to the next page to start the setting
To select the On-screen language for the setting menu-Step
Go to To select the monitor type on the next
To select the monitor type-Step
Go to To select the output signal type on the next
Guidelines to select the monitor type
Playback Output signals
To select the output signal type-Step
Guidelines to select the output signal type
Disc
To show the clock when the unit is turned on
Setting the Clock
To turn off the clock indication
Remote control
Basic and Common Operations
Turning On the Power
To turn off the unit automatically Auto Power Off
Selecting the Sources and Starting Play
Adjusting the Volume
To turn down the volume level temporarily
To listen to the sound from external equipment, press
Adjusting the Tone
Reinforcing the Bass Sound
To create your favorite colors
Changing the Display Illumination
To select the illumination color
To change the display brightness
Adjusting the Audio Input Level Prohibiting Disc Ejection
On the main unit only
Listening to FM and AM Broadcasts
Remote control
10 0 +10
Tuning in to a Station
Setting the AM Tuner Interval Spacing
To change the FM reception mode
Press the number buttons to select a preset number
Presetting Stations
Tuning in to a Preset Station
Press SET again
Playing Back Discs
DVD
On-screen guide icons
Loading a Disc
To prevent screen burn-out with the screen saver
To go to another chapter
DVD Basic Operations
To show the on-screen indication
Current disc information
SVCD/VCD/Audio CD Basic Operations
To increase the DVD’s sound level
Disc playing information
While playing a disc
To go to another track
To stop play for a moment, press DVD #¥8 or 8 on
To erase the on-screen indication, press on Screen
Unavailable functions for MP3 disc
MP3 Basic Operations
About MP3 disc
Available for MP3
Forward search
Searching for a Particular Point
To go to another group
Reverse search
When playing a DVD
Playing Back by Using the Disc Menu
When playing a Svcd or VCD
PBC operation concept
Repeating Playback
Repeat play
For SVCD, VCD, or Audio CD
On the remote control only Press Play Mode during play
B repeat play
Press Cursor 3/2 to move to A-B Repeat
Press Cursor 3/2 to move to PROGRAM, then press Enter
Press Play Mode
Programming the Playing Order Program Play
To program other titles, tracks, or groups, repeat step
To modify the program
To check the programed contents
To exit from the program play
Press Cursor 3/2 to move to RANDOM, then press Enter
Playing at Random-Random Play
To exit from the random play
To skip the playing title, track, or group, press ¢
Playing Back Tapes
To play both sides-Reverse mode
Playing Back a Tape
Special Disc Playback
Functions in this section do not work for MP3 discs
Enter a chapter number by pressing the number buttons 0 to
To erase the on-screen indication, press Play Mode
Press Cursor 3/2 to move to Chap SEARCH, then press Enter
Press Cursor 3/2 to move to Time SEARCH, then press Enter
Viewing the Desired Chapters/Tracks- Digest
To change angle views
Selecting Multi-Angle Views
To show all angle views
Selecting the Audio Language or Sound
Selecting the Subtitle Language
Playing a Still Picture/Frame-by-Frame
Playing Back in Slow-Motion-Slow
You can zoom a picture by 2 times
Zooming in the Picture-Zoom
Enjoying Virtual Surround Sound
To go back to normal play, press Zoom while holding
Recording
DVD Tape FM/AM AUX/MD
To protect your recordings
To clean the heads, capstans, and pinch rollers
Before You Start Recording on a Tape
To keep the best recording and playback sound quality
Press REC on the main unit
Recording a Disc onto a Tape -Disc Synchronized Recording
Prepare a disc
To stop recording, press
To record a single track during play
When you press REC while pausing a track
Recording Other Sources onto a Tape
To record from external equipment
Using the Microphone
Digital
Singing Along Karaoke
To adjust the key
If howling or squealing feedback occurs while using
To apply an echo to your voice
Changing the DVD Initial Settings
TOP Menu
Basic Procedure
Setting menu
Changing the Various Audio Settings
Changing the Initial Language Settings
More about Down MIX
On the System menu, you can change the following settings
Changing the Display Settings
Changing the System Settings
More about Compression
Unlocking the Parental Lock Temporarily
Setting the parental lock
On the remote control only Press Enter while holding down
Press Cursor 5/∞ to select YES, then press
Using the Timers
Display
Using the Recording Timer
How the Recording Timer actually works
How the Daily Timer actually works
Using the Daily Timer
To turn off the Recording Timer after its setting is done
To turn on the Daily Timer again
Volume setting appears in the main display
To turn off the Daily Timer after its setting is done
You can also use the source selecting buttons
Timer Priority
Using the Sleep Timer
How the Sleep Timer actually works
Press Sleep
AV Compu Link Connection
Using AV Compu Link Control System
Set AV Compulink Mode in the System menu as follows
One-touch DVD play
General Notes
Maintenance
Cleaning the unit
Handling discs
Possible Cause
Troubleshooting
Symptom
Action
Disc Tape
Table of Language Codes
Table of Country/Area Codes
Zimbabwe
Specifications
230V
127V
110V