B-RAID Level Comparison Table
Appendix B: RAID Level Comparison Table
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
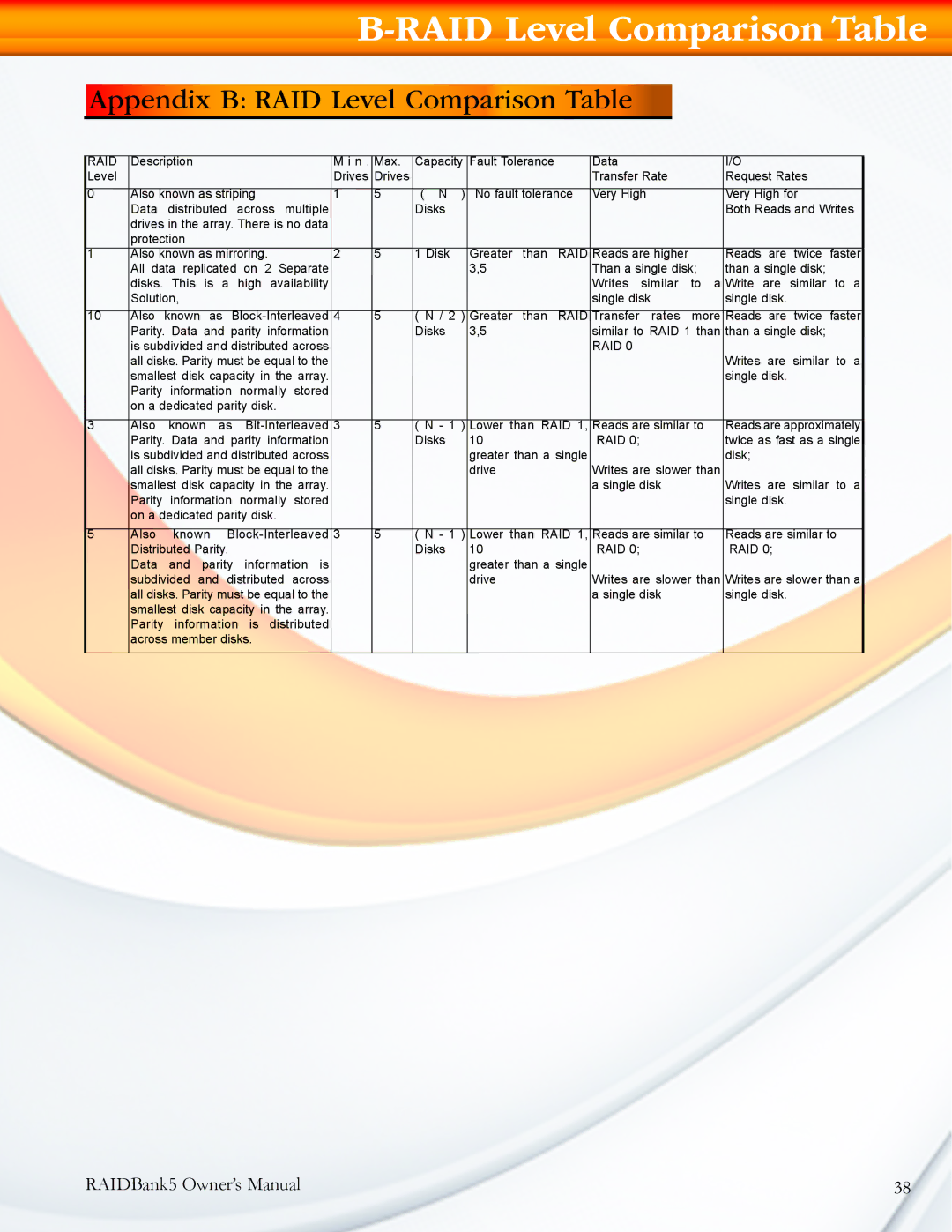
RAID | Description |
|
| M i n . | Max. | Capacity | Fault Tolerance |
| Data |
|
| I/O | ||
Level |
|
|
|
| Drives | Drives |
|
|
|
| Transfer Rate |
| Request Rates | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||
0 | Also known as striping | 1 | 5 | ( N ) | No fault tolerance | Very High |
| Very High for | ||||||
| Data | distributed | across multiple |
|
| Disks |
|
|
|
|
|
| Both Reads and Writes | |
| drives in the array. There is no data |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
| protection |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
1 | Also known as mirroring. | 2 | 5 | 1 Disk | Greater | than | RAID | Reads are higher |
| Reads are twice faster | ||||
| All data replicated on 2 Separate |
|
|
| 3,5 |
|
| Than a single disk; | than a single disk; | |||||
| disks. This is a high availability |
|
|
|
|
|
| Writes | similar | to a | Write are similar to a | |||
| Solution, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| single disk |
| single disk. | ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
10 | Also | known as | 4 | 5 | ( N / 2 ) | Greater | than | RAID | Transfer | rates | more | Reads are twice faster | ||
| Parity. Data and parity information |
|
| Disks | 3,5 |
|
| similar to RAID 1 than | than a single disk; | |||||
| is subdivided and distributed across |
|
|
|
|
|
| RAID 0 |
|
|
| |||
| all disks. Parity must be equal to the |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Writes are similar to a | |||
| smallest disk capacity in the array. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| single disk. | |||
| Parity | information | normally stored |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| on a dedicated parity disk. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||
3 | Also | known as | 3 | 5 | ( N - 1 ) | Lower than RAID 1, | Reads are similar to | Reads are approximately | ||||||
| Parity. Data and parity information |
|
| Disks | 10 |
|
| RAID 0; |
|
| twice as fast as a single | |||
| is subdivided and distributed across |
|
|
| greater than a single |
|
|
| disk; | |||||
| all disks. Parity must be equal to the |
|
|
| drive |
|
| Writes are slower than |
| |||||
| smallest disk capacity in the array. |
|
|
|
|
|
| a single disk |
| Writes are similar to a | ||||
| Parity | information | normally stored |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| single disk. | |
| on a dedicated parity disk. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
5 | Also | known | 3 | 5 | ( N - 1 ) | Lower than RAID 1, | Reads are similar to | Reads are similar to | ||||||
| Distributed Parity. |
|
|
| Disks | 10 |
|
| RAID 0; |
|
| RAID 0; | ||
| Data and parity information is |
|
|
| greater than a single |
|
|
|
| |||||
| subdivided and | distributed across |
|
|
| drive |
|
| Writes are slower than | Writes are slower than a | ||||
| all disks. Parity must be equal to the |
|
|
|
|
|
| a single disk |
| single disk. | ||||
| smallest disk capacity in the array. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
| Parity | information | is distributed |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| across member disks. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RAIDBank5 Owner’s Manual | 38 |