August
Technical Support
RF Exposure Requirements
Radio Frequency Interference Requirements
Regulatory Compliance Information
EN 55 022 Declaration of Conformance
0470
August
Contents
Chapter Maintenance
Appendix a Specifications
Glossary Index
Scope
Manual Specifications
Chapter About This Manual
Audience
Special Message Formats
Typographical Conventions
Html version of this manual
How to Use the Html Version of this Manual
How to Print this Manual
Chapter Introduction
About the ME103 802.11b ProSafe Wireless Access Point
Supported Standards and Conventions
Key Features
802.11b Standards-based Wireless Networking
System Requirements
Autosensing Ethernet Connections with Auto Uplink
Compatible and Related Netgear Products
Hardware Description
What’s In the Box?
ME103 front panel
ME103 Wireless Access Point Front Panel
ME103 rear panel
ME103 Wireless Access Point Rear Panel
Observing Placement and Range Guidelines
Chapter Basic Installation and Configuration
Cabling Requirements
Feature Factory Default Settings
Default Factory Settings
Understanding ME103 Wireless Security Options
SET UP the ME103 Access Point
Installing the ME103 802.11b ProSafe Wireless Access Point
Configure LAN and Wireless Access
Verify Wireless Connectivity
Example ME103 NetBIOS name in browser address bar
How to Log In to the ME103 Using Its Default NetBIOS Name
Web browser will then display the ME103 home
How to Log In to the ME103 Using Its Default IP Address
Basic Wireless Settings menu
Understanding Basic Wireless Settings
Basic Wireless Security options
Understanding Basic Wireless Security Options
Field Description Network
Authentication. Circle one Open System or Shared Key
How to Set Up and Test Basic Wireless Connectivity
10 Wireless Card Access List Setup
How to Restrict Wireless Access by MAC Address
How to Configure WEP
11 Basic IP Settings Menu
Using the Basic IP Settings Options
Access Point Name NetBIOS
Viewing General, Log, Station, and Statistical Information
Chapter Maintenance
General Information Fields
Field Description Access Point Information
Statistics
Field Description System Up Time
Statistics Fields
Activity Log screen
Activity Log
Information Station List of associated devices
Viewing a List of Attached Devices
ME103 Upgrade menu
Upgrading the Wireless Access Point Software
Settings Backup menu
Configuration File Management
Saving and Retrieving the Configuration
Restoring the ME103 to the Factory Default Settings
Using the Reset Button to Restore Factory Default Settings
Set Password menu
Changing the Administrator Password
Chapter Advanced Configuration
Configuring Advanced Security 802.1x Options
Basic Requirements for
Key Exchange Configuration Worksheet
How to Configure the 802.1x Key Exchange Option
Advanced Configuration
Request a certificate
View the ME103 log and check the connection
Running a Ping test from Windows
Ping test results
Advanced Wireless Settings screen
Understanding Advanced Wireless Settings
Field Description Operating Mode
Advanced Wireless Settings Fields
How to Configure a ME103 as a Point-to-Point Bridge
Configuring Wireless Operating Modes
10 Multi-Point bridging
How to Configure Multi
Advanced Configuration
Antenna Installation
EAP-TLS Configuration Worksheet
Blank Configuration Worksheet
No lights are lit on the access point
Chapter Troubleshooting
LAN light is not lit
Wireless LAN activity light does not light up
Am using EAP-TLS security but get disconnected
Cannot connect to the ME103 to configure it
When I enter a URL or IP address I get a timeout error
Using the Reset Button to Restore Factory Default Settings
Specifications for the ME103
Appendix a Specifications
Specifications
Appendix B Wireless Networking Basics
Wireless Networking Overview
Infrastructure Mode
Authentication, WEP, and WPA
Ad Hoc Mode Peer-to-Peer Workgroup
Network Name Extended Service Set Identification Essid
Open System Authentication
Authentication
802.11b Authentication Open System Steps
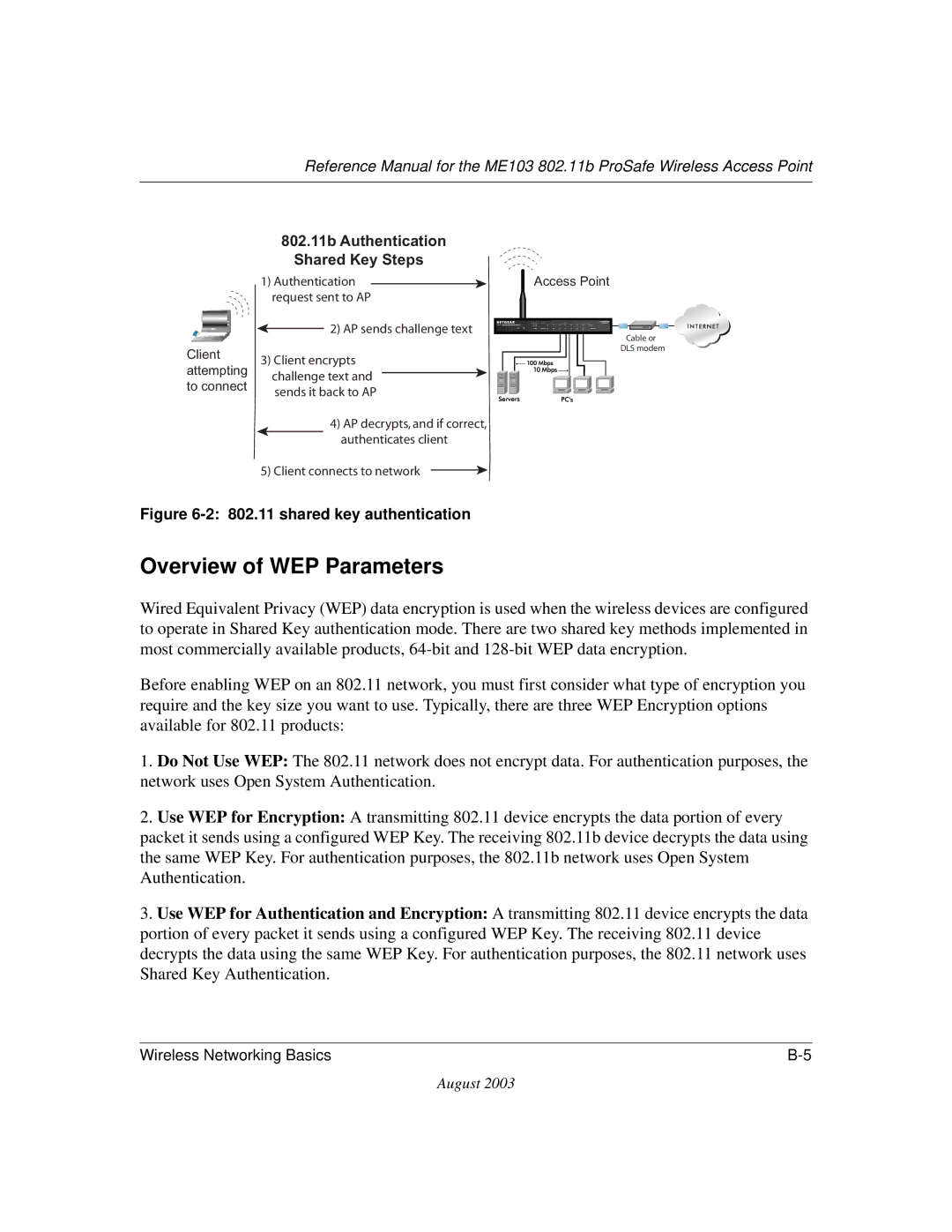
802.11b Authentication Shared Key Steps
Key Size
WEP Configuration Options
Wireless Channels
Table B-1 802.11b Radio Frequency Channels
Radio frequency channels used are listed in Table B-1
Understanding 802.1x Port Based Network Access Control
Wireless Networking Basics
Wireless Networking Basics
Wireless Networking Basics
Basic Router Concepts
Appendix C Network, Routing, Firewall, and Cabling Basics
IP Addresses and the Internet
What is a Router?
Class E Class E addresses are for experimental use
Subnet Addressing
Netmask
Example of Subnetting a Class B Address
Netmask Formats
Netmask Notation Translation Table for One Octet
Private IP Addresses
Single IP Address Operation Using NAT
Single IP Address Operation Using NAT
IP Configuration by Dhcp
Routing Protocols
Domain Name Server
MAC Addresses and ARP
Internet Security and Firewalls
What is a Firewall?
Denial of Service Attack
Stateful Packet Inspection
Uplink Switches, Crossover Cables, and MDI/MDIX Switching
UTP Ethernet cable wiring, straight-through
Ethernet Cabling
Cable Quality
Network, Routing, Firewall, and Cabling Basics
Preparing Your Computers for TCP/IP Networking
Appendix D Preparing Your PCs for Network Access
Configuring Windows 98 and Me for TCP/IP Networking
Install or Verify Windows Networking Components
Preparing Your PCs for Network Access
Choose Settings, and then Control Panel
Enabling Dhcp to Automatically Configure TCP/IP Settings
Primary Network Logon is set to Windows logon
Verifying TCP/IP Properties
Selecting Windows’ Internet Access Method
Configuring Windows 2000 or XP for TCP/IP Networking
Dhcp Configuration of TCP/IP in Windows XP
TCP/IP details are presented on Support tab
Right click on Local Area Connection and select Properties
Dhcp Configuration of TCP/IP in Windows
Obtain an IP address automatically is selected
Verifying TCP/IP Properties for Windows XP or
Preparing Your PCs for Network Access
Glossary
DMZ
DSL
Internet service provider
Radius
TLS
Wins
Glossary
Numerics
Index
RFC