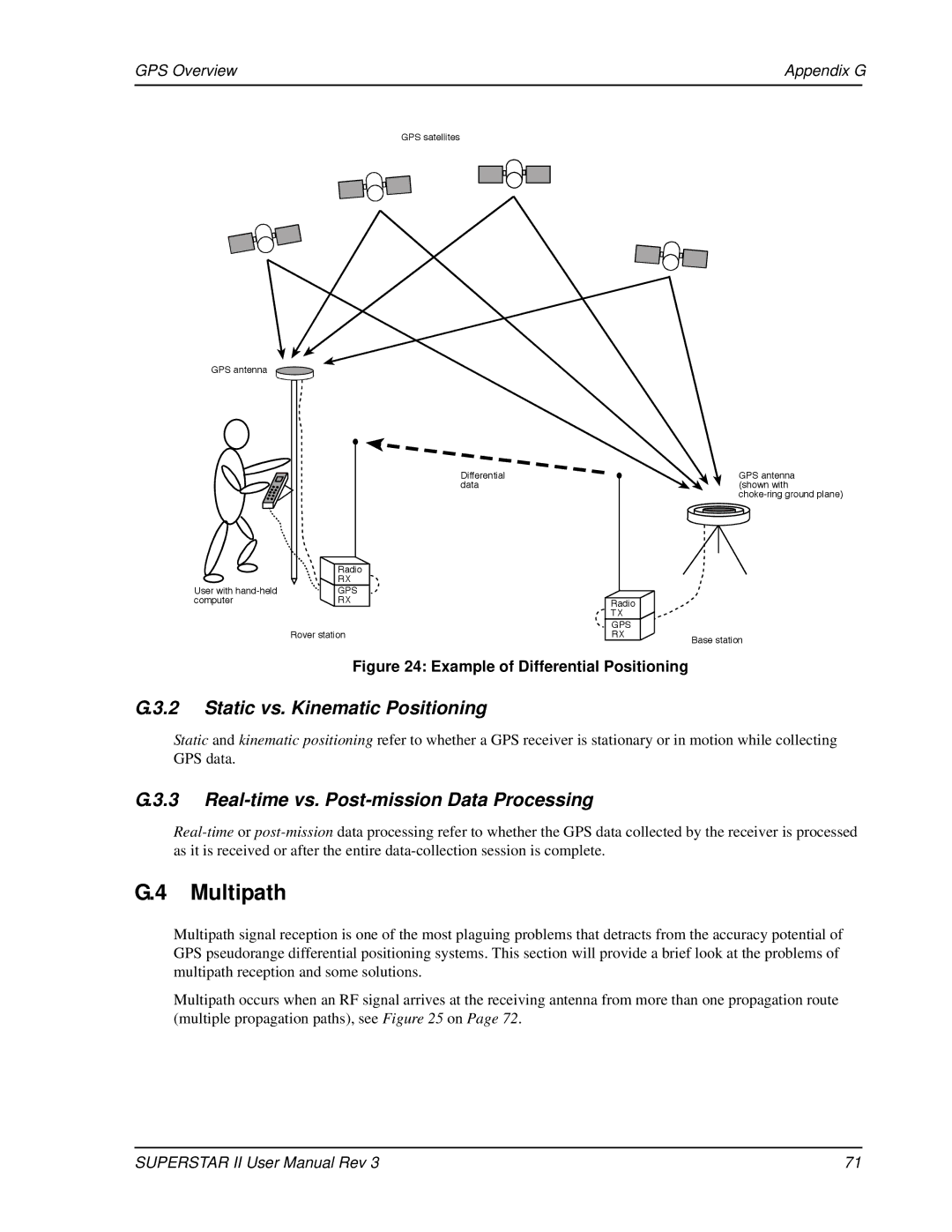
GPS Overview | Appendix G | |
|
|
|
GPS satellites
GPS antenna
Differential data
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Radio | |
User with |
|
|
| RX | |
| |||||
|
|
| GPS | ||
computer |
|
|
| RX | |
| Rover station | ||||
Radio
TX
GPS
RX
GPS antenna (shown with
Base station
Figure 24: Example of Differential Positioning
G.3.2 Static vs. Kinematic Positioning
Static and kinematic positioning refer to whether a GPS receiver is stationary or in motion while collecting GPS data.
G.3.3 Real-time vs. Post-mission Data Processing
G.4 Multipath
Multipath signal reception is one of the most plaguing problems that detracts from the accuracy potential of GPS pseudorange differential positioning systems. This section will provide a brief look at the problems of multipath reception and some solutions.
Multipath occurs when an RF signal arrives at the receiving antenna from more than one propagation route (multiple propagation paths), see Figure 25 on Page 72.
SUPERSTAR II User Manual Rev 3 | 71 |