Selecting Power Fasteners and Power Loads
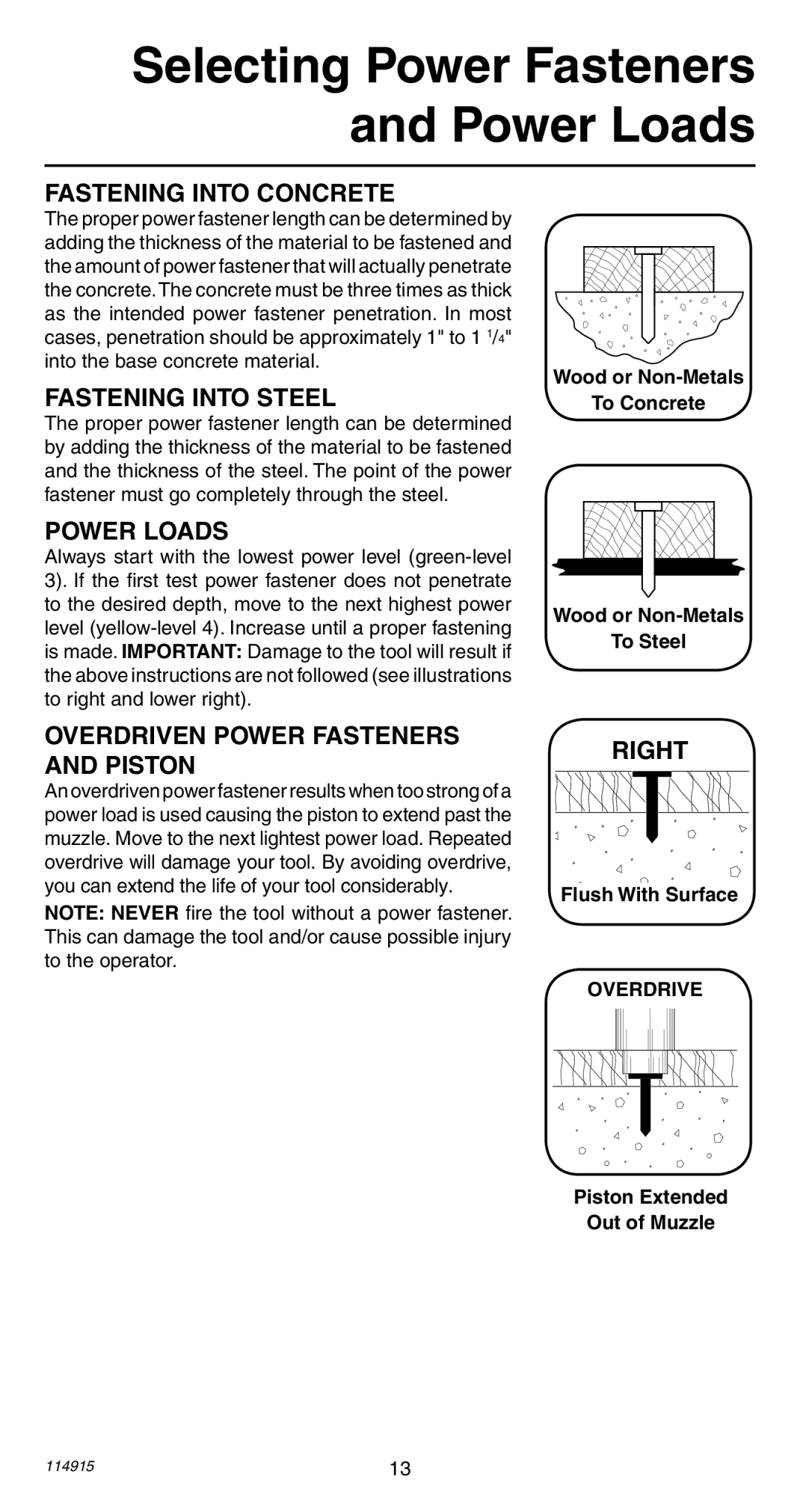
FASTENING INTO CONCRETE
The proper power fastener length can be determined by adding the thickness of the material to be fastened and the amount of power fastener that will actually penetrate the concrete.The concrete must be three times as thick as the intended power fastener penetration. In most cases, penetration should be approximately 1" to 1 1/4" into the base concrete material.
FASTENING INTO STEEL
The proper power fastener length can be determined by adding the thickness of the material to be fastened and the thickness of the steel. The point of the power fastener must go completely through the steel.
POWER LOADS
Always start with the lowest power level
OVERDRIVEN POWER FASTENERS AND PISTON
An overdriven power fastener results when too strong of a power load is used causing the piston to extend past the muzzle. Move to the next lightest power load. Repeated overdrive will damage your tool. By avoiding overdrive, you can extend the life of your tool considerably.
NOTE: NEVER fire the tool without a power fastener. This can damage the tool and/or cause possible injury to the operator.
Wood or
To Concrete
Wood or
To Steel
RIGHT
Flush With Surface
OVERDRIVE
Piston Extended
Out of Muzzle
114915 | 13 |