OPERATION
TOO SLOW FEEDING (Continued)
You can detect
DEPTH OF CUT
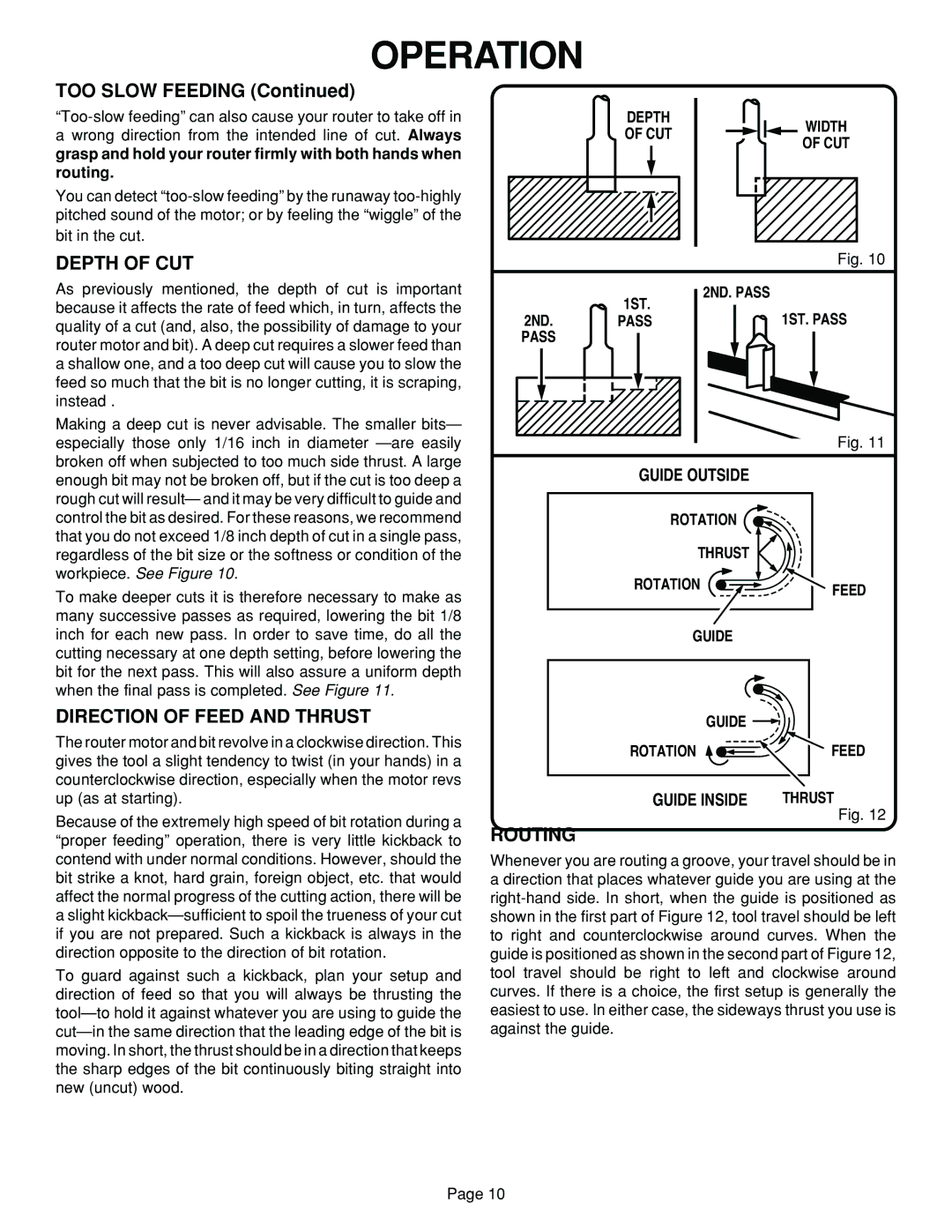
As previously mentioned, the depth of cut is important because it affects the rate of feed which, in turn, affects the quality of a cut (and, also, the possibility of damage to your router motor and bit). A deep cut requires a slower feed than a shallow one, and a too deep cut will cause you to slow the feed so much that the bit is no longer cutting, it is scraping, instead .
Making a deep cut is never advisable. The smaller bits— especially those only 1/16 inch in diameter
To make deeper cuts it is therefore necessary to make as many successive passes as required, lowering the bit 1/8 inch for each new pass. In order to save time, do all the cutting necessary at one depth setting, before lowering the bit for the next pass. This will also assure a uniform depth when the final pass is completed. See Figure 11.
DIRECTION OF FEED AND THRUST
The router motor and bit revolve in a clockwise direction. This gives the tool a slight tendency to twist (in your hands) in a counterclockwise direction, especially when the motor revs up (as at starting).
Because of the extremely high speed of bit rotation during a “proper feeding” operation, there is very little kickback to contend with under normal conditions. However, should the bit strike a knot, hard grain, foreign object, etc. that would affect the normal progress of the cutting action, there will be a slight
To guard against such a kickback, plan your setup and direction of feed so that you will always be thrusting the
|
|
|
| DEPTH |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| WIDTH |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
| OF CUT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| OF CUT | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fig. 10
| 1ST. | 2ND. PASS | |
2ND. | 1ST. PASS | ||
PASS | |||
PASS |
|
|
Fig. 11
GUIDE OUTSIDE
ROTATION |
|
THRUST |
|
ROTATION | FEED |
| |
GUIDE |
|
| GUIDE |
ROTATION | FEED |
GUIDE INSIDE | THRUST |
| Fig. 12 |
ROUTING
Whenever you are routing a groove, your travel should be in a direction that places whatever guide you are using at the
Page 10