1. INTRODUCTION
1.2 RAID Explained
RAID - Redundant Array of Independent Disks
RAID technology manages multiple disk drives to enhance I/O performance and provide redundancy in order to withstand the failure of any individual member, without loss of data.
SATA Raid provides four popular RAID Set types, Striped (RAID 0), Mirrored (RAID 1), a combination of RAID 0 and RAID 1 (RAID 0+1), and Data Striping with Striped Parity (RAID 5) which will be supported by Tekram next generation SATA products.
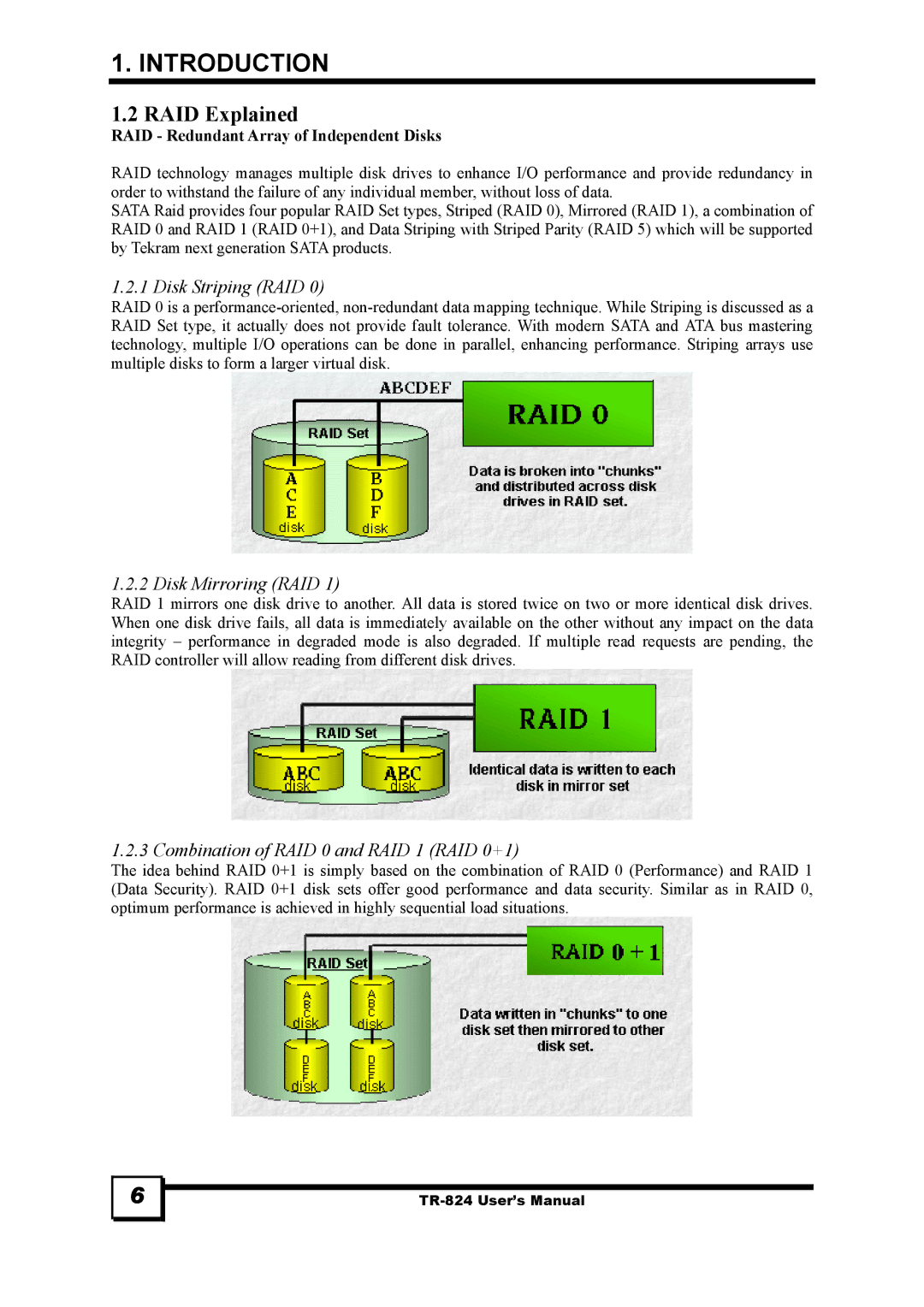
1.2.1 Disk Striping (RAID 0)
RAID 0 is a
1.2.2 Disk Mirroring (RAID 1)
RAID 1 mirrors one disk drive to another. All data is stored twice on two or more identical disk drives. When one disk drive fails, all data is immediately available on the other without any impact on the data integrity – performance in degraded mode is also degraded. If multiple read requests are pending, the RAID controller will allow reading from different disk drives.
1.2.3 Combination of RAID 0 and RAID 1 (RAID 0+1)
The idea behind RAID 0+1 is simply based on the combination of RAID 0 (Performance) and RAID 1 (Data Security). RAID 0+1 disk sets offer good performance and data security. Similar as in RAID 0, optimum performance is achieved in highly sequential load situations.
6