2. SUPPLY SPECIFICATIONS
(Revision Date: Apr. 24, 2008)
2.4 SPECIFICATION OF RFID TAG (for
5) Cutter
When an RFID label or tag is used in cut issue mode, care must be taken not to cut an antenna of the RFID tag or an IC chip in order not to damage the cutter.
6) Static Electricity
When printing is performed in a place where humidity is low or under some specific conditions, writing data on an RFID tag may fail due to static electricity generated by a label or a ribbon.
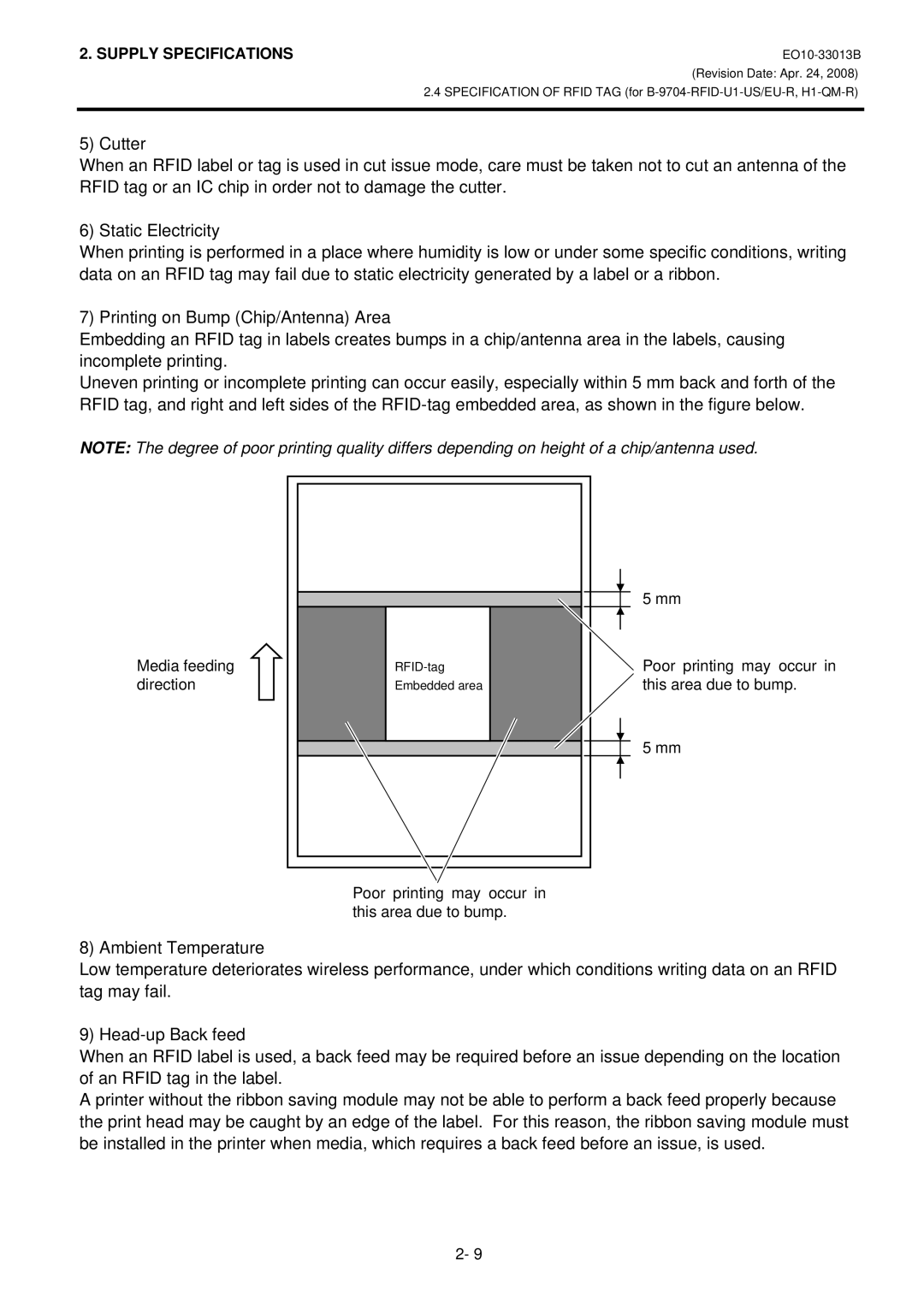
7) Printing on Bump (Chip/Antenna) Area
Embedding an RFID tag in labels creates bumps in a chip/antenna area in the labels, causing incomplete printing.
Uneven printing or incomplete printing can occur easily, especially within 5 mm back and forth of the RFID tag, and right and left sides of the
NOTE: The degree of poor printing quality differs depending on height of a chip/antenna used.
Media feeding direction
Embedded area
Poor printing may occur in this area due to bump.
5 mm
Poor printing may occur in this area due to bump.
5 mm
8) Ambient Temperature
Low temperature deteriorates wireless performance, under which conditions writing data on an RFID tag may fail.
9)
When an RFID label is used, a back feed may be required before an issue depending on the location of an RFID tag in the label.
A printer without the ribbon saving module may not be able to perform a back feed properly because the print head may be caught by an edge of the label. For this reason, the ribbon saving module must be installed in the printer when media, which requires a back feed before an issue, is used.
2- 9