Battery Types
Battery Sizing Example
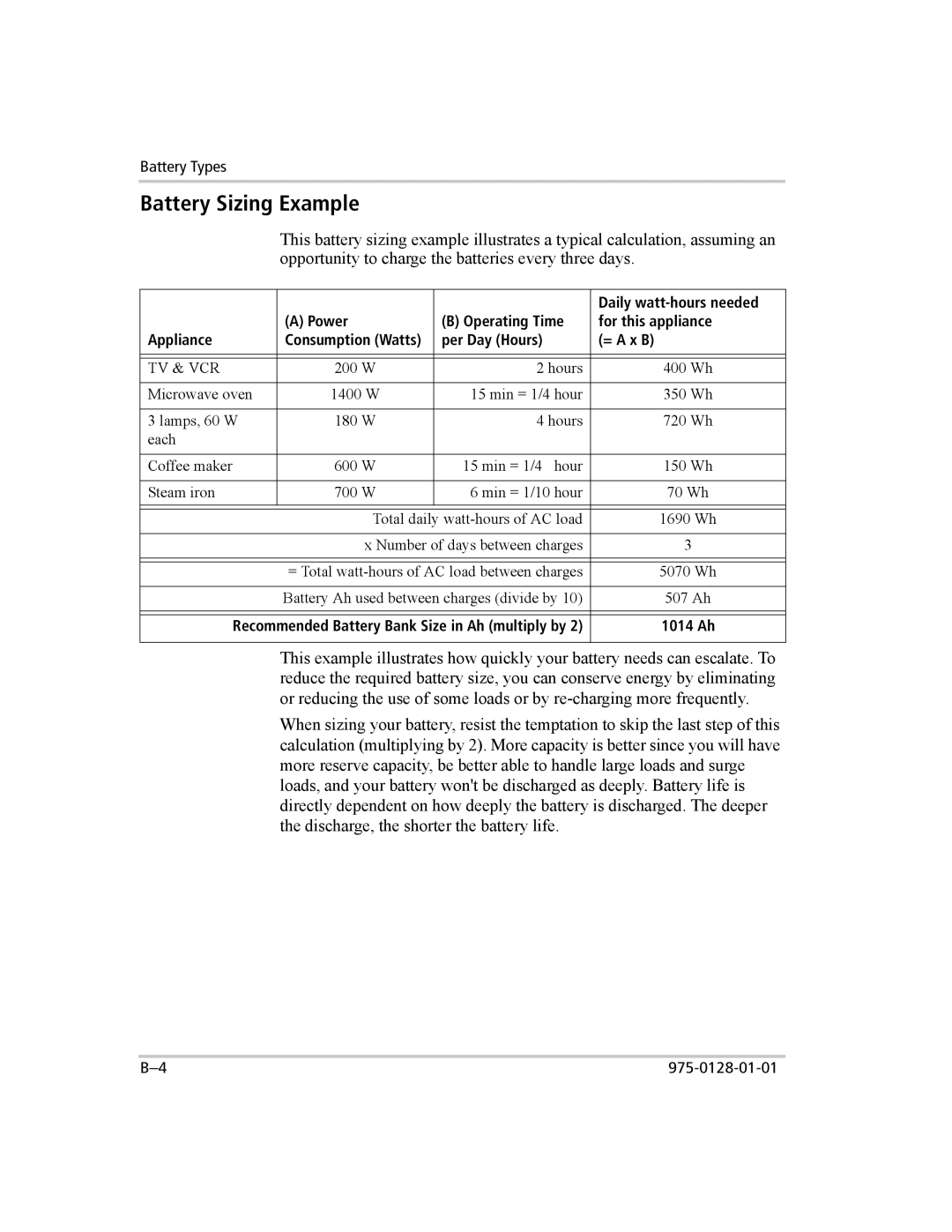
This battery sizing example illustrates a typical calculation, assuming an opportunity to charge the batteries every three days.
|
|
| Daily |
| (A) Power | (B) Operating Time | for this appliance |
Appliance | Consumption (Watts) | per Day (Hours) | (= A x B) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TV & VCR | 200 W | 2 hours | 400 Wh |
|
|
|
|
Microwave oven | 1400 W | 15 min = 1/4 hour | 350 Wh |
|
|
|
|
3 lamps, 60 W | 180 W | 4 hours | 720 Wh |
each |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Coffee maker | 600 W | 15 min = 1/4 hour | 150 Wh |
|
|
|
|
Steam iron | 700 W | 6 min = 1/10 hour | 70 Wh |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| Total daily | 1690 Wh | |
|
|
| |
| x Number of days between charges | 3 | |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
| = Total | 5070 Wh | |
|
|
| |
| Battery Ah used between charges (divide by 10) | 507 Ah | |
|
| ||
|
| ||
Recommended Battery Bank Size in Ah (multiply by 2) | 1014 Ah | ||
|
|
|
|
This example illustrates how quickly your battery needs can escalate. To reduce the required battery size, you can conserve energy by eliminating or reducing the use of some loads or by
When sizing your battery, resist the temptation to skip the last step of this calculation (multiplying by 2). More capacity is better since you will have more reserve capacity, be better able to handle large loads and surge loads, and your battery won't be discharged as deeply. Battery life is directly dependent on how deeply the battery is discharged. The deeper the discharge, the shorter the battery life.