SELECTION GUIDE FOR SCREWDRIVERS.
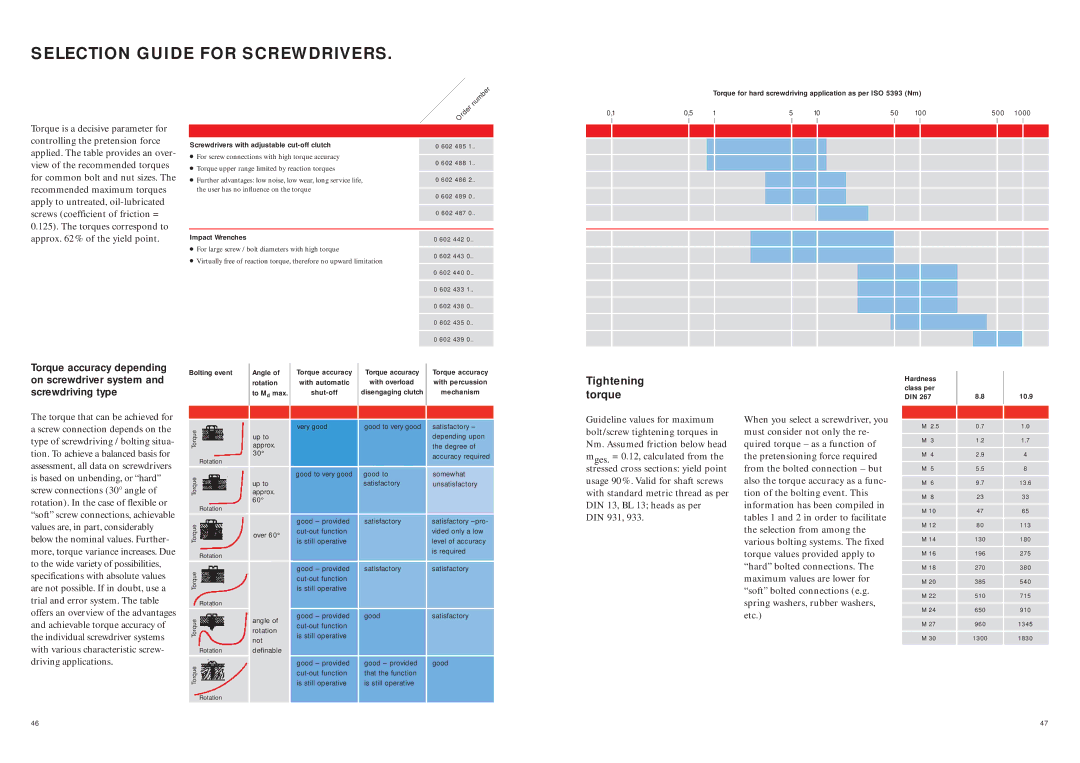
Torque for hard screwdriving application as per ISO 5393 (Nm)
0,1 | 0,5 | 1 | 5 | 10 | 50 | 100 | 500 | 1000 |
Torque is a decisive parameter for controlling the pretension force applied. The table provides an over- view of the recommended torques for common bolt and nut sizes. The recommended maximum torques apply to untreated,
Screwdrivers with adjustable | 0 602 485 1.. | |
For screw connections with high torque accuracy |
| |
| ||
0 602 488 1.. | ||
Torque upper range limited by reaction torques | ||
| ||
|
| |
Further advantages: low noise, low wear, long service life, | 0 602 486 2.. | |
the user has no influence on the torque |
| |
| ||
0 602 489 0.. | ||
| ||
|
| |
|
| |
| 0 602 487 0.. | |
|
| |
|
| |
Impact Wrenches |
| |
0 602 442 0.. | ||
For large screw / bolt diameters with high torque |
| |
|
0 602 443 0..
Virtually free of reaction torque, therefore no upward limitation
0 602 440 0..
0 602 433 1..
0 602 438 0..
0 602 435 0..
0 602 439 0..
Torque accuracy depending | Bolting event | |
on screwdriver system and | ||
| ||
screwdriving type |
| |
The torque that can be achieved for |
| |
a screw connection depends on the | Torque | |
type of screwdriving / bolting situa- | ||
| ||
tion. To achieve a balanced basis for | Rotation | |
assessment, all data on screwdrivers | ||
| ||
is based on unbending, or “hard” | Torque | |
screw connections (30° angle of | ||
rotation). In the case of flexible or | Rotation | |
“soft” screw connections, achievable | ||
| ||
values are, in part, considerably | Torque | |
below the nominal values. Further- | ||
more, torque variance increases. Due | Rotation | |
to the wide variety of possibilities, | ||
Torque | ||
specifications with absolute values | ||
| ||
are not possible. If in doubt, use a |
| |
trial and error system. The table | Rotation | |
offers an overview of the advantages | Torque | |
and achievable torque accuracy of | ||
| ||
the individual screwdriver systems |
| |
with various characteristic screw- | Rotation | |
driving applications. | Torque | |
| ||
| Rotation |
Angle of | Torque accuracy | Torque accuracy | Torque accuracy |
rotation | with automatic | with overload | with percussion |
to Md max. | disengaging clutch | mechanism | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| very good | good to very good | satisfactory – |
up to |
|
| depending upon |
approx. |
|
| the degree of |
30° |
|
| accuracy required |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| good to very good | good to | somewhat |
up to |
| satisfactory | unsatisfactory |
approx. |
|
|
|
60° |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| good – provided | satisfactory | satisfactory |
over 60° |
| vided only a low | |
is still operative |
| level of accuracy | |
|
| ||
|
|
| is required |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| good – provided | satisfactory | satisfactory |
|
|
| |
| is still operative |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
angle of | good – provided | good | satisfactory |
|
| ||
rotation |
|
| |
is still operative |
|
| |
not |
|
| |
|
|
| |
definable |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| good – provided | good – provided | good |
| that the function |
| |
| is still operative | is still operative |
|
|
|
|
|
Tightening torque
Guideline values for maximum bolt/screw tightening torques in Nm. Assumed friction below head mges. = 0.12, calculated from the stressed cross sections: yield point usage 90%. Valid for shaft screws with standard metric thread as per DIN 13, BL 13; heads as per DIN 931, 933.
When you select a screwdriver, you must consider not only the re- quired torque – as a function of the pretensioning force required from the bolted connection – but also the torque accuracy as a func- tion of the bolting event. This information has been compiled in tables 1 and 2 in order to facilitate the selection from among the various bolting systems. The fixed torque values provided apply to “hard” bolted connections. The maximum values are lower for “soft” bolted connections (e.g. spring washers, rubber washers, etc.)
Hardness class per DIN 267
M 2.5
M 3
M 4
M 5
M 6
M 8
M 10
M 12
M 14
M 16
M 18
M 20
M 22
M 24
M 27
M 30
8.8
0.7
1.2
2.9
5.5
9.7
23
47
80
130
196
270
385
510
650
960
1300
10.9
1.0
1.7
4
8
13.6
33
65
113
180
275
380
540
715
910
1345
1830
46 | 47 |