∙
∙
∙
Master FIDB
∙
∙
∙
Customer FIDB
(same for all a/c
in fleet) |
| AMI/HGI |
|
| (same for all |
| ||
|
| a/c in fleet) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
A319
∙
∙
∙
∙
∙
∙
GEX
∙
∙
∙
∙
∙
∙
Customer Aircraft Types:
A319
Aircraft
Type:
APM
(specific to a/c type & configuration)
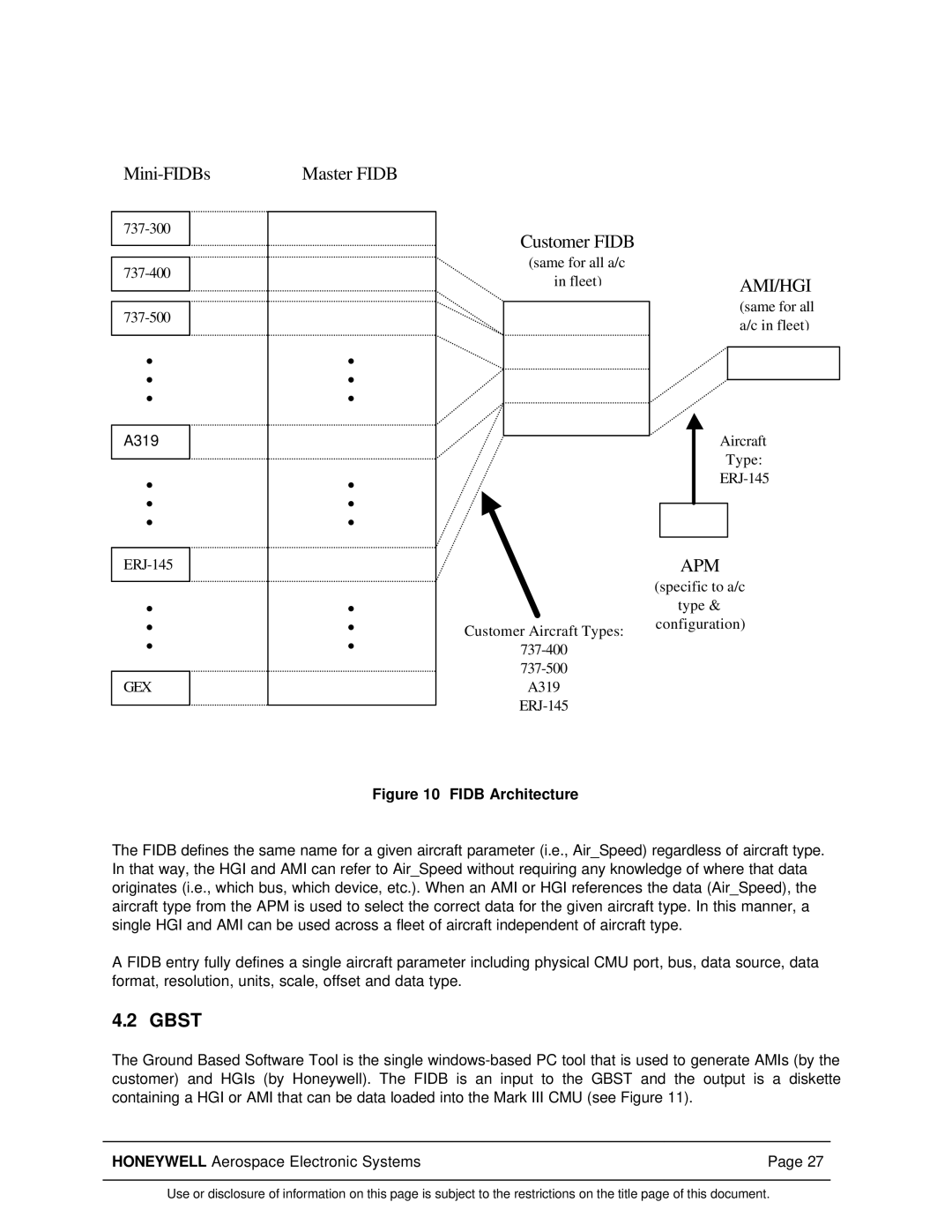
Figure 10 FIDB Architecture
The FIDB defines the same name for a given aircraft parameter (i.e., Air_Speed) regardless of aircraft type. In that way, the HGI and AMI can refer to Air_Speed without requiring any knowledge of where that data originates (i.e., which bus, which device, etc.). When an AMI or HGI references the data (Air_Speed), the aircraft type from the APM is used to select the correct data for the given aircraft type. In this manner, a single HGI and AMI can be used across a fleet of aircraft independent of aircraft type.
A FIDB entry fully defines a single aircraft parameter including physical CMU port, bus, data source, data format, resolution, units, scale, offset and data type.
4.2 GBST
The Ground Based Software Tool is the single
HONEYWELL Aerospace Electronic Systems | Page 27 |
Use or disclosure of information on this page is subject to the restrictions on the title page of this document.