AIR SYSTEMS - Continued
Calculating Compressor Size
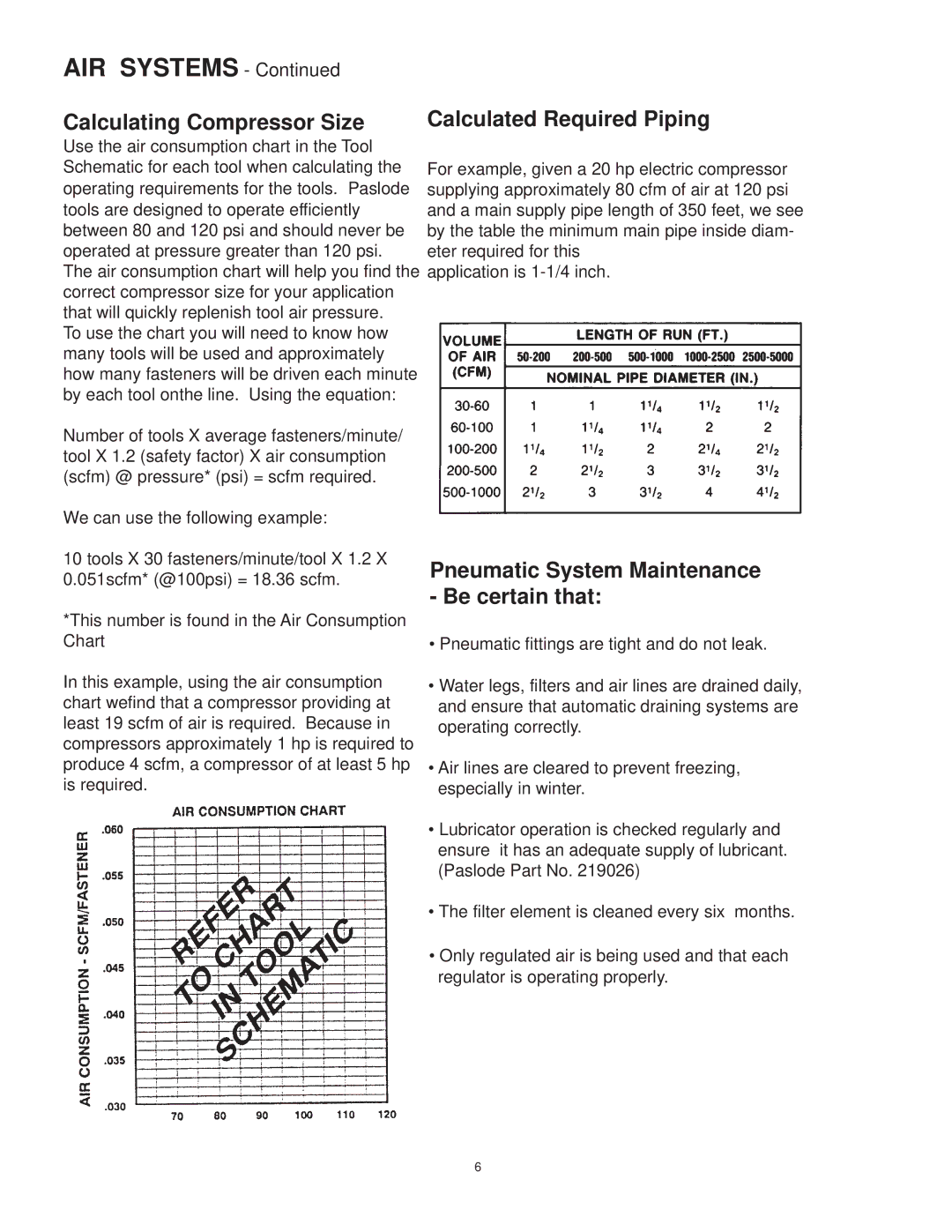
Use the air consumption chart in the Tool Schematic for each tool when calculating the operating requirements for the tools. Paslode tools are designed to operate efficiently between 80 and 120 psi and should never be operated at pressure greater than 120 psi. The air consumption chart will help you find the correct compressor size for your application that will quickly replenish tool air pressure.
To use the chart you will need to know how many tools will be used and approximately how many fasteners will be driven each minute by each tool onthe line. Using the equation:
Number of tools X average fasteners/minute/ tool X 1.2 (safety factor) X air consumption (scfm) @ pressure* (psi) = scfm required.
We can use the following example:
10 tools X 30 fasteners/minute/tool X 1.2 X 0.051scfm* (@100psi) = 18.36 scfm.
*This number is found in the Air Consumption Chart
In this example, using the air consumption chart wefind that a compressor providing at least 19 scfm of air is required. Because in compressors approximately 1 hp is required to produce 4 scfm, a compressor of at least 5 hp is required.
Calculated Required Piping
For example, given a 20 hp electric compressor supplying approximately 80 cfm of air at 120 psi and a main supply pipe length of 350 feet, we see by the table the minimum main pipe inside diam- eter required for this
application is
Pneumatic System Maintenance
-Be certain that:
•Pneumatic fittings are tight and do not leak.
•Water legs, filters and air lines are drained daily, and ensure that automatic draining systems are operating correctly.
•Air lines are cleared to prevent freezing, especially in winter.
•Lubricator operation is checked regularly and ensure it has an adequate supply of lubricant. (Paslode Part No. 219026)
•The filter element is cleaned every six months.
•Only regulated air is being used and that each regulator is operating properly.
6